Ensuring the security of your NAS is of utmost importance in safeguarding valuable data from cyber threats in today’s digital landscape. The consequences of a compromised system, such as identity theft, financial loss, or reputational damage, can be severe. By following this comprehensive security guideline, users can mitigate the risk of malware infections, unauthorized access attempts, and ransomware attacks by leveraging available capabilities to maintain the integrity of their NAS ecosystem. For this article, we will utilize a QNAP NAS to exemplify the process of how to secure your NAS.
Ensuring the security of your NAS is of utmost importance in safeguarding valuable data from cyber threats in today’s digital landscape. The consequences of a compromised system, such as identity theft, financial loss, or reputational damage, can be severe. By following this comprehensive security guideline, users can mitigate the risk of malware infections, unauthorized access attempts, and ransomware attacks by leveraging available capabilities to maintain the integrity of their NAS ecosystem. For this article, we will utilize a QNAP NAS to exemplify the process of how to secure your NAS.

1) Disable Default Logins and Update Firmware
Generally speaking, NAS solutions can achieve an acceptable level of security by following two essential practices. First, and this is crucial, avoid using the default admin/password login credentials that come with the NAS device. This is often the first (and only) attack used when trying to gain unauthorized access. Disabling the default login and creating new, strong administrator credentials significantly mitigates the risk of unauthorized access.
Secondly, regularly updating the NAS firmware is essential to fixing known vulnerabilities or security flaws. There are options to complete these updates automatically, so there’s not much work on the client side. Keeping the NAS firmware up to date is vital in preventing a large percentage of malware and ransomware attacks. We’ll cover more on this topic later in the article. QNAP allows its users to change/disable their login accounts easily and has the option to enable auto firmware updates.
It’s crucial to adhere to these two fundamental guidelines to safeguard the countless NAS systems utilized. This approach will shield many of these devices from possible security threats and enhance the overall security of the NAS ecosystem.
In addition to these fundamental practices, there are several more comprehensive steps you can take to further enhance NAS security. In an era of increasingly sophisticated malware, advanced hacking techniques, and persistent brute force attacks, it is crucial to be as diligent as possible when securing your NAS. Let’s explore these advanced practices in detail.
2) Strong Passwords and 2-Step Authentication
Strong passwords and enabling 2-step authentication for all user accounts are also crucial in preventing unauthorized access attempts. It is advisable to implement a password policy for organizations or businesses that enforces the following:
- The use of complex passwords
- Regular password changes
By implementing strong passwords and enabling 2-step authentication, users can bolster the security of their NAS devices. QNAP provides features that easily facilitate these security measures. QNAP’s Authenticator offers multiple options for logging into your NAS, such as time-based one-time passwords (which can be used offline), QR code scanning, login approval, and online verification codes. Additionally, you have the option to access your NAS system without using a password. By scanning a QR code or approving a sign-in request, you can effortlessly log in to your NAS.
3) IP Access Protection Prevents Brute Force Attacks
A brute force attack is when an intruder attempts multiple login combinations using different usernames and passwords to gain unauthorized access to the NAS. This method relies on the attacker’s persistence and computational power to break through weak login credentials, reinforcing the importance of strong, unique passwords and additional security measures like account lockouts.
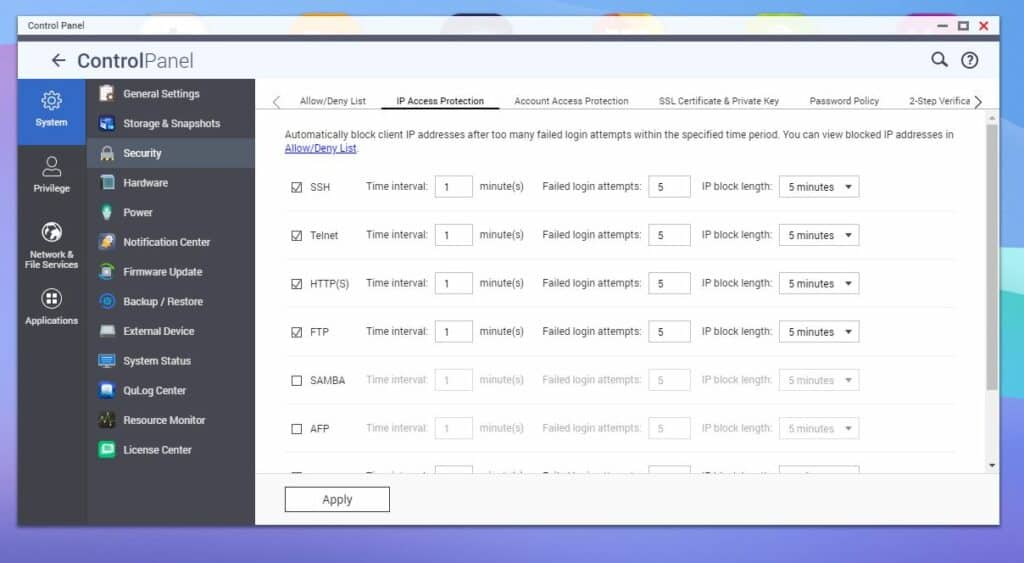
Enabling QNAP’s IP Access Protection helps to proactively safeguard against this, as you can configure account lockouts that activate after a specific number of unsuccessful login attempts.
To access this feature from the Control Panel, navigate to System > Security, then click IP Access Protection at the top. Here you can change the time interval and adjust allowed failed login attempts for a range of connectivity types.
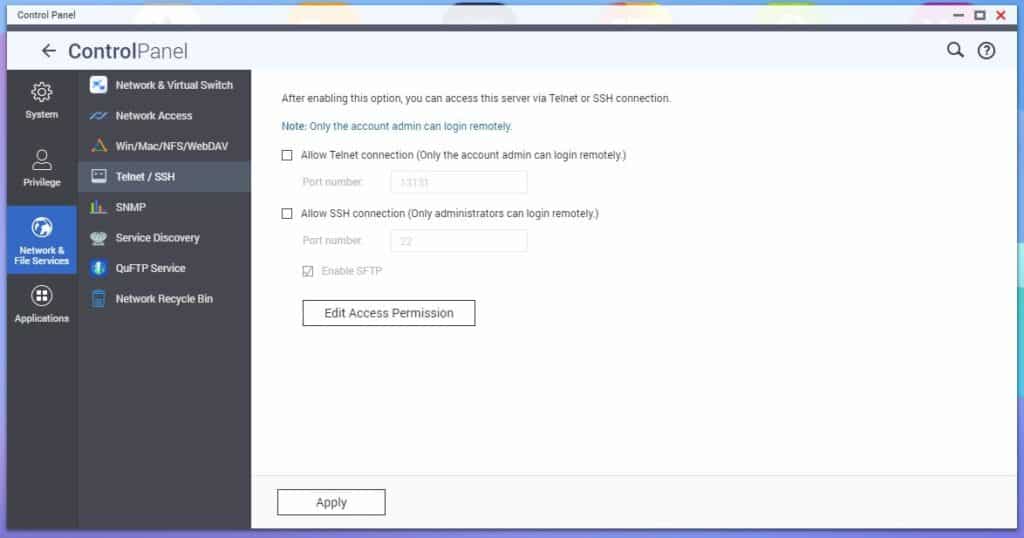
That said, disabling unused services like SSH (a popular network protocol that offers remote access to systems, even across unsecured networks) and Telnet (another remote access protocol where users interact with the system’s command-line interface from a remote location) minimizes potential entry points for attackers.
This can be disabled on a QNAP NAS via the Network & Files Services > Telnet / SSH section.
4) Port Security
Unless you have advanced knowledge of network security, you should avoid enabling manual or auto port forwarding and demilitarized zone (DMZ) configurations. Inexperience can lead to misconfigurations, exposing your NAS to external threats. Additionally, you should avoid using default port numbers commonly targeted by attackers, such as 433 and 8080.
Accessing your NAS remotely is made easy with QNAP’s myQNAPcloud link and doesn’t require opening any ports. This is the most secure and straightforward way to remotely access your NAS.
5) Enable Snapshots for Quick Backup and Recovery
Snapshots play a pivotal role in data protection and recovery strategies. They are a point-in-time copy (or image) of the file system/stored data. This is particularly useful with ransomware attacks, which allow users to easily and quickly recover their data and restore its previous state.
QNAP’s block-based snapshots offer an efficient way to back up data by capturing only the changes since the last snapshot, reducing storage requirements and backup time. This feature lets users quickly restore data to a previous, unaffected state, nullifying the ransomware attack. The Snapshot Replica feature allows for the seamless replication of snapshots to another QNAP NAS, ensuring backup redundancy.
Sometimes ransomware is programmed to continuously write data to maximize the impact and damage caused to the victim’s NAS system. The ultimate goal is to create more panic and urgency, influencing many users to pay the ransom quickly. This technique also helps hackers evade system security by concealing encryption patterns, mimicking legitimate file modification behavior, and creating heavy network traffic.
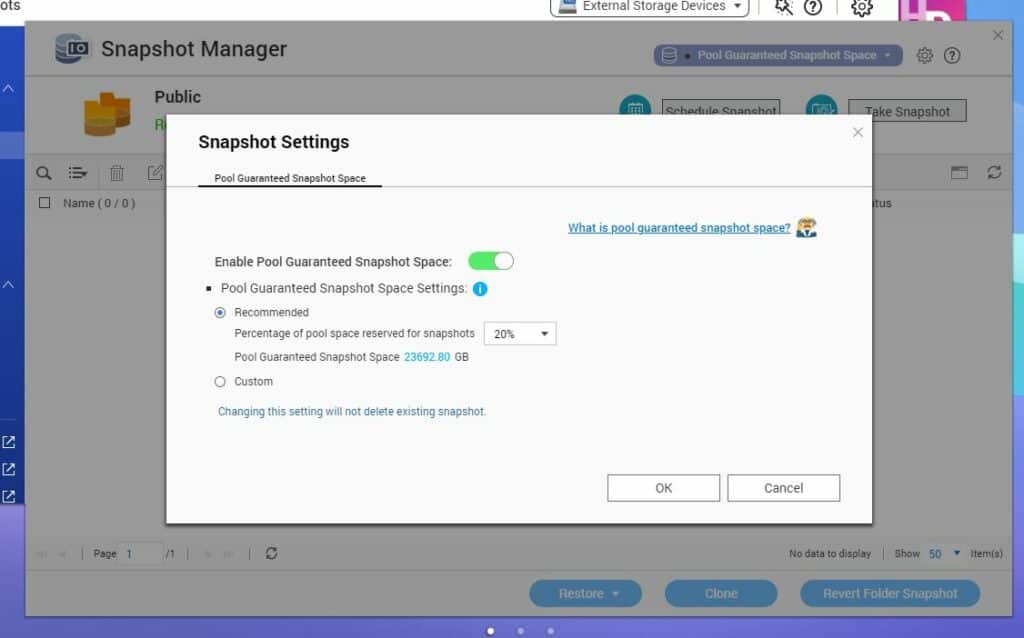
QNAP’s Snapshot reserve space feature (Pool Guaranteed Snapshot Space) tackles this issue by reserving dedicated storage space for snapshots, preventing failure due to insufficient capacity.
To access this feature, go to the Storage & Snapshots settings, and navigate to the Storage/Snapshots section within the Storage menu. From there, choose either a thick or thin volume or LUN, then click the Snapshot option and select Snapshot Manager. Within the Snapshot Manager, click the Pool Guaranteed Snapshot Space button at the top right of the window and click Configure. Activate Enable Pool Guaranteed Snapshot Space, then specify the desired amount of reserved space. Finalize everything by clicking OK.
6) Implement a Robust Disaster Recovery Plan
Disasters such as hardware failures, natural disasters, or unforeseen incidents pose a significant risk to NAS solutions that can result in permanent data loss or damage. It is advisable to implement a comprehensive disaster recovery plan to ensure the integrity and accessibility of the data stored on your NAS ecosystem.
Diversifying backup locations helps mitigate the risk of data loss and enhances data resilience during hardware anomalies and even when disastrous events occur. Disparate storage spaces include, but are not limited to, the following:
- other NAS devices
- remote servers
- cloud services
- storage expansion units
- external hard drives
QNAP has addressed backup diversity by implementing a “3-2-1 rule” guideline for data backup, QNAP’s Hybrid Backup Sync, which strongly encourages users to store multiple copies of their data on different media types and in separate locations to maximize protection against this type of data loss.
The 3-2-1 general rule for backup includes the following:
- Maintain three copies of your data,
- stored in at least two different types of media,
- with one copy stored offsite.
7) Auto-Updates for Firmware and Apps
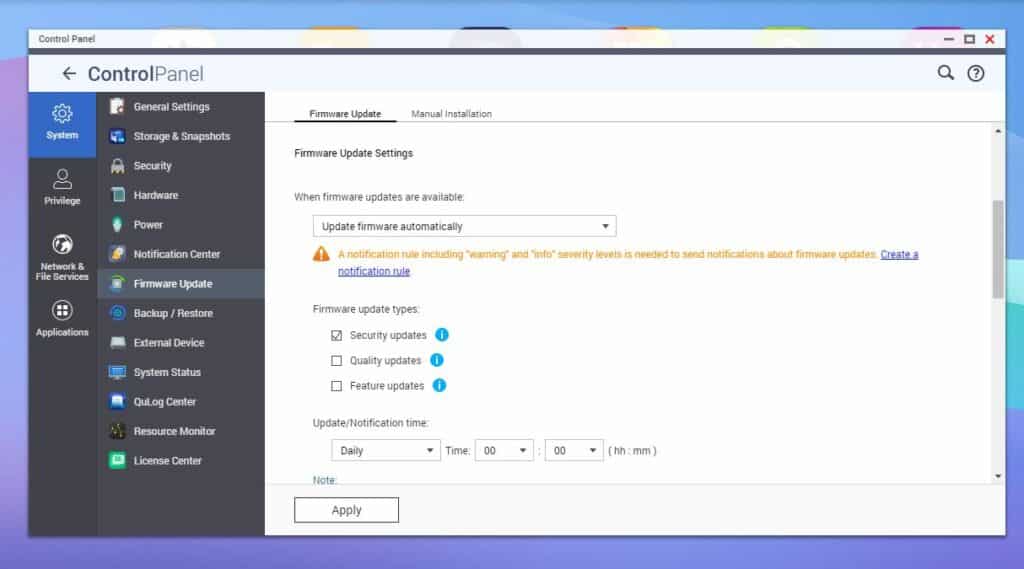
Enabling the firmware auto-update feature is critical to maintaining the security and performance of your NAS. As indicated above, just keeping your firmware current prevents many easy attacks.
Here are some of the ways updated firmware can help secure your NAS.
- Fixing vulnerabilities: Firmware updates address known vulnerabilities in the operating system and hardware, sealing potential security loopholes that attackers could exploit to gain unauthorized access or encrypt your files.
- Enhancing security features: Firmware updates often introduce new security features or improve existing ones, strengthening the overall security of your NAS. These enhancements make it more challenging for attackers to compromise your data and NAS systems.
- Detecting and preventing the latest malware: By enabling the Auto-Update feature, your NAS can automatically install firmware and application updates, including advanced security features that detect and prevent the latest malware attacks. This reduces the need for manual updates while ensuring your NAS remains current with the latest security patches, bug fixes, and enhancements.
QNAP provides an easy way to enable this feature from their Control Panel. Go to Firmware Update and select Update firmware automatically under Firmware Update Settings, and you’re done. There’s even an option to select the type of automated firmware updates.
8) Security Apps
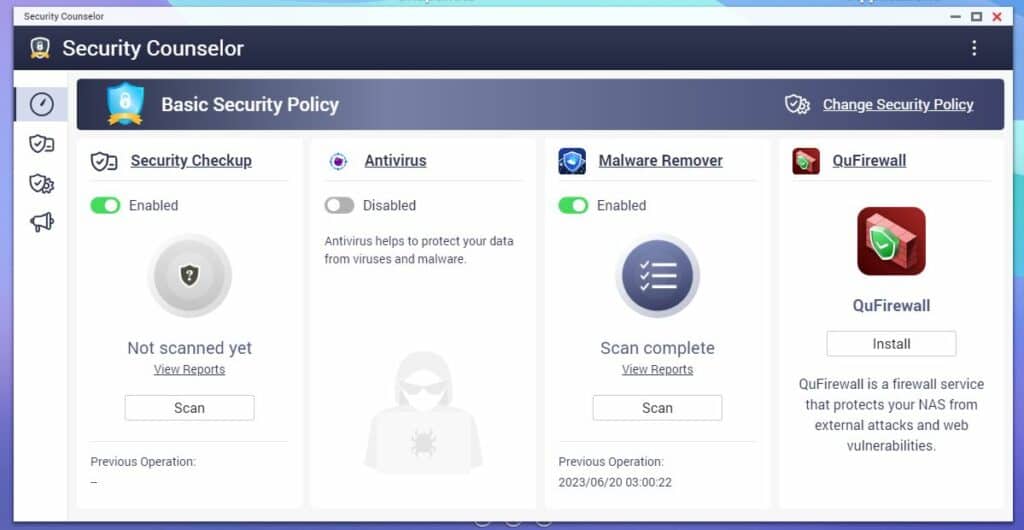
NAS security apps, available via the device’s web-based OS and accessible through the NAS app store, provide additional protection to bolster security for NAS solutions. These apps offer specialized features like vulnerability scanning, malware removal, real-time security alerts, and firewall capabilities, ensuring comprehensive system protection against potential weaknesses and threats. By leveraging these dedicated security applications, users can significantly enhance the overall security of their NAS.
Available via the QTS OS, the QNAP App Center is a comprehensive repository that offers a range of dedicated security applications to enhance the overall protection of your NAS. Some of these include:
- Security Counselor: QNAP Security Counselor is a comprehensive security solution for QNAP NAS devices, encompassing vulnerability scanning, malware removal, and real-time security alerts to ensure system protection. It provides actionable recommendations and proactive measures to address potential weaknesses and threats, enhancing overall NAS security.
- QuFirewall: QNAP QuFirewall is a robust firewall application designed for QNAP NAS devices, offering granular control over network traffic to enhance NAS security. It allows you to define traffic profiles and control access. The application also offers features like port forwarding, DDoS protection, IP blocking, and comprehensive logging and monitoring capabilities to detect and respond to suspicious network activity.
Conclusion
While your data is never 100% safe, adhering to these best practices will significantly enhance the security architecture of your NAS system. By implementing a comprehensive foundation, leveraging snapshot technology for data backup and restoration, creating a disaster recovery plan (like QNAP’s 3-2-1 backup strategy), staying up to date with firmware and app updates, and utilizing dedicated security applications, you can effectively protect your most important data and maintain the integrity of your NAS ecosystem.
Engage with StorageReview
Newsletter | YouTube | Podcast iTunes/Spotify | Instagram | Twitter | TikTok | RSS Feed