The new Zen 5 mobile AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 processor, featured 12 cores and 24 threads for exceptional multi-threaded performance.
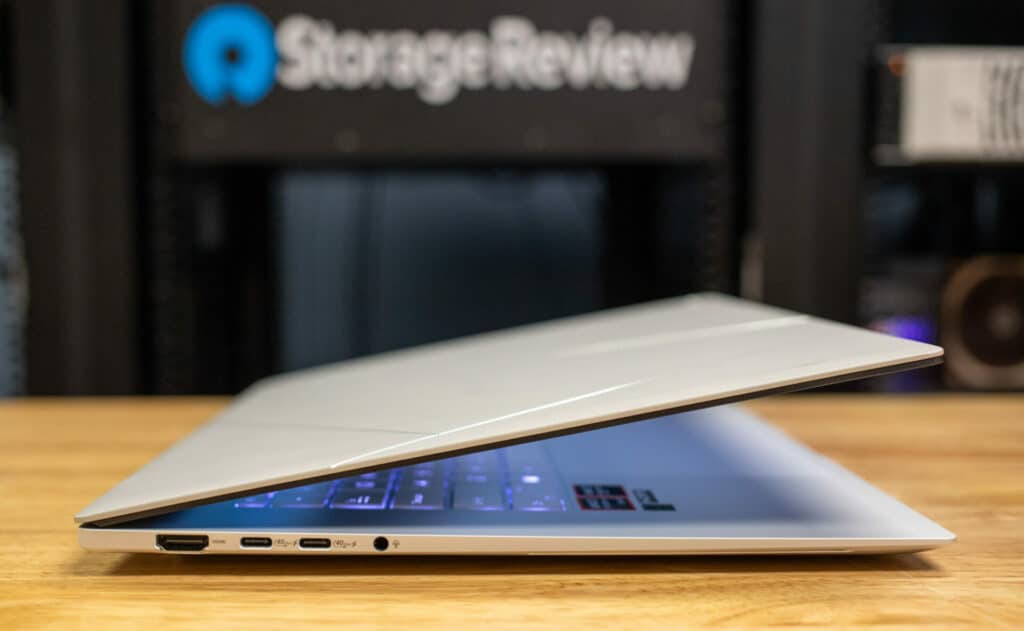
The ASUS Zenbook S16 is the latest high-performance, ultra-slim laptop from ASUS, showcasing cutting-edge technology to meet the modern demands of computing. At its core lies the AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 processor, featuring the advanced Zen 5 architecture. This next-generation architecture integrates a powerful CPU, GPU, and NPU, promising a balance of performance and power efficiency, positioning the S16 as a leading contender in the Ultrabook category
ASUS Zenbook S16 Processor and Power Efficiency
With 12 cores and 24 threads, the AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 is capable of exceptional multi-threaded performance, making it ideal for demanding tasks such as content creation, gaming, and data processing. Additionally, its integrated AI capabilities, powered by the AMD XDNA 2 NPU, provide up to 50 TOPS of AI performance, significantly enhancing productivity and enabling advanced AI applications directly on the device. Compared to its predecessors, the Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 offers a 16% increase in instructions per clock (IPC), ensuring substantial improvements in efficiency and processing power. These advancements position the Zenbook S16 as a good choice for users who require robust performance and sophisticated AI functionalities in a mobile form factor.
Here’s a quick rundown of its specifications:
| Specification | Details |
| Architecture | Zen 5 |
| Core Count | 12 cores |
| Thread Count | 24 threads |
| Base Clock Speed | 2.0 GHz |
| Max Boost Clock Speed | Up to 5.1 GHz |
| Cache | 36MB (L2 + L3) |
| Process Technology | 4 nm |
| AI Processing | 50 TOPS with AMD XDNA 2 NPU |
| Graphics | Integrated AMD Radeon 890M |
| Thermal Design Power (TDP) | 15W – 54W |
The AMD processor is also optimized for low power consumption. To test its battery longevity, we used the PCMark 10 battery benchmark, which simulates a range of modern office tasks such as video conferencing, web browsing, and document editing. Results showed that the laptop achieved a performance score of 5,449. More notably, it sustained these tasks for an impressive duration of 15 hours and 11 minutes, starting from a full battery and ending at 2% remaining charge.
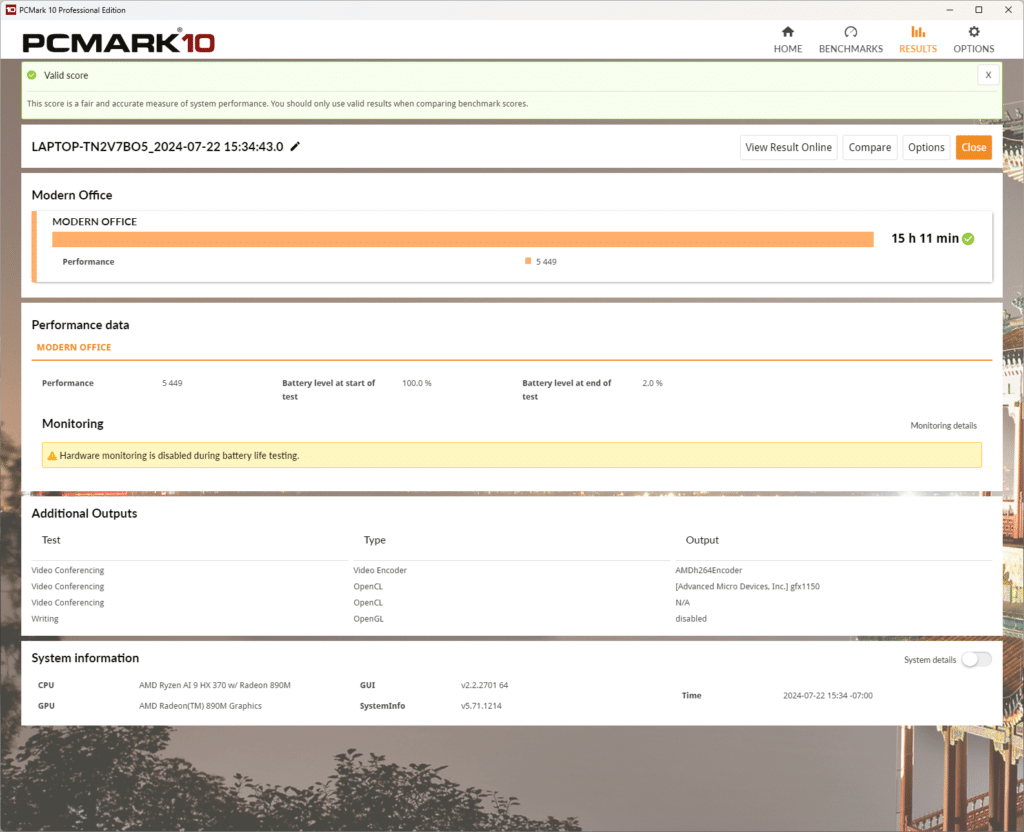
This lengthy battery life makes it suitable for professionals and users who require long-lasting performance throughout a typical workday without the need for frequent recharging. It is certainly a reliable companion for mobile productivity in this regard.
ASUS Zenbook S16 Display and Visual Experience
The laptop features a beautiful 16-inch 3K (2880 x 1800) OLED touchscreen with a 16:10 aspect ratio and a 120Hz refresh rate for smooth workflows. This resolution ensures that every visual element, from text to graphics, is sharp and clear.
With HDR support and a peak brightness of up to 500 nits—considered excellent for a laptop display—the ASUS Zenbook S16 provides vibrant colors and deep contrasts, making it ideal for media consumption, photo editing, and other visual tasks. Many premium ultrabooks feature screens with brightness levels ranging between 400 and 500 nits, positioning the Zenbook S16’s display at the higher end of the spectrum.
During our testing, we noticed that the display is impressively crisp and offers a good range of brightness settings, ensuring superior visibility and color accuracy, even in brightly lit environments. Additionally, the screen is designed to resist smudges, which is a significant advantage over some other laptops that can easily become fingerprint magnets.
The inclusion of stylus support further enhances its versatility, catering to artists and designers who can take advantage of precise input for their creative projects. The stylus offers USB-C charging in its sleeve, comes with four tip options, and has customizable buttons for gestures and functions.
ASUS Zenbook S16 Graphics and Memory
Complementing the processor is the AMD Radeon 890M graphics, built on the RDNA 3.5 architecture. The AMD Radeon 890M is a mobile GPU designed for ultra-thin laptops, offering performance that rivals most entry-level discrete GPUs with efficient AI processing and robust gaming capabilities.
The 890M features the following specifications:
| Specification | Details |
| Architecture | RDNA 3.5 |
| Core Count | 16 Compute Units (CUs) |
| Base Clock Speed | 2.9 GHz |
| Memory | 512 MB Framebuffer |
| Peak Performance | Up to 50 TOPS AI Performance |
| Process Technology | 4 nm |
| Power Consumption | Optimized for low power |
| Supported Technologies | DirectX 12 Ultimate, Vulkan, OpenGL 4.6 |
| Display Support | Up to 3 displays with HDR |
| Ray Tracing | Yes, Hardware-accelerated |
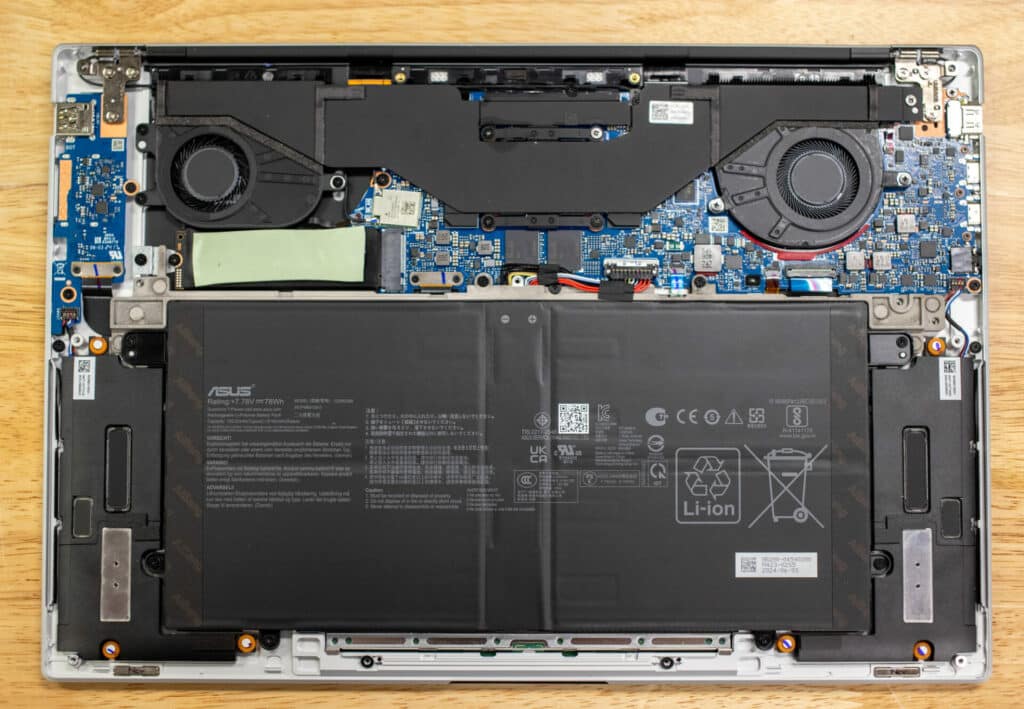
Our build of the Zenbook is equipped with 32GB of LPDDR5x-7500 SDRAM, which is sufficient for most demanding tasks; though professionals working in image and video editing will certainly opt for more memory. Additionally, we have a 1TB Micron 2400 NVMe SSD, featuring 176-layer QLC NAND technology and sequential read/write speeds up to 4,500MB/s and 3,600MB/s, respectively.
ASUS Zenbook S16 Advanced AI Capabilities
The Zenbook S16 also features the AMD XDNA 2 NPU. This neural processing unit enables a range of AI applications to run directly on the device, from AI assistants and chatbots to generative AI models. This capability enhances user interaction and productivity, allowing for real-time AI processing without relying on cloud services. The AI features provides practical benefits in daily use, such as improving battery life through intelligent power management and enhancing security with advanced biometric authentication.
ASUS Zenbook S16 Design and Build Quality
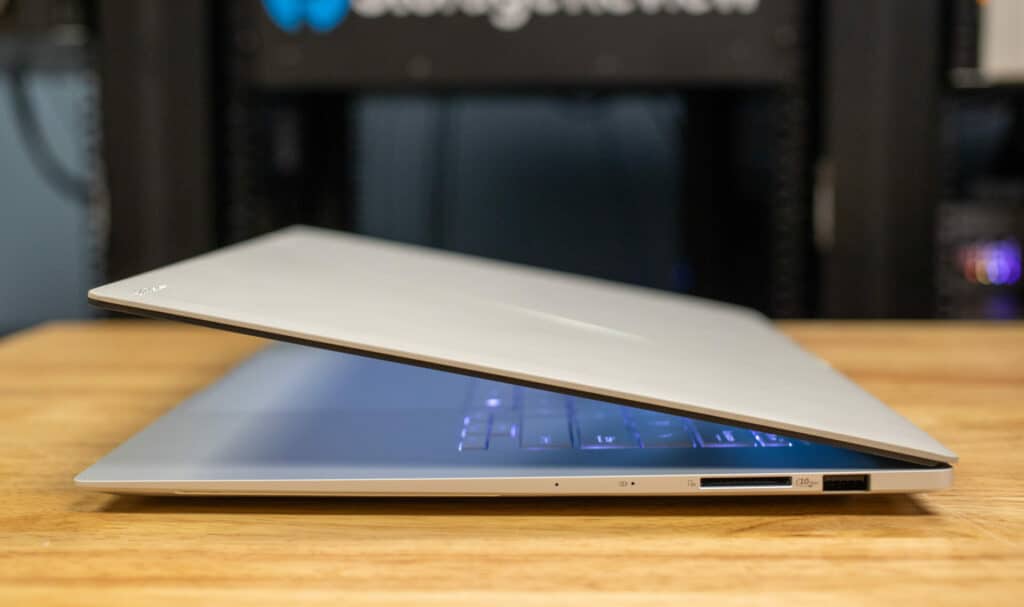
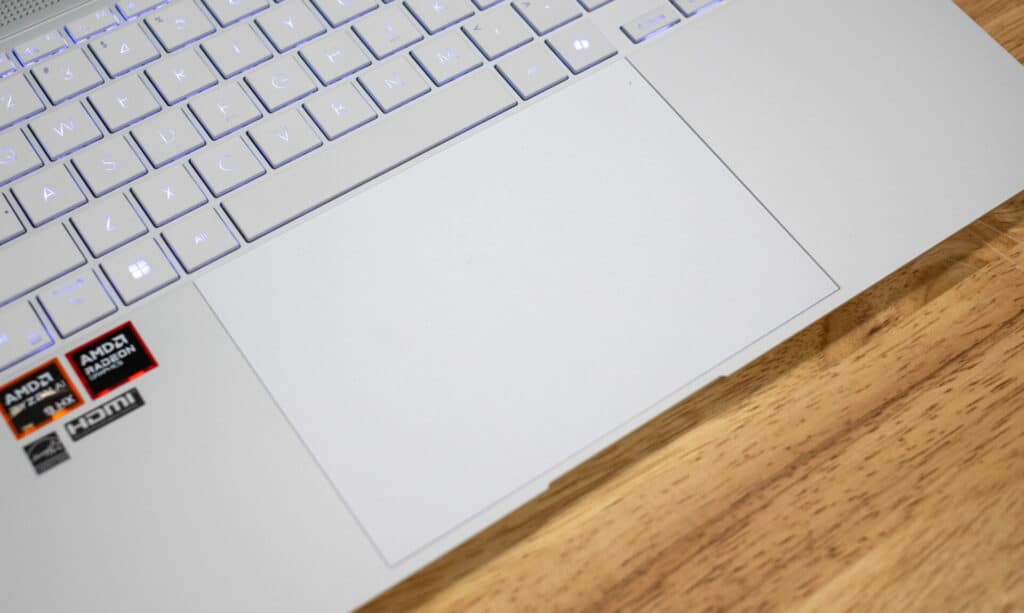
The design of the ASUS Zenbook S 16 is both functional and slick. The laptop features high-tech ceramic materials, which give it a premium look and enhance its durability. Despite its robust build, the Zenbook S 16 remains incredibly lightweight at just 1.50 kg, and its dimensions of 35.36 x 24.30 x 1.19 cm make it highly portable. The keyboard is well-spaced and comfortable to type on, and the large touchpad ensures precise navigation. It also supports the latest WiFi-7 standard, for fast and stable internet connections for those on the go or in the office/at home.
Thanks to an efficient fan and heat pipe setup, the Zenbook S16 is designed to keep the laptop cool even during intense workloads. This helps to eliminate performance throttling, and makes the device comfortable to use, even on your lap.
The audio system (certified by Harman Kardon and featuring Dolby Atmos support) provides decent sound for those who use the ultrabook without a headset.
3DMark Benchmarks
First up is a range of tests from 3Dmark–a popular benchmarking tool used to evaluate the performance of computer hardware, particularly focusing on graphics processing units GPUs, and CPUs. It runs a series of demanding tests that simulate real-world gaming and computational tasks to provide an overall performance score. These scores help users compare different systems and understand how well a particular setup handles graphical and processing workloads.
Fire Strike Extreme
Fire Strike Extreme is a DirectX 11 benchmark designed for high-performance gaming PCs. It tests the system’s ability to handle advanced graphical features such as tessellation, volumetric lighting, and particle effects.
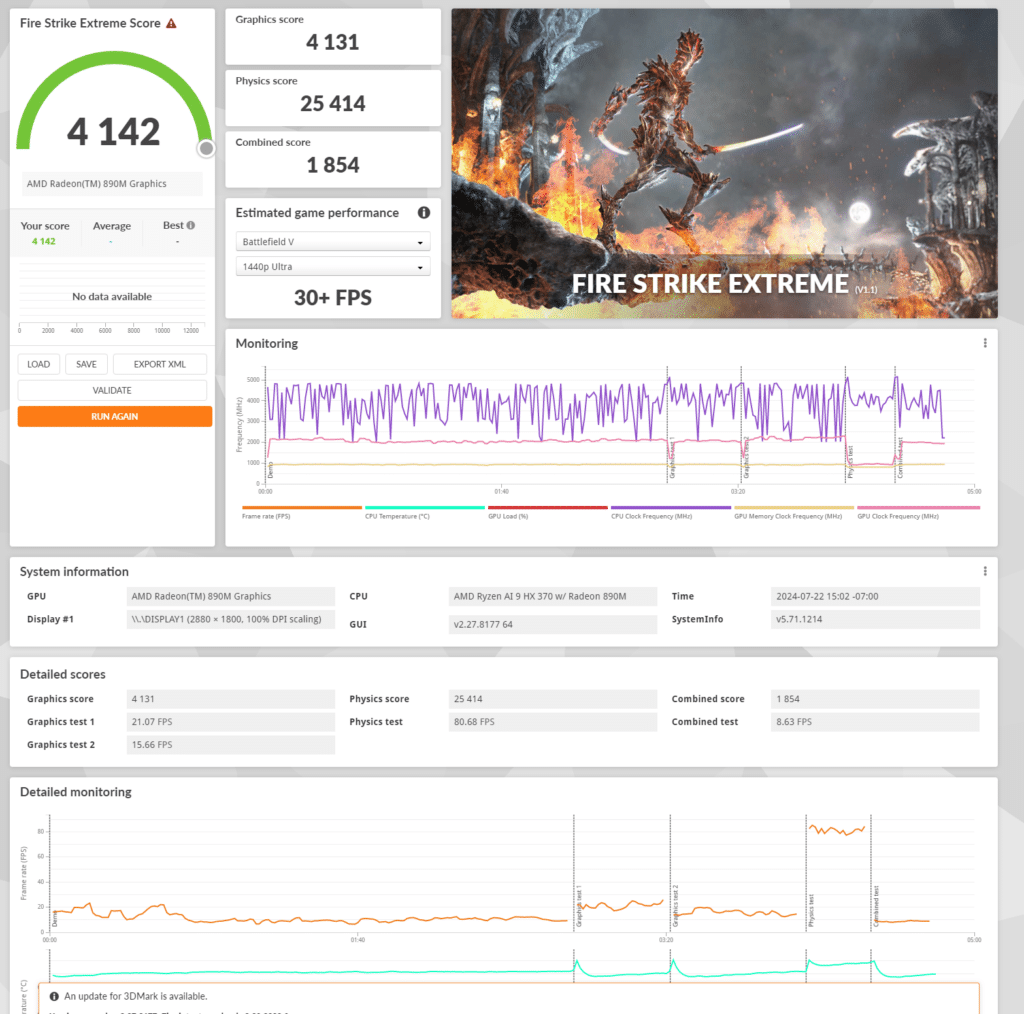
The AMD Radeon 890M in the Fire Strike Extreme test scored 4,142 with a graphics score of 4,131 and a physics score of 25,414. The combined score was 1,854. This indicates that the Radeon 890M is capable of handling most demanding graphical tasks and modern games at high settings with decent performance. However, while the graphics performance is solid, the combined score suggests that there might be some limitations in handling simultaneous CPU and GPU loads, which could affect performance in very demanding scenarios.
Fire Strike Ultra
Fire Strike Ultra is another DirectX 11 benchmark but with a focus on 4K resolution. It pushes the system to its limits by rendering at a much higher resolution to test its capabilities in ultra-high-definition gaming environments.
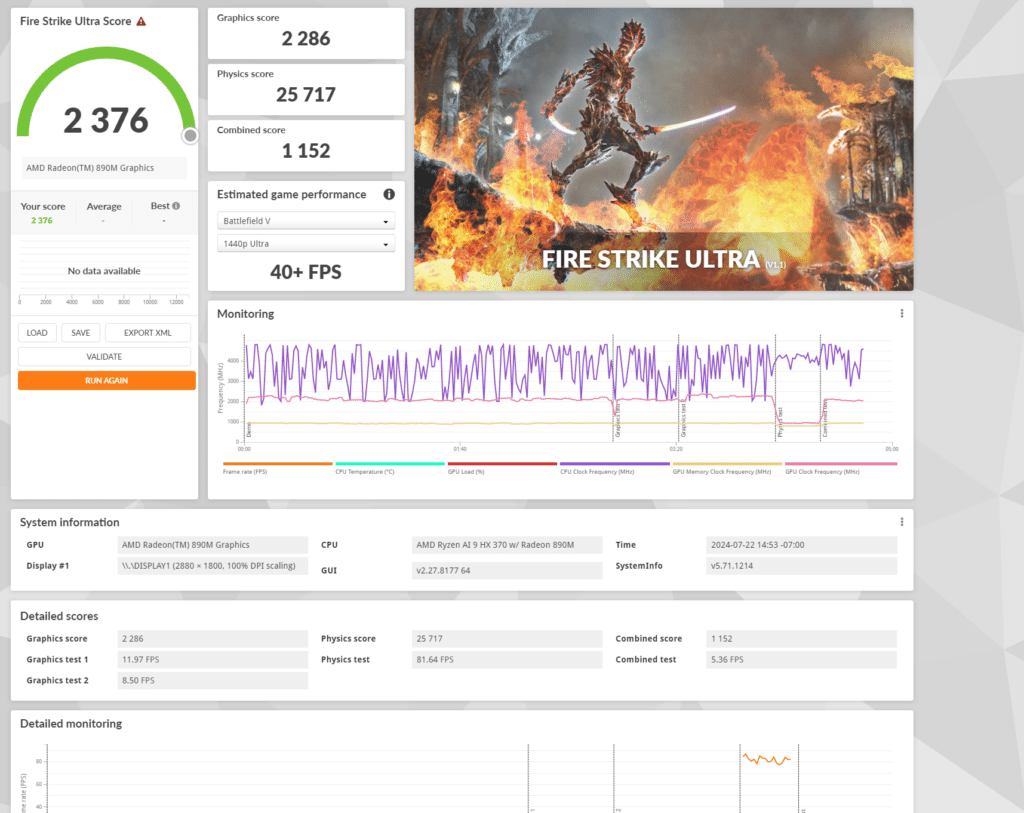
In the Fire Strike Ultra test, the AMD Radeon 890M scored 2,376, with a graphics score of 2,286 and a physics score of 25,717. The combined score was 1,152. These results show a significant drop in graphics performance compared to Fire Strike Extreme, as expected due to the higher resolution and more intense processing requirements. The physics score remains strong, indicating that the CPU performance is consistently high, but the GPU struggles more (as expected) with the increased demands of 4K rendering.
Port Royal
Port Royal is a DirectX 12 benchmark specifically designed for real-time ray tracing performance. It evaluates how well the GPU handles ray-traced reflections, shadows, and other advanced lighting effects in real time.
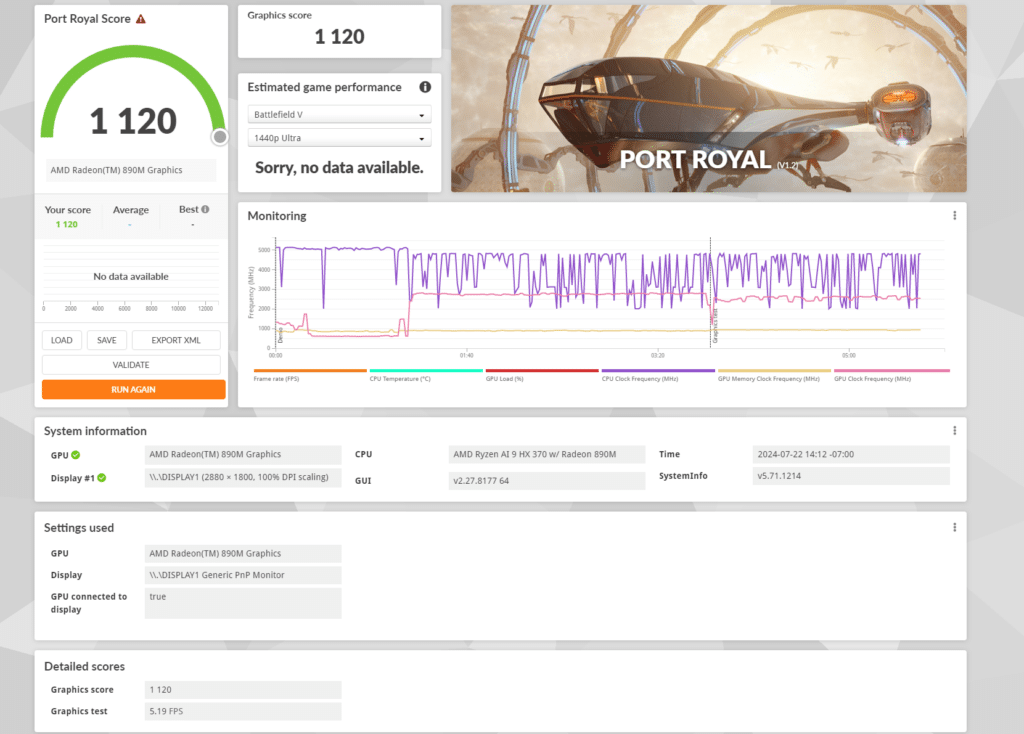
The AMD Radeon 890M showed a score of 1,120 in the Port Royal test. We weren’t expecting a great result when handling the extreme computational load of real-time ray tracing, especially compared to top-tier dedicated GPUs. Nonetheless, its performance was sufficient for basic ray tracing effects but will certainly struggle with more complex scenes or higher resolutions.
Speedway
Speedway is a high-fidelity benchmark that simulates a futuristic racing game environment, testing the GPU’s ability to render detailed graphics and maintain smooth frame rates under intense conditions.
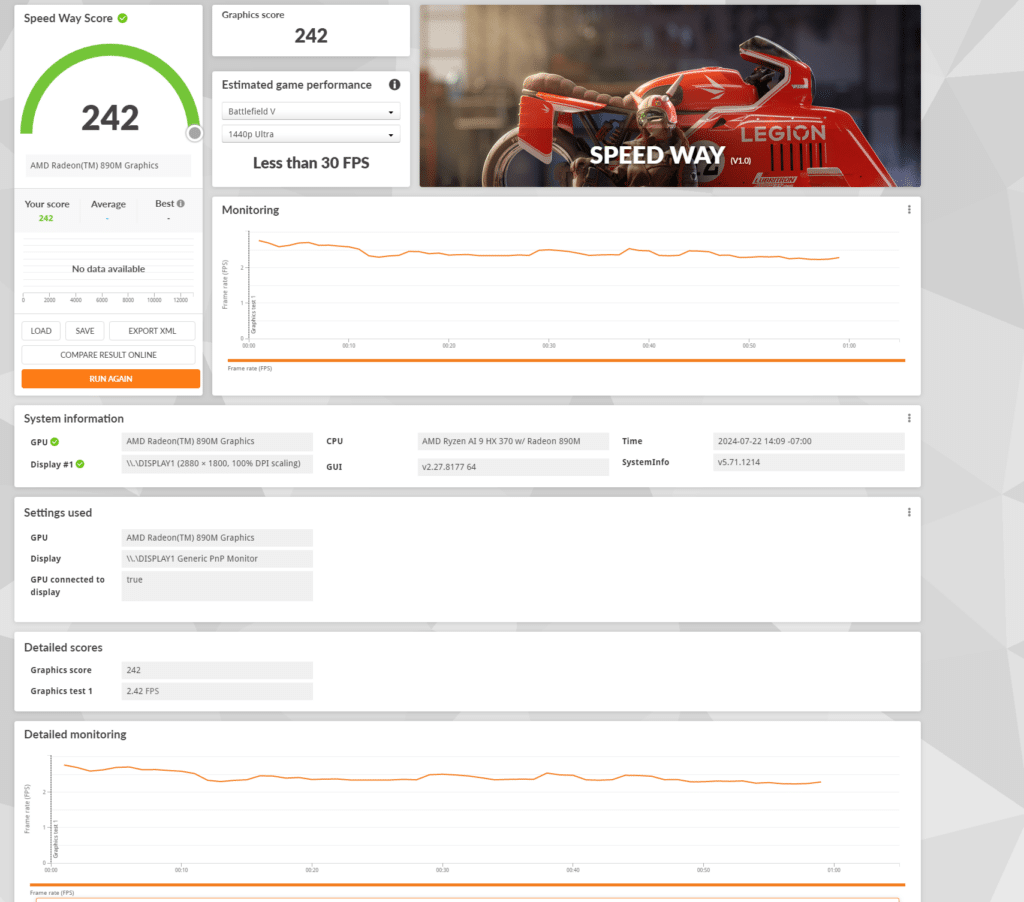
Here, the AMD Radeon 890M scored 242, with an average frame rate of 2.42 FPS. This indicates that the GPU faces significant challenges when rendering highly detailed and fast-paced scenes. The low frame rate suggests that while the Radeon 890M can handle less demanding tasks, it is not well-suited for very high-end gaming or simulation applications requiring rapid and complex graphical computations. Again, this was expected due to the lower-end specs of the AMD GPU.
Time Spy
Time Spy is a DirectX 12 benchmark that measures the GPU’s ability to handle modern gaming workloads. It includes a range of graphical tests and a CPU test to provide a comprehensive performance overview.
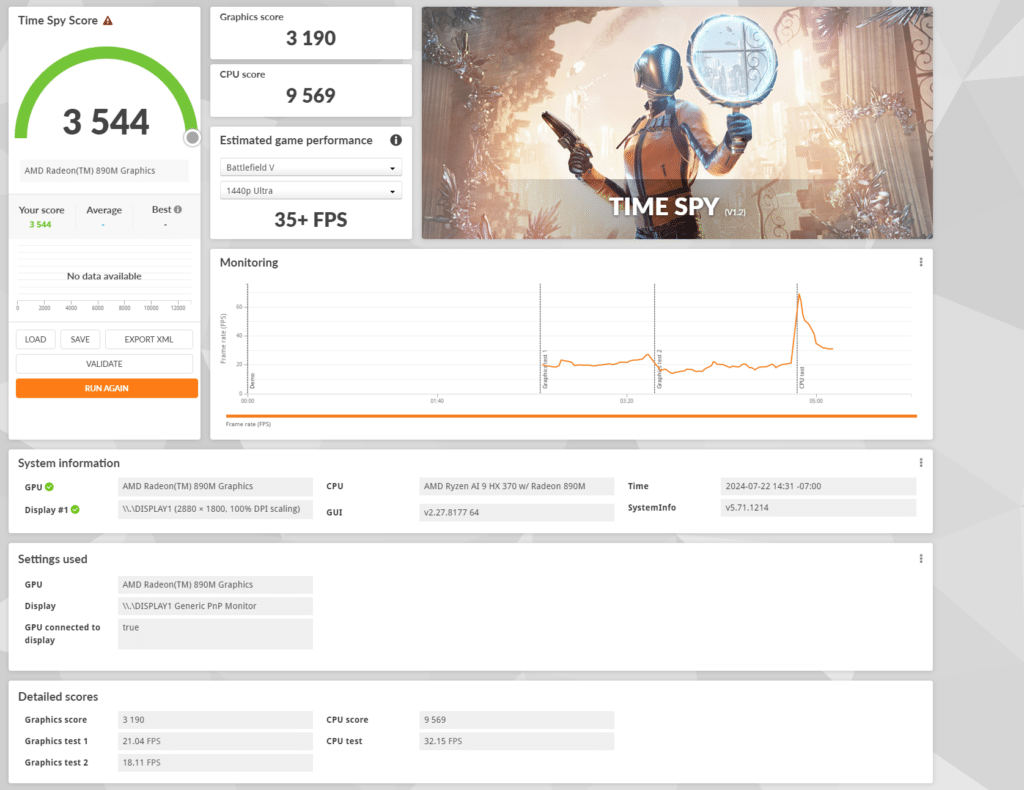
The AMD Radeon 890M scored 3,544 in the Time Spy test, with a graphics score of 3,190 and a CPU score of 9,569. These results highlight the GPU’s capability to handle modern DirectX 12 titles effectively, offering fairly smooth gameplay and detailed graphics. The high CPU score indicates that the Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 processor provides decent computational power, complementing the GPU’s performance well.
Time Spy Extreme
Time Spy Extreme is a more demanding version of the Time Spy benchmark, running at 4K resolution to push the system’s capabilities further.
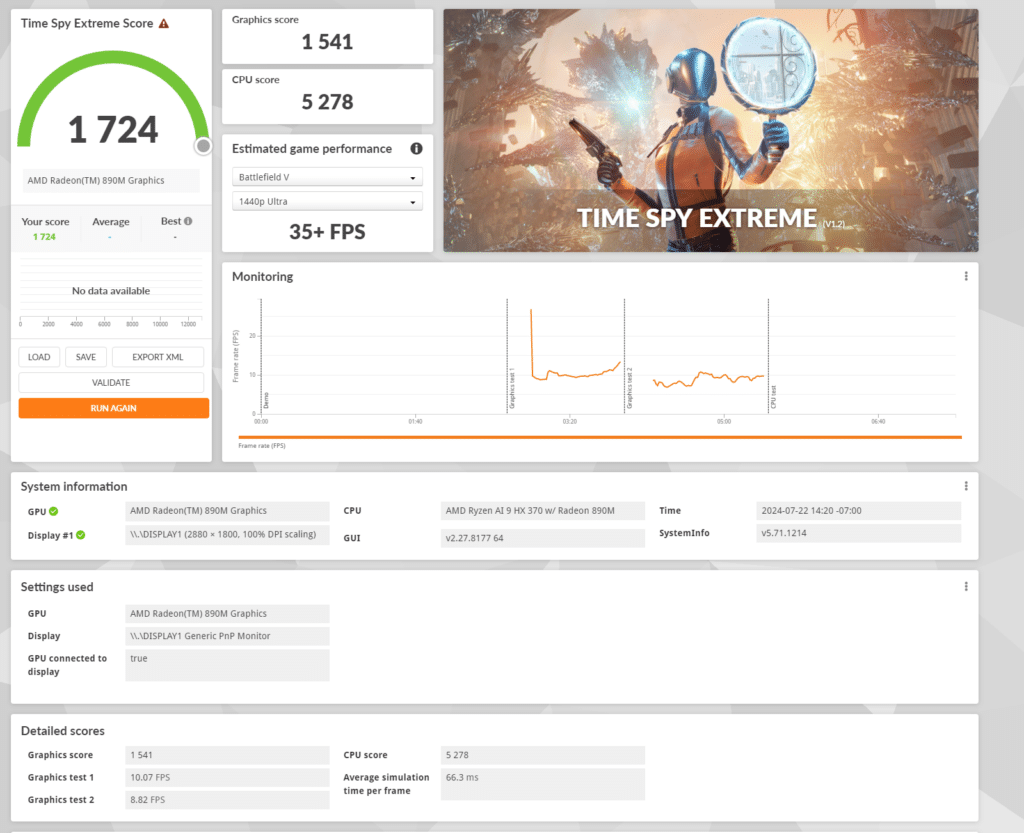
Here, the AMD Radeon 890M scored 1,724, with a graphics score of 1,541 and a CPU score of 5,278. These scores reflect the increased difficulty of rendering at 4K, showing a significant drop in graphics performance. The CPU score also decreases, although it remains strong relative to the increased workload. This demonstrates that, while the Radeon 890M and Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 can handle high-resolution tasks, they are more suited for lower resolutions where they can deliver better performance.
SPECviewperf 2020
Our first test is SPECviewperf 2020, the worldwide standard for measuring graphics performance of professional applications under the OpenGL and Direct X application programming interfaces. The viewsets (or benchmarks) represent graphics content and behavior from actual applications without having to install the applications themselves. The newest version of this benchmark went through significant updates late last year, including new viewsets taken from traces of the latest versions of 3ds Max, Catia, Maya, and Solidworks applications. In addition, they added support within all viewsets for both 2K and 4K resolution displays.
The ASUS Zenbook S16 demonstrates competent performance across various professional applications in the SPECviewperf 2020 benchmark. It scores 43.55 in 3dsmax-07, indicating decent capabilities in 3D modeling and rendering tasks, albeit behind high-end workstation GPUs. The Catia-06 score of 34.75 reflects decent enough performance in CAD and precision engineering, while a score of 53.05 in Creo-03 highlights its efficiency in handling complex product designs. It performed well for an entry-level GPU in Maya-06 (high-end graphics and animation workloads) with a score of 127.66.
| SPECviewperf2020 Viewsets (Higher is better) | ASUS Zenbook S16 (AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 CPU, AMD Radeon 890M GPU) |
| 3dsmax-07 | 43.55 |
| Catia-06 | 34.75 |
| Creo-03 | 53.05 |
| Energy-03 | 21.72 |
| Maya-06 | 127.66 |
| Medical-03 | 35.95 |
| Snx-04 | 121.61 |
| Sw-05 | 71.21 |
Luxmark
LuxMark is a benchmarking utility designed to measure the performance of OpenCL-enabled GPUs. It focuses on rendering complex scenes using the LuxRender engine, making it a useful tool for evaluating how well a system can handle GPU-intensive tasks such as 3D rendering and computational workloads.
Here, the ASUS Zenbook S16’s performance showed 1,899 in the Hallbench scene, which is right around what we expected from the workstation’s capability in rendering complex environments. The Food scene score of 1,000, while lower, still represents decent performance for an ultra-slim laptop in computationally heavy tasks.
| Luxmark (Higher is better) | ASUS Zenbook S16 (AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 CPU, AMD Radeon 890M GPU) |
| Hallbench | 1,899 |
| food | 1,000 |
Blackmagic Disk Speed Test
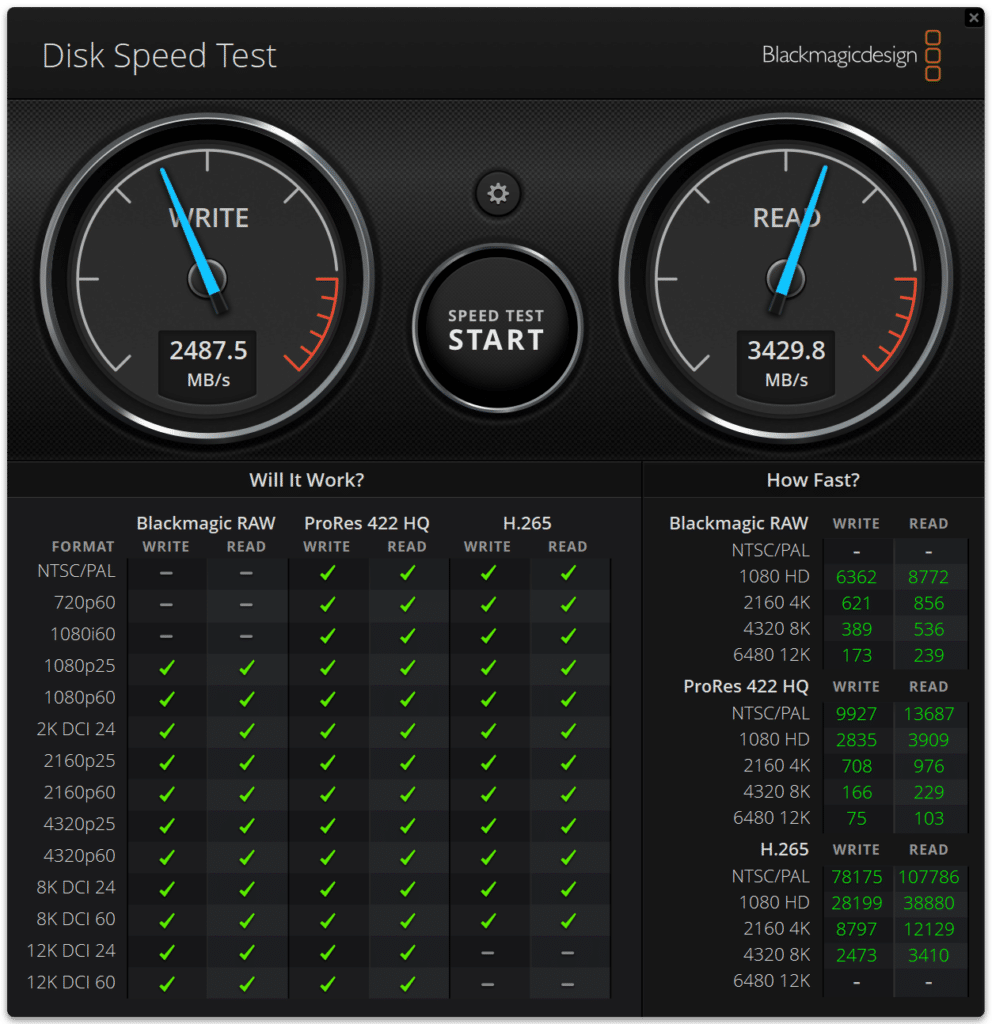
In Blackmagic’s disk speed test, we saw 3,439.8MB/s read and 2,487.5MB/s write with the 1TB Micron 2400 SSD.
Blackmagic RAW Speed Test
The Blackmagic RAW Speed Test is a performance benchmarking tool designed to measure the capabilities of a system in handling video playback and editing using the Blackmagic RAW codec. It evaluates how well a system can decode and play back high-resolution video files, providing frame rates for both CPU and GPU-based processing.
A score of 52 FPS for 8K video playback on the CPU is pretty good, meaning that the AMD processor can handle 8K video editing and playback with relative ease.
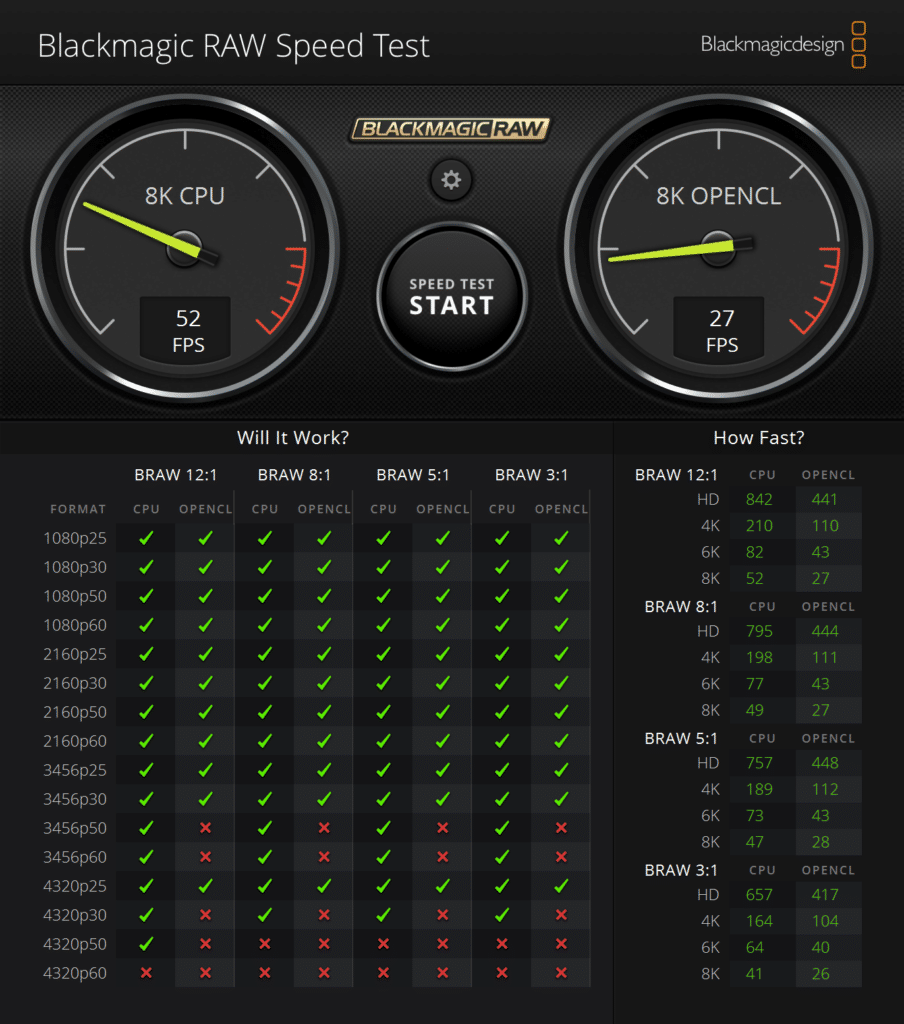
A score of 27 FPS for 8K CUDA playback means that while the AMD Radeon 890M can handle 8K video, it does so with less efficiency than the CPU. For context, in video editing, 24 FPS is often considered the minimum threshold for acceptable playback performance, as it matches the standard frame rate for most films.
| Blackmagic RAW Speed Test (Higher is better) | ASUS Zenbook S16 (AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 CPU, AMD Radeon 890M GPU) |
| 8K CPU | 52FPS |
| 8K CUDA | 27FPS |
7-Zip Compression
The built-in memory benchmark in the popular 7-Zip utility measures the performance of a system’s CPU and memory during compression and decompression tasks, providing an indication of how well the system can handle data-intensive operations.
Here, the ASUS Zenbook S16 achieved a total rating of 93.173 GIPS with a CPU usage of 2212%. The current compression rating of 85.225 GIPS and resulting rating of 87.498 GIPS reflect the laptop’s efficient data handling capabilities. During decompression, the performance remains solid with a current rating of 107.383 GIPS and a resulting rating of 98.848 GIPS.
| 7-Zip Compression Benchmark (Higher is better) | ASUS Zenbook S16 (AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 CPU, AMD Radeon 890M GPU) |
| Current CPU Usage | 2282% |
| Current Rating/Usage | 3.735 GIPS |
| Current Rating | 85.225 GIPS |
| Resulting CPU Usage | 2228% |
| Resulting Rating/Usage | 3.927 GIPS |
| Resulting Rating | 87.498 GIPS |
| Decompressing | |
| Current CPU Usage | 2208% |
| Current Rating/Usage | 4.864 GIPS |
| Current Rating | 107.383 GIPS |
| Resulting CPU Usage | 2195% |
| Resulting Rating/Usage | 4.502 GIPS |
| Resulting Rating | 98.848 GIPS |
| Total Rating | |
| Total CPU Usage | 2212% |
| Total Rating/Usage | 4.214 GIPS |
| Total Rating | 93.173 GIPS |
UL Procyon AI Inference
UL’s Procyon suite is designed to estimate a workstation’s performance across various professional applications. This particular test evaluates the inference times of different AI models, providing insights into how well the system can handle AI workloads. The test was run on both the Zenbook’s CPU and GPU.
The MobileNet V3 model achieves a fast inference time of 1.28 ms on the GPU compared to 1.53 ms on the CPU, showcasing the efficiency of the Radeon 890M GPU in handling lightweight models. More complex models like ResNet 50 and Inception V4 show significant improvements on the GPU, with inference times of 8.71 ms and 21.47 ms, respectively, compared to the CPU’s 11.29 ms and 34.49 ms. The most dramatic difference is seen in the Real-ESRGAN model, where the GPU’s 729.15 ms far outperforms the CPU’s 3685.49 ms, highlighting the substantial advantage of GPU acceleration for high-complexity AI tasks.
| UL Procyon Average Inference Times (Lower is better) | ASUS Zenbook S16 CPU test (Ryzen AI 9 HX 370) | ASUS Zenbook S16 GPU test (AMD Radeon 890M GPU) |
| MobileNet V3 | 1.53 ms | 1.28 ms |
| ResNet 50 | 11.29 ms | 8.71 ms |
| Inception V4 | 34.49 ms | 21.47 ms |
| DeepLab V3 | 39.00 ms | 31.01 ms |
| YOLO V3 | 84.50 ms | 27.56 ms |
| Real-ESRGAN | 3,685.49 ms | 729.15 ms |
y-cruncher
y-cruncher is a multi-threaded and scalable program that can compute Pi and other mathematical constants to trillions of digits. Since its launch in 2009, it has become a popular benchmarking and stress-testing application for overclockers and hardware enthusiasts.
In this test, the ASUS Zenbook S16 delivered respectable performance in the y-cruncher benchmark, with total computation times of 29.871 seconds for 1 billion digits, 84.266 seconds for 2.5 billion digits, and 205.098 seconds for 5 billion digits. These results show that the S16 is capable of handling intensive computational tasks, although it falls behind high-end desktop CPUs typically used for such benchmarks.
| y-cruncher (Total Computation time) | ASUS Zenbook S16 (AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 CPU, AMD Radeon 890M GPU) |
| 1 billion digits | 29.871 |
| 2.5 billion | 84.266 |
| 5 billion | 205.098 |
Geekbench 6
Geekbench 6 is a cross-platform benchmark that measures overall system performance. You can find comparisons to any system you want in the Geekbench Browser.
With a single-core score of 2,873 and a multi-core score of 13,488, it demonstrated good performance for its form factor in handling both single-threaded and multi-threaded tasks, indicating that it can efficiently manage a variety of demanding applications. The GPU’s OpenCL score of 35,002 highlights the strong computational capabilities of the AMD Radeon 890M GPU, meaning that the it can certainly get the job done during most intensive graphical and parallel computing workloads.
| Geekbench 6 (Higher is better) | ASUS Zenbook S16 (AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 CPU, AMD Radeon 890M GPU) |
| CPU Single-Core | 2,873 |
| CPU Multi-Core | 13,488 |
| GPU (GPU OpenCL) | 35,002 |
Cinebench R23
Cinebench R23 is a benchmark tool that evaluates a system’s CPU performance by rendering a complex 3D scene using the Cinema 4D engine. It measures both single-core and multi-core performance, providing a comprehensive view of the CPU’s capabilities in handling 3D rendering tasks.
With a multi-core score of 15,809 points, it shows that is can handle multi-threaded tasks, such as 3D rendering and complex simulations. The single-core score of 2,003 points indicates robust performance in tasks that rely on single-thread efficiency. The MP ratio of 7.89x reflects the effective scaling of multi-core performance. These results position the Zenbook S16 as a solid performer for both single-threaded and multi-threaded applications, making it suitable for professional content creation and 3D rendering workflows.
| Cinebench R23 (Higher is better) | ASUS Zenbook S16 (AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 CPU, AMD Radeon 890M GPU) |
| Multi-Core | 15,809 pts |
| Single-Core | 2,003 pts |
| MP ratio | 7.89x |
Worth noting here that the performance measurement of Cinebench gets better with subsequent runs. This can be attributed to the architecture of the benchmark itself. We generally run with the default 10 minute looping test and then capture the score for reviews, but on request for this review, we ran the single run multiple times to capture a peak score.
| Cinebench R23 – Second round of testing (Multi-core) | |
| Run 1 | 14,837 pts |
| Run 2 | 17,602 pts |
| Run 3 | 17,604 pts |
| Run 4 | 17,556 pts |
Cinebench 2024
Cinebench 2024 extends the benchmark capabilities of R23 by adding GPU performance evaluation. It continues to test CPU performance but also includes tests that measure the GPU’s ability to handle rendering tasks.
While the multi-core score is significantly lower compared to Cinebench R23, it reflects the increased complexity and additional GPU tasks included in the 2024 version of the benchmark. The single-core score also highlights the system’s capability to handle single-threaded processes effectively, making it a competent device for tasks that require both CPU and GPU power.
| Cinebench R24 (Higher is better) | ASUS Zenbook S16 (AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 CPU, AMD Radeon 890M GPU) |
| Multi-Core | 823 pts |
| Single-Core | 115 pts |
| MP Ratio | 7.18x |
Conclusion
Overall, the ASUS Zenbook S16 is a great example of integrating advanced technology in a sleek, ultra-slim laptop, delivering excellent performance and power efficiency. At its core is the new Zen 5 architecture-based AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 processor, featuring 12 cores and 24 threads for exceptional multi-threaded performance ideal for content creation, gaming, and data processing. Combined with the AMD Radeon 890M GPU, the Zenbook excelled in both single-threaded and multi-threaded scenarios during our extensive tests.
Not only did it perform well, but the Zenbook is extremely power-efficient, achieving an impressive 15 hours and 11 minutes of continuous use on the PCMark 10 battery benchmark, thanks to the cutting edge efficiency of the new AMD Zen 5 CPU. This proves it can support long work sessions or extended periods of use without frequent recharging, making it an excellent choice for professionals who need reliable performance throughout the day.
Additionally, the Zenbook S16 features a high-tech ceramic material build, a vibrant 16-inch 3K OLED display, and an efficient cooling system, ensuring it stands out as a top-tier choice for those seeking great performance, long battery life, and sleek design.
Engage with StorageReview
Newsletter | YouTube | Podcast iTunes/Spotify | Instagram | Twitter | TikTok | RSS Feed









