In this detailed article, we provide real-world NVIDIA® H100 GPU Performance Analysis for Western Digital OpenFlex™ Data24. By enabling direct data paths between GPU memory and storage, the OpenFlex Data24 significantly reduces latency and maximizes bandwidth.
This report is sponsored by Western Digital. All views and opinions expressed in this report are based on our unbiased view of the product(s) under consideration.
AI is all the buzz these days, and while some hyperscalers are off making bespoke solutions to their AI data problem, Western Digital (WD) has an answer for the rest of us. The Western Digital OpenFlex™ Data24™ offers a robust and scalable storage solution to meet the high throughput demands of AI and other GPU-accelerated workloads. By enabling direct data paths between GPU memory and storage, the OpenFlex Data24 significantly reduces latency. It also maximizes bandwidth, ensuring efficient data handling and optimal GPU utilization for faster, more effective processing of large-scale datasets.
By leveraging NVMe-oF™, Western Digital can share disaggregated high-speed storage across multiple servers, ensuring rapid data access and transfer. The OpenFlex Data24 seamless integration with high-performance GPUs allows it to deliver the immense throughput required for AI training and inference, positioning it as a key enabler of next-generation data center operations. These features make OpenFlex Data24 a powerful tool for any organization looking to harness the full potential of AI and other advanced computational workloads.
Western Digital OpenFlex Data24 4000
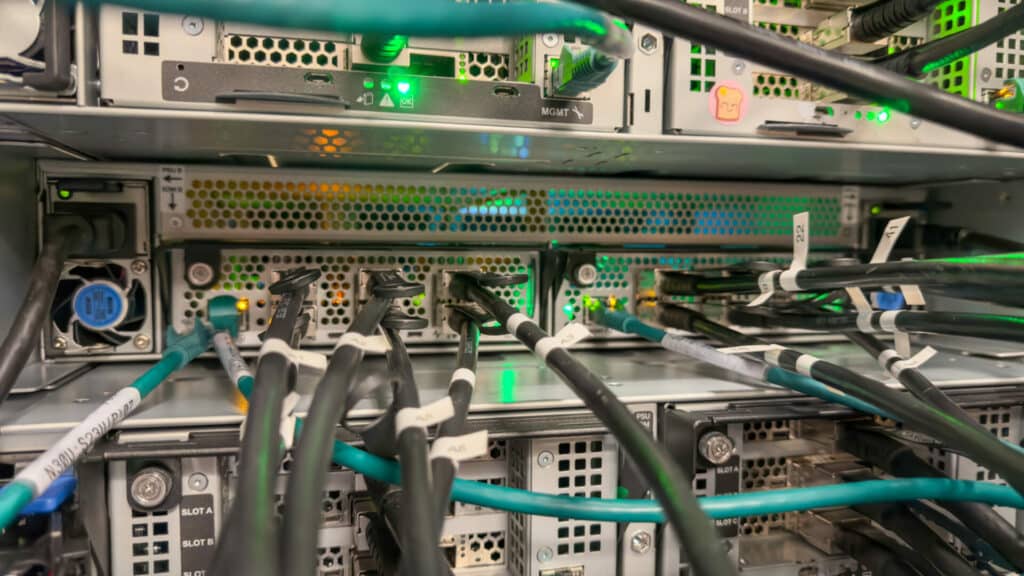
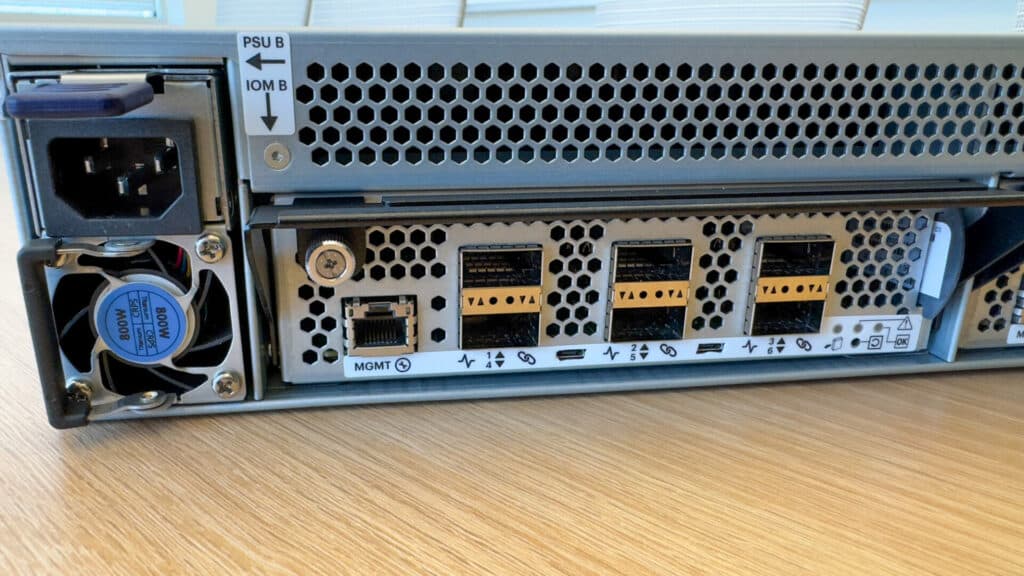
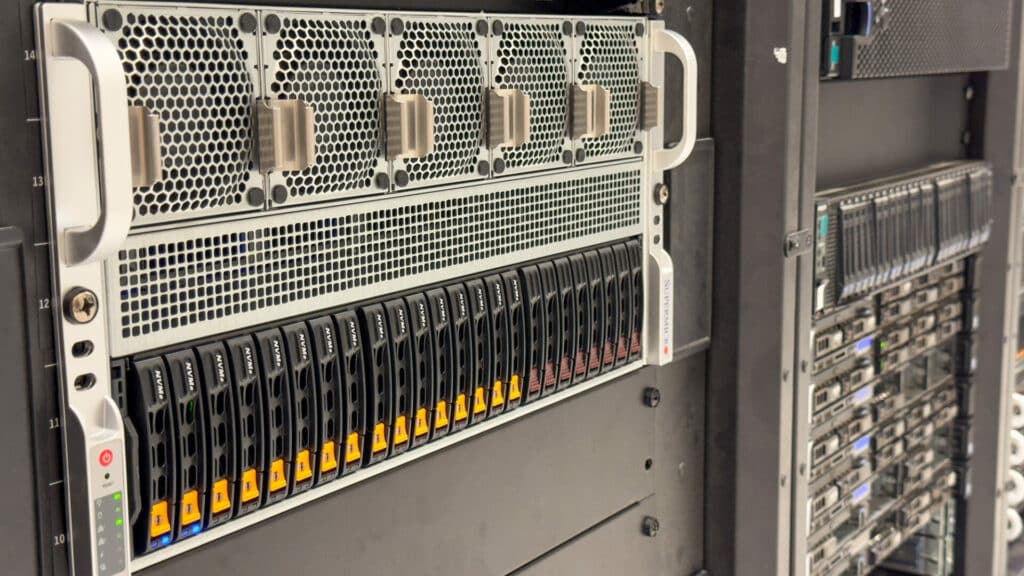
The OpenFlex Data24 4000 series NVMe-oF storage platform from Western Digital brings unparalleled performance to shared storage environments. This high-performance platform extends the capabilities of NVMe™ flash, providing low-latency sharing over an Ethernet fabric. The Data24 4000 series leverages six Western Digital RapidFlex™ A2000 Fabric Bridge devices to deliver seamless network connectivity using up to twelve 100GbE ports. These interfaces support both RoCEv2 and TCP protocols, providing versatile options for data transfer.
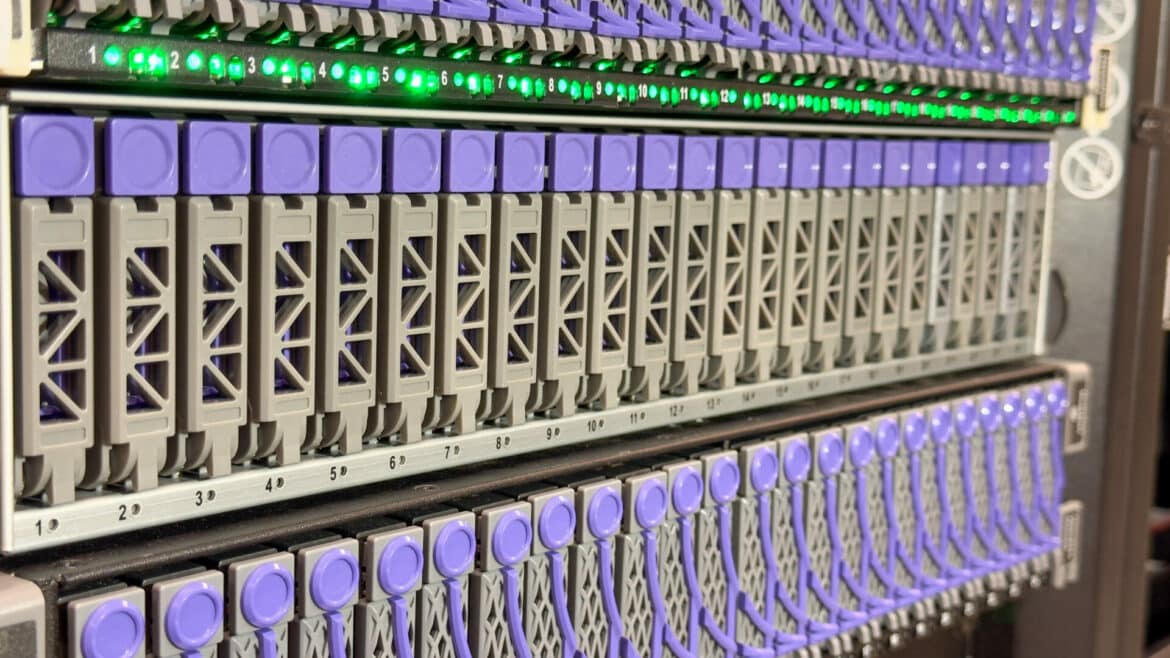
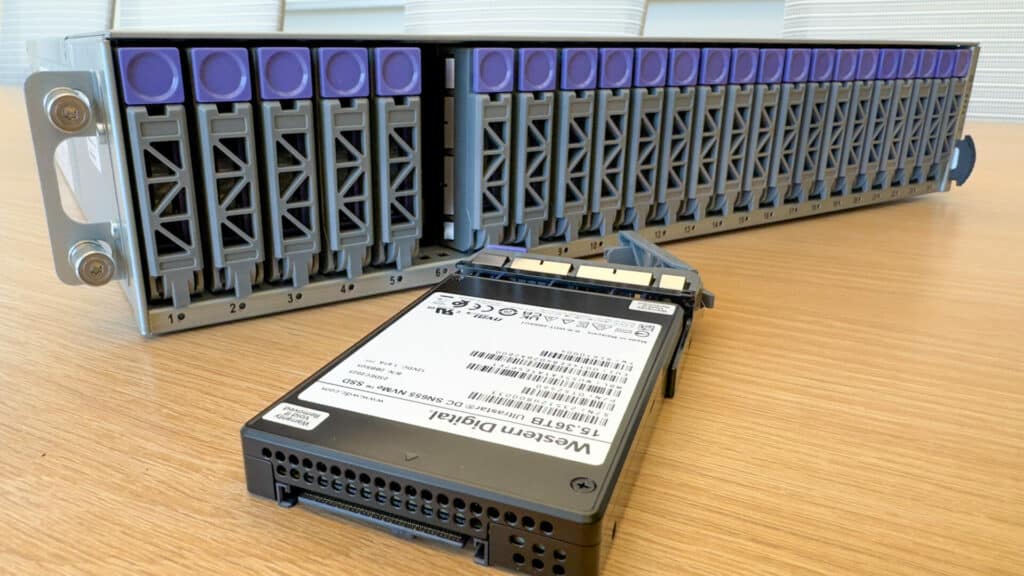
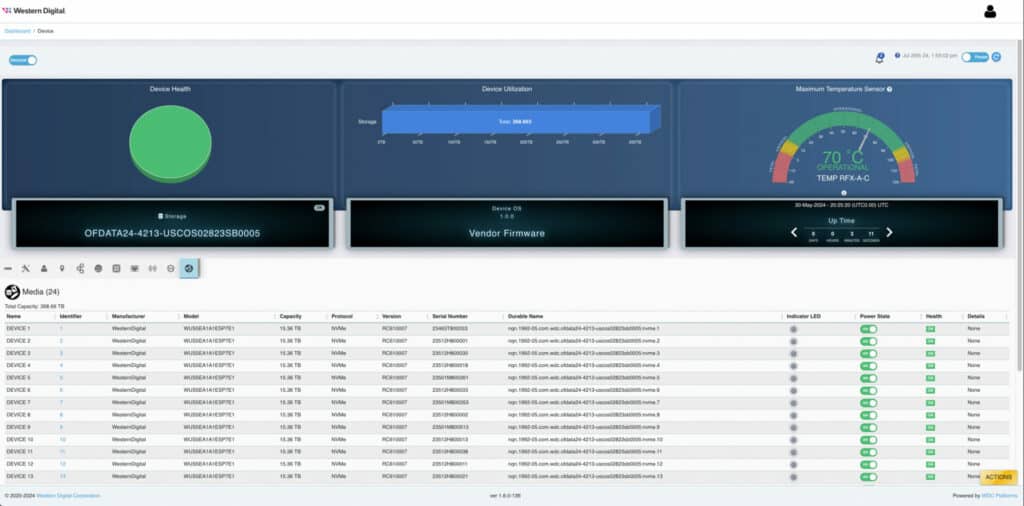
The chassis is designed within a 2U form factor, accommodating up to 24 dual-port U.2 NVMe SSDs. With support for PCIe® Gen4, this platform is architected to fully utilize each SSD’s performance, maintaining high bandwidth throughout the chassis. The NVMe SSDs are available in various capacities and endurance options, including the Ultrastar® DC SN655 SSDs with up to 15.36TB capacity for a total raw capacity of 368TB¹.
The platform’s design eliminates oversubscription, ensuring balanced access that preserves NVMe performance. The Data24 4000 series also incorporates RESTful API support for streamlined management, enhancing ease of use and integration into existing IT infrastructures.
High availability and enterprise-class reliability are critical attributes of the Data24 4000 series. Touches like dual I/O modules and N+2 fan redundancy provide peace of mind to ensure continuous operation even during unforeseen component failures. The entire platform, including SSDs, is backed by a 5-year limited warranty.
Western Digital OpenFlex Data24 Key Specifications
| OpenFlex Data24 Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Max Storage Capacity | 368TB |
| Input Voltage | 120V – 240V |
| PSU | Dual 800W |
| Data Transfer Rate | 12x 100Gbps NVMe-oF |
| Form Factor | 2U |
| Operational Temperature | 10°C to 35°C |
| Weight | 18.25 kg / 40.2 lbs |
| Dimensions (W x L x H) | 491.9 mm x 628.65 mm x 85.5 mm / 19.37 in. x 24.75 in. x 3.37 in. |
| Power Consumption (Max/Typical) | 750W / ~550W |
| PSU Efficiency | 80 Plus Titanium |
| Drive Slots | 24 |
| Cooling | 4 System Fans (N+2 Supported) |
| Rack Units (U) | 2U |
| Required Rack Depth | 1000 mm (39.4 in.) |
| Required Rack Width | 450mm (17.72 in.) |
Testing the OpenFlex Data24
To stretch the legs of the OpenFlex Data24, we had to pull together a few key pieces: NVIDIA GPUDirect™, NVIDIA IndeX®, and a whopping 5.9TB of Tornado Simulation data. By leveraging NVIDIA GPUDirect, we enabled direct communication between the GPU memory and the OpenFlex Data24, drastically reducing latency and maximizing data throughput. Utilizing NVIDIA’s IndeX allowed us to visualize and interact more efficiently with the massive tornado dataset, showcasing the system’s real-time processing capabilities. This setup provided a perfect testbed for demonstrating OpenFlex Data24’s ability to handle intensive AI workloads and large-scale data processing with remarkable speed and efficiency.
NVIDIA GPUDirect
NVIDIA GPUDirect technology significantly enhances data transfer efficiency within high-performance GPU computing environments. This suite of technologies optimizes data movement between GPUs and other system components. By reducing latency and overhead, GPUDirect enables more direct communication between GPUs and peripherals like network adapters, storage devices, and other GPUs. Traditional data transfer processes involve routing data through the CPU and system memory, creating bottlenecks that hinder performance. GPUDirect mitigates these bottlenecks by allowing direct memory access (DMA) to the GPU’s memory, bypassing the CPU and system memory, thereby enhancing the overall throughput.
According to Harry Petty, NVIDIA’s Sr. Technical Marketing Manager:
“NVIDIA’s technologies deliver low latency and fast data transfer from storage, optimizing the performance of AI workloads by reducing GPU idle time. This delivers faster model training times and more accurate results, enabling faster discoveries and more efficient workflows.”
GPUDirect comprises several vital features, including GPUDirect RDMA, which facilitates direct data transfers between the GPU and RDMA-capable network adapters. This direct communication is crucial for applications requiring rapid data exchanges, such as scientific simulations and large-scale data analytics. By enabling faster data transfers, GPUDirect RDMA reduces latency and increases the efficiency of GPU clusters. Additionally, GPUDirect Storage integrates GPUs more tightly with high-speed storage systems, allowing data-intensive applications to leverage the maximum bandwidth of modern NVMe storage. This integration accelerates data access and reduces the time spent waiting for data to be loaded into GPU memory, crucial for real-time analytics and large-scale machine learning workloads.
GPUDirect’s capabilities are particularly impactful in environments where multiple GPUs work in tandem, such as deep learning training clusters. By facilitating direct communication between GPUs, GPUDirect optimizes parallel processing and significantly reduces the overhead associated with inter-GPU data transfers. This enhancement is particularly beneficial in training complex neural networks, where large volumes of data must be exchanged rapidly across multiple GPUs. The efficiency gains from GPUDirect are also evident in applications like molecular dynamics simulations and fluid dynamics, where computational workloads are distributed across numerous GPUs to achieve faster results.
NVIDIA IndeX
NVIDIA IndeX is an advanced volumetric visualization tool designed to handle massive datasets with high fidelity. IndeX leverages GPU acceleration to provide real-time interactive visualization of 3D volumetric data, making it indispensable for industries such as oil and gas exploration, medical imaging, and scientific research. Traditional visualization tools often struggle with the sheer size and complexity of modern datasets, leading to slower rendering times and less interactive user experiences. IndeX overcomes these limitations by utilizing NVIDIA’s GPU technology to deliver high-performance rendering and data processing, ensuring users can interact with their data in real-time.
IndeX’s capabilities are driven by its ability to harness the parallel processing power of GPUs, enabling it to manage and render large-scale volumetric data efficiently. This capability is valuable in applications that require high-resolution visualization, such as seismic interpretation and reservoir simulation in the oil and gas sector. By providing detailed and accurate visual representations of subsurface structures, IndeX helps geoscientists make more informed decisions. In the medical field, IndeX facilitates the visualization of complex anatomical structures from imaging modalities like MRI and CT scans, aiding diagnosis and treatment planning.
The real-time rendering capability of IndeX is also crucial for scientific research, where large datasets from simulations and experiments need to be visualized and analyzed promptly. Researchers can interactively manipulate and explore their data, allowing faster hypothesis testing and discovery. IndeX’s scalability ensures it can handle the growing data volumes generated by advanced scientific instruments and simulations, providing researchers with the tools to visualize and interpret their data effectively. By integrating seamlessly with existing workflows and supporting various data formats, IndeX enhances productivity and accelerates the pace of discovery across multiple disciplines.
Tying it All Together
Integrating the Data24 4000 series with NVIDIA GPUDirect technology significantly enhances the performance of GPU-intensive applications by streamlining data transfers between GPUs and storage. GPUDirect facilitates direct memory access, allowing data movement to bypass the CPU and system memory to reduce latency and increase throughput. When combined with the high-performance NVMe-oF capabilities of the Data24 4000 series, GPUDirect ensures that GPUs can rapidly access large datasets stored on the NVMe SSDs.
This integration is particularly beneficial in environments where high-speed data exchange between GPUs and storage is crucial, such as deep learning and scientific simulations. The low latency and high bandwidth of the Data24 4000 series, coupled with the direct data paths enabled by GPUDirect, minimize data transfer times and allow for more efficient GPU utilization. This synergy optimizes the performance of parallel processing tasks, where multiple GPUs require fast and frequent access to shared data.
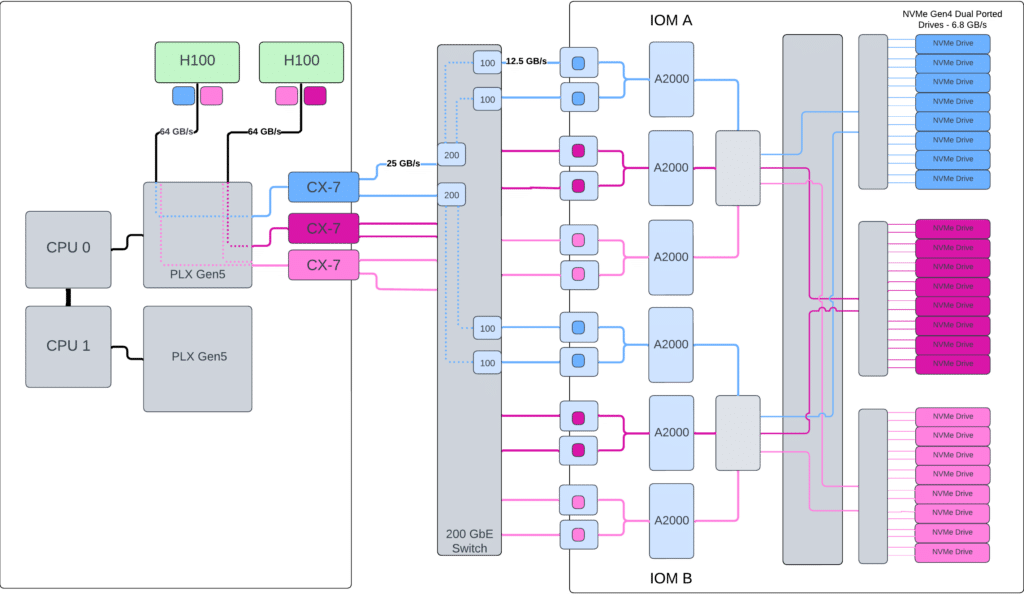
For this testing, the OpenFlex Data24 4000 and GPU server are connected through a 200GbE switch using the NVMe-oF RoCEv2 protocol with matched MTUs of 5000. The GPU server uses 3 Mellanox® CX7 RNICs with 2x 200 GbE per RNIC. The OpenFlex Data24 4000 is available with 12x 100GbE ports. Each CX7 port has 2 IP addresses, allowing a single CX7 to map to four ports on the Data24. This provides connectivity to all 4 PCIe lanes on each dual-ported drive. The 6x 200 GbE links equal the bandwidth potential of 12x 100GbE links for a non-blocking network architecture.
Each NVIDIA H100 is connected via a PCIe Gen5 x16 slot, which can theoretically achieve 64GB/s of bandwidth bidirectionally. Each 200GbE and 100GbE RNIC port can theoretically reach 25 GB/s and 12.5 GB/s respectively. A critical design consideration is to ensure a non-blocking architecture. This requires that the GPUs, RNICs, and NVMe-oF drives are all mapped physically on the same CPU, NUMA, and PLX switch. This allows the configuration to take full advantage of GPUDirect. As seen in this implementation, a mirrored configuration on the second CPU, NUMA, and PLX switch would allow a predictable compute scale and a theoretical doubling of performance.
In AI training clusters, the combination of Data24 4000 and GPUDirect can allow for faster training times by reducing the bottlenecks associated with data loading. The efficient data paths ensure that GPUs can continuously receive data without interruption, maintaining high processing speeds and improving overall system efficiency. This setup is also advantageous for real-time analytics and other applications that demand rapid data access and processing, providing a significant performance boost to various computational workloads.
NVIDIA IndeX Server Configuration
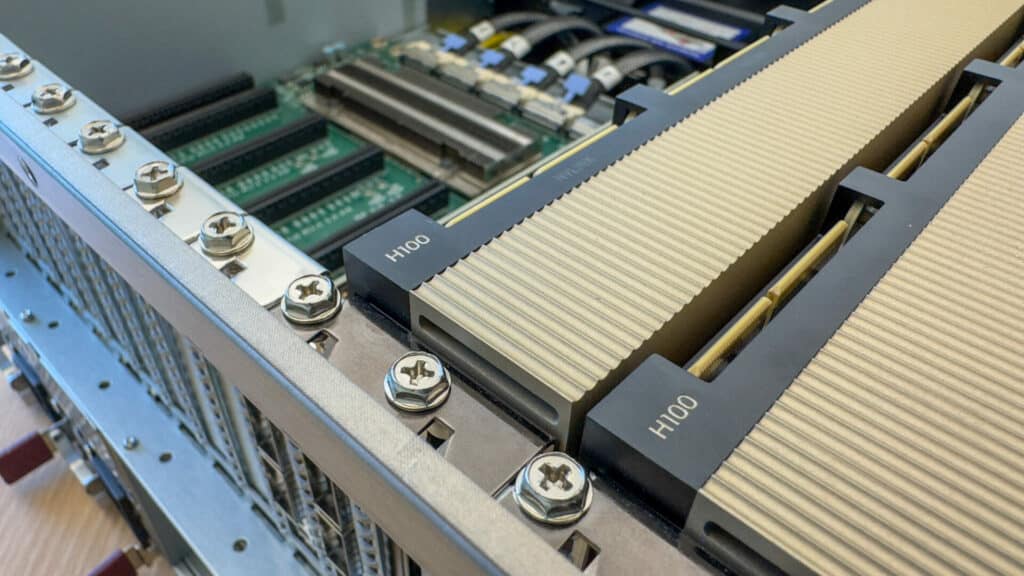
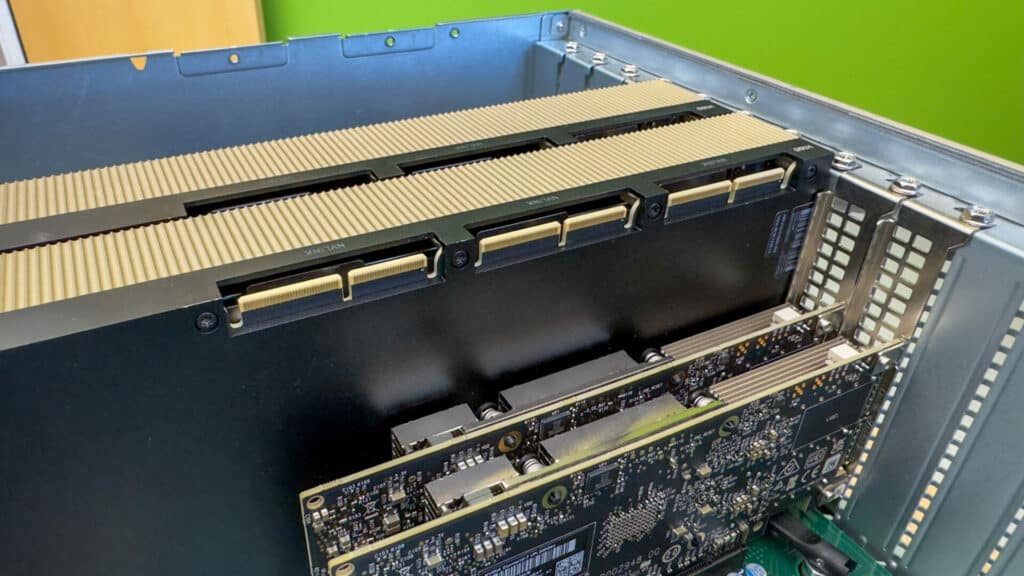
For the NVIDIA IndeX test, we employed the Supermicro 521GE-TNRT equipped with the switched PCIe Backplane, a pair of NVIDIA H100s, and three NVIDIA ConnectX-7 network cards.
| Supermicro® 521GE-TNRT Key Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Model | Supermicro 521GE-TNRT |
| Processor | 2x Intel® Xeon® Platinum 8462Y+ |
| Memory | 1TB DDR5 |
| GPU | 2x NVIDIA H100 PCIe |
| Network Interface | 3x NVIDIA ConnectX-7 NICs |
GDSIO Synthetic Testing
The benchmarking tool used for this purpose is GDSIO, a specialized proprietary NVIDIA utility designed to measure storage performance in GPU-direct storage (GDS) environments. We looked at a few configurations for this round of testing: a single GPU with 12 drives and 24 drives, as well as two GPUs with 24 drives.
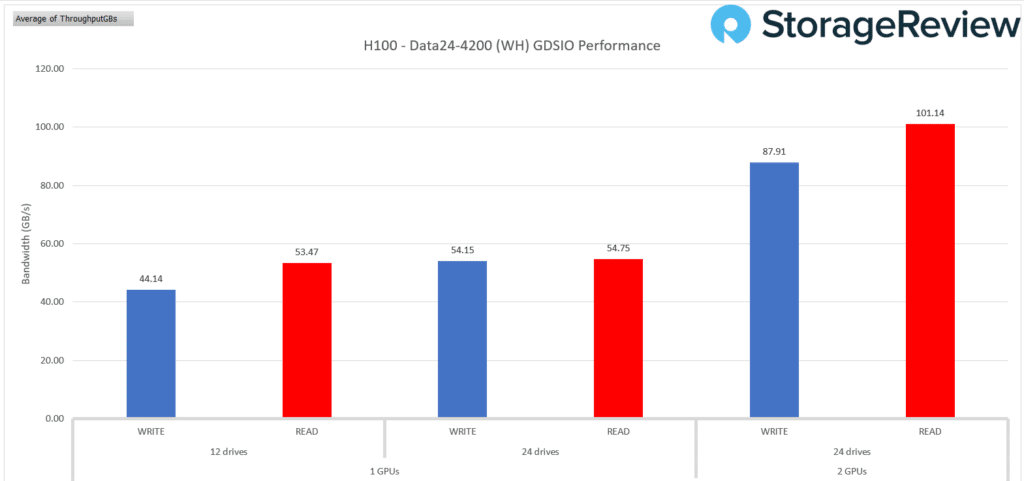
The performance of the Western Digital OpenFlex Data24 in the GDSIO Performance test, paired with NVIDIA H100 GPUs, reveals insights into the raw power of the drives. When configured with 12 drives and a single GPU, the system achieved a write bandwidth of 44.14 GB/s. Increasing the drive count to 24 while utilizing one GPU showed a modest improvement, with write performance reaching 54.15 GB/s. Introducing a second GPU in the 24-drive setup resulted in a substantial boost, elevating the write bandwidth to 87.91 GB/s.
Read performance follows a similar trend. The 12-drive, one-GPU configuration yielded a read bandwidth of 53.47 GB/s. Expanding to 24 drives with one GPU increases it slightly to 54.75 GB/s. However, the most dramatic improvement came with the dual-GPU setup, where the system achieved an impressive 101.14 GB/s read bandwidth. These results underscore the capability of the OpenFlex Data24 to scale predictably with an increased number of drives.
The addition of GPUs plays a crucial role in maximizing performance. The configuration with 24 drives and two GPUs emerged as the optimal setup, delivering the highest bandwidth for read and write operations. This test underscores the importance of GPU acceleration in harnessing the full potential of the GDSIO framework. The OpenFlex Data24, when paired with NVIDIA H100 GPUs, demonstrates exceptional performance, making it a robust solution for demanding storage environments.
For AI workloads, where rapid data ingestion and processing are paramount, the performance observed with the OpenFlex Data24 can translate to significant reductions in training times and more efficient handling of large datasets. The ability to move data swiftly from storage to GPU memory ensures that the computational resources of powerful GPUs are fully leveraged, facilitating faster and more efficient model training and inference.
Using the OpenFlex Data24 to Feed H100’s Tornadoes
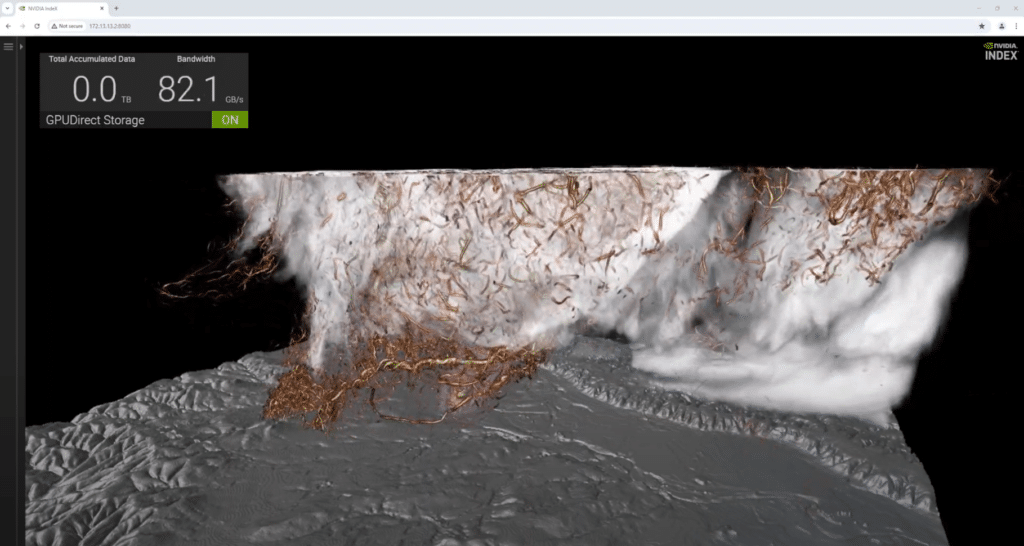
Climate researchers have long studied supercell thunderstorms, the atmospheric phenomena responsible for the world’s most violent and dangerous tornadoes. These storms are dynamic and complex, making accurate simulations time-consuming and data-intensive. Exploring such data has been a slow, cumbersome process, often taking hours to render new visualizations.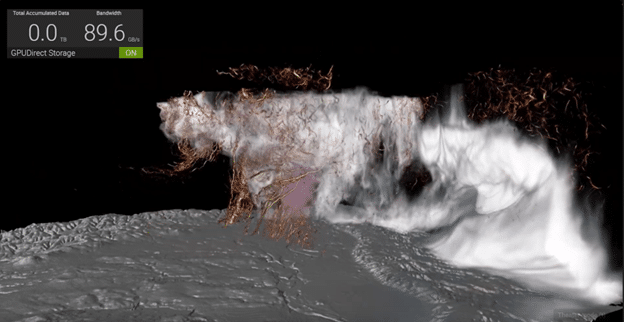
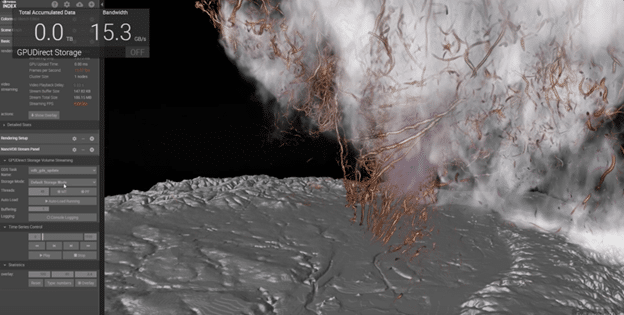
The use of NVIDIA GPUs and NVIDIA IndeX has revolutionized this field. Scientists can now perform volumetric visualizations in real-time. The simulation we ran on the Supermicro system with H100s (being fed data by the OpenFlex Data24) showcases a 2011 Oklahoma storm simulated by Professor Leigh Orf. This simulation, mathematically derived from initial conditions just before the tornado formed, includes 250 billion grid points, each with over a dozen attributes such as rain, hail, pressure, and wind speed. This detailed visualization, showing 6000 simulation steps, provides unprecedented insight into the tornado’s dynamics.
Key to this simulation is NanoVDB, a compact sparse-volume data structure that reduces dataset sizes and memory footprint by mapping data directly into the GPU’s memory. Coupled with GPUDirect Storage technology and the OpenFlex Data24, we achieved up to 89GB/s and can view results at over 13 frames per second. This approximated to about 5.9TB of dataset ingested every 66 seconds. This combination allows for interactive navigation, on-the-fly parameter adjustments, and scrubbing through the simulation with ease.
With GPUDirect disabled (and, therefore, data now traversing the CPU complex), bandwidth is reduced to around 15 GB/s, and the frame rate drops significantly to 4 frames per second.
Speed is crucial, but photorealistic quality is also essential for validating the accuracy of simulations. If simulation and reality don’t align, models must be corrected. NVIDIA Iray, a GPU-based path-tracer that renders physically correct light transport, is used alongside NVIDIA IndeX volume data to power this visualization. The tornado’s funnel, ground contact, and detailed elements like cloud-water ratio and rain, represented by blue-grey pores, are clearly visible.
Conclusion
The performance, time, and cost benefits that a well-configured, non-blocking architecture can offer GPU-accelerated workloads are well demonstrated in this project. Put simply, driving GPUs to their maximum throughput or processing capability drives more efficient outcomes and return on investment.
Western Digital’s architecture supports Open Composable Infrastructure (OCI), and the OpenFlex Data24 4000 platform leverages this OCI approach by disaggregating data storage using NVMe-over-Fabrics (NVMe-oF). This decoupling of the storage resources from the GPU server not only helps free up the servers’ resources (releasing those resources from traditional lockstep upgrades), but in doing so, also allows a fine-tuning of NVMe Drive mapping to GPUs. This precise drive matching to GPU requirements allows GPU capability, performance, and data capacity needs to be closely addressed, which in turn offers the predictable scale and flexibility required for those resources.
As the data is no longer siloed, it becomes an accessible networked storage resource, shareable amongst multiple GPU servers as needed, further increasing flexibility.
The Western Digital OpenFlex Data24, combined with NVIDIA GPUDirect technology, demonstrates a formidable capability in handling AI and other GPU-accelerated workloads. By enabling direct data paths between GPU memory and NVMe storage, the Data24 significantly reduces latency and maximizes bandwidth, ensuring efficient data handling and optimal GPU utilization. This integration allows faster, more effective processing of large-scale datasets, making the Data24 an invaluable asset in modern data-intensive environments.
Our real-world testing, involving a substantial tornado simulation dataset, showcased the remarkable performance gains achieved through this setup. The OpenFlex Data24’s ability to deliver high throughput and low-latency data transfers, coupled with NVIDIA IndeX’s real-time visualization capabilities, underscores its potential in demanding applications such as AI training, scientific simulations, and real-time analytics.
Utilizing the Data24 series and GPUDirect technology for AI training clusters can significantly reduce training times by ensuring seamless data flow from storage to GPUs. This setup minimizes bottlenecks and enhances overall system efficiency, making it a critical component in pursuing faster and more accurate AI models.
Beyond AI, the benefits of OpenFlex Data24 extend to other GPU-accelerated workloads, including high-performance computing and real-time data analytics. The reduced latency and increased throughput enabled by this platform ensure that applications requiring rapid data access and processing can operate at peak performance, delivering timely and precise results.
See this demo in action August 6-8, 2024, at FMS 2024 booth #607.
Western Digital OpenFlex Platforms
[1] One terabyte (TB) is equal to one trillion bytes. Actual user capacity may be less due to the operating environment.
Engage with StorageReview
Newsletter | YouTube | Podcast iTunes/Spotify | Instagram | Twitter | TikTok | RSS Feed