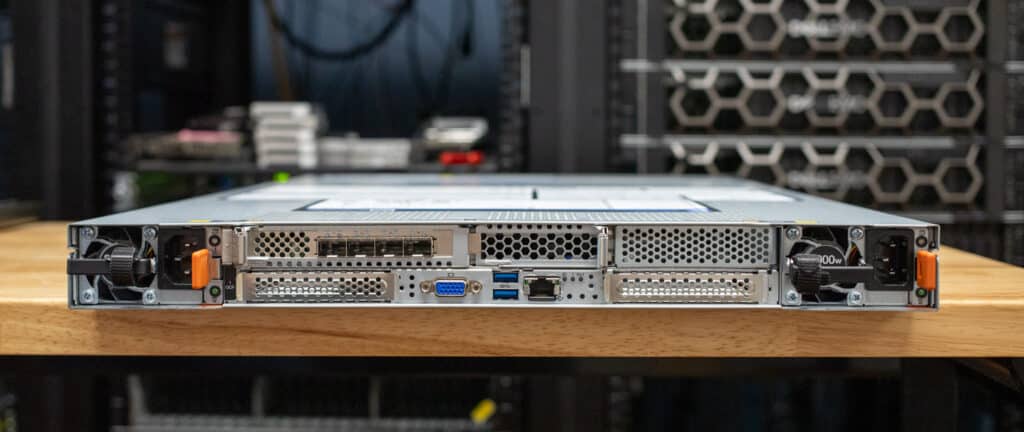
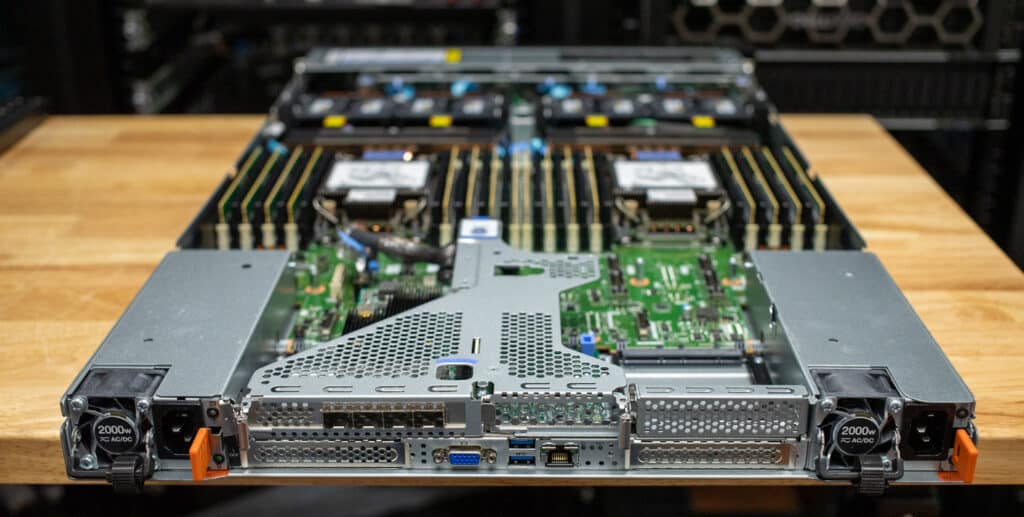
The Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 is a flexible, powerful 2-socket, 1U rack server designed for mainstream compute applications.
The Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 is a flexible and powerful 2-socket, 1U rack server designed to address the needs of industries like cloud services and telecommunications. Whether optimizing for scale-out workloads or future-proofing your data center, the SR630 V4 offers meaningful upgrades over its predecessor, the SR630 V3. In this review, we examined what’s new and how Lenovo has fine-tuned this enterprise server to meet the challenges of modern IT environments.
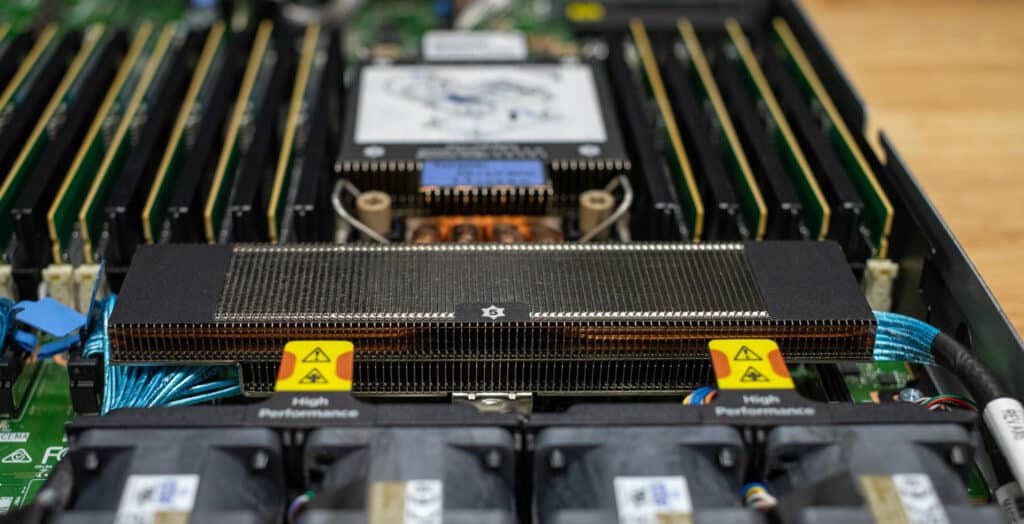

Differences Between Lenovo SR630 V4 and SR630 V3
Processors
The processor capabilities mark one of the more significant upgrades in the SR630 V4. While the SR630 V3 relied on Intel Xeon 4th and 5th Gen Scalable Processors with up to 64 cores and Hyper-Threading, the SR630 V4 introduces the Intel Xeon 6700-series processors with up to 144 efficient cores (E-cores). This transition doubles the core count while focusing on efficiency, though Hyper-Threading support is omitted. Additionally, the V4 offers planned support for Intel Xeon P-cores, which could provide an even more significant boost for specific workloads. The higher core density in the V4 allows organizations to consolidate more applications on the same number of servers, reducing operational costs and physical server requirements.
Here’s a rundown of all of SR630 V4’s supported 6700-series processors:
| PU Model | Cores/Threads | Core Speed (Base/TB max) | L3 Cache | Mem. Chan | Max Memory Speed | UPI 2.0 Links & Speed | PCIe Lanes | TDP |
| 6710E | 64 / 64 | 2.4 / 3.2 GHz | 94 MB | 8 | 5600 MHz | 4 / 16 GT/s | 88 | 205W |
| 6731E | 96 / 96 | 2.2 / 3.1 GHz | 96 MB | 8 | 5600 MHz | None‡ | 88 | 250W |
| 6740E | 96 / 96 | 2.4 / 3.2 GHz | 96 MB | 8 | 6400 MHz | 4 / 20 GT/s | 88 | 250W |
| 6746E | 112 / 112 | 2.2 / 2.7 GHz | 96 MB | 8 | 5600 MHz | 4 / 16 GT/s | 88 | 250W |
| 6756E | 128 / 128 | 1.8 / 2.6 GHz | 96 MB | 8 | 6400 MHz | 4 / 24 GT/s | 88 | 225W |
| 6766E | 144 / 144 | 1.9 / 2.7 GHz | 108 MB | 8 | 6400 MHz | 4 / 24 GT/s | 88 | 250W |
| 6780E | 144 / 144 | 2.2 / 3 GHz | 108 MB | 8 | 6400 MHz | 4 / 24 GT/s | 88 | 330W |
Memory
Regarding memory, the SR630 V4 improves on the V3’s DDR5 memory, operating up to 5600 MHz by supporting DDR5 memory speeds of up to 6400 MHz for E-cores. Both systems feature 32 DIMMs (16 per processor) and two DIMMs per channel across eight channels per CPU. Still, the V4 introduces future-proofing with planned support for advanced memory technologies like Compute Express Link (CXL) and MCRDIMMs for P-cores.
While the SR630 V3 could support up to 8TB of memory, the V4 focuses on a more targeted capacity of 2TB for E-cores, optimizing cost and performance for specific workloads.
Storage
The Lenovo SR630 V4 storage capabilities demonstrate a shift toward high-performance NVMe drives while reducing reliance on traditional SAS/SATA options. The SR630 V3 provided flexibility with 3.5-inch SAS/SATA drive bays and up to 16 onboard NVMe ports. However, the SR630 V4 supports up to 12 NVMe drives across front and rear configurations, adding future options for E3.S drive formats, which promise greater capacities and density.
The V4 eliminates support for 3.5-inch drives but introduces M.2 hot-swap options for operating system boot, enhancing performance and serviceability. By focusing on NVMe and eliminating the need for additional adapters, the V4 maximizes I/O bandwidth and system efficiency.
Networking
For networking, the SR630 V4 builds on the V3’s single OCP slot by offering dual OCP 3.0 slots, both supporting PCIe Gen 5 x16. This upgrade doubles the networking flexibility, allowing for enhanced connectivity and throughput with dual-port 200GbE network adapters or other advanced networking solutions.
The increased PCIe bandwidth (32GT/s in Gen 5 vs. 16GT/s in Gen 4) means the V4 can better handle demanding data center and cloud workloads, making it a more versatile option for modern networking needs.
Power
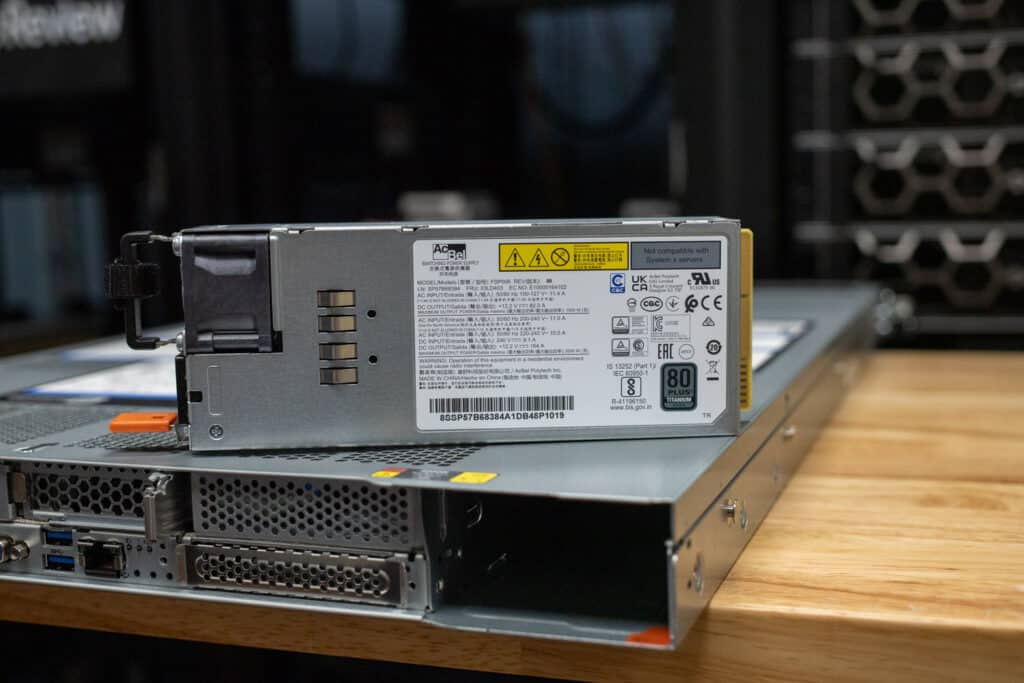
Finally, the SR630 V4 offers enhanced power supply options, moving from the SR630 V3’s 750W–1800W AC Platinum/Titanium options to a broader range of 800W–2000W, including ErP Lot 9-compliant models for energy efficiency. The V4 also retains Telco-friendly -48VDC power supply support while introducing new 1300W HVDC options for specific regional requirements. These enhancements make the V4 more adaptable to diverse power environments, ensuring it meets the energy demands of more complex, high-performance configurations.
Overall, the SR630 V4 delivers a solid leap forward on paper to better address the need for more performance, flexibility, and efficiency in modern IT environments.
Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 Specifications
| Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 Specifications | |
| Form Factor | 1U rack |
| Processor | One or two Intel Xeon 6700E-series processors (up to 144 cores, 2.4 GHz, and 330 W TDP). Support for Intel Xeon 6700P-series processors planned for 1Q/2025. |
| Memory | 32 DIMM slots (16 per processor), supports TruDDR5 RDIMMs at up to 6400 MHz (1DPC) or 5200 MHz (2DPC). CXL memory is planned for Intel Xeon 6700P-series in 1Q/2025. |
| Memory Maximum | Up to 2TB using 32x 64GB RDIMMs |
| Disk Drive Bays |
|
| Maximum Internal Storage | 184.3TB using 12x 15.36TB 2.5-inch NVMe SSDs |
| Storage Controller | Up to 16x Onboard NVMe ports with RAID support (Intel VROC). Planned support for 12Gb SAS/SATA RAID and non-RAID adapters. |
| Network Interfaces | Two OCP 3.0 SFF slots with PCIe 5.0 host interface (x8 or x16), supporting up to 100 GbE network adapters. |
| PCI Expansion Slots |
|
| GPU Support | Planned support for up to 3x single-wide GPUs |
| Ports | Front:
Rear:
|
| Cooling | Up to 8x hot-swap fans (N+1 redundancy), with an additional fan integrated into each power supply. |
| Power Supply | Up to two hot-swap redundant AC power supplies (800W, 1300W, 2000W). 80 PLUS Platinum and Titanium certifications. |
| Video | Embedded graphics with dual video ports (rear VGA and optional Mini DisplayPort), supporting resolutions up to 1920×1200 at 60Hz. |
| Hot-Swap Parts | Drives, power supplies, and fans |
| Systems Management |
|
| Security Features | Chassis intrusion switch, power-on and administrator passwords, TPM 2.0, and optional lockable front security bezel. |
| Operating Systems Supported | Microsoft Windows Server, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, Ubuntu Server. |
| Warranty | Three-year or one-year (model dependent) with optional service upgrades for faster response times and extended coverage. |
| Dimensions | Width: 440 mm (17.3 in), Height: 43 mm (1.7 in), Depth: 788 mm (31 in). |
| Weight | Maximum weight: 20.2 kg (44.5 lb) |
Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 Design and Build
The Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 maintains the compact 1U form factor that is standard for many enterprise rack servers. Its design focuses on a combination of functionality, accessibility, and flexibility. We liked its straightforward yet efficient layout, which maximizes airflow, modularity, and ease of use for IT administrators.
Let’s dive into the specifics.
Front panel
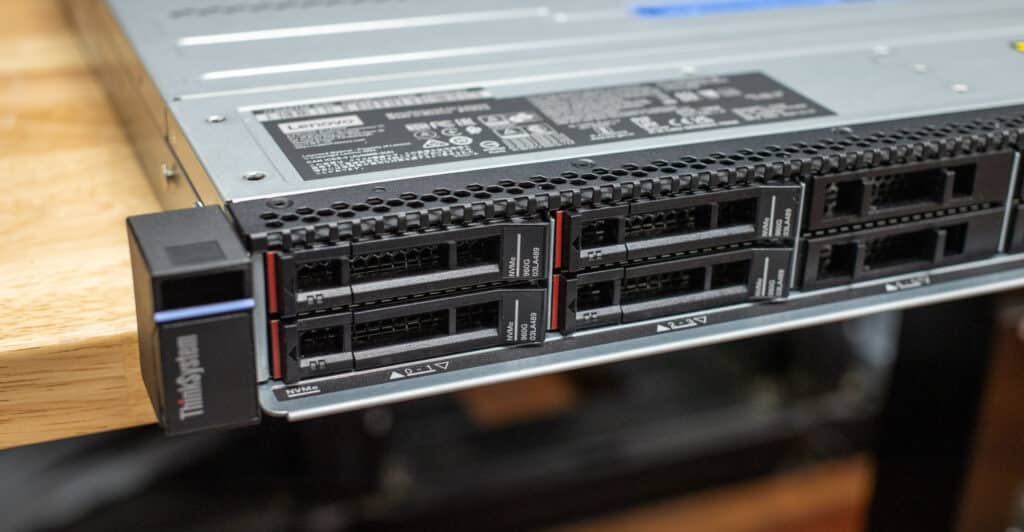
The front panel supports up to 10x 2.5-inch hot-swap drive bays and offers flexibility for various storage configurations, including SAS, SATA, NVMe, or AnyBay drives. This allows enterprises to customize the storage to suit their workloads, whether they prioritize speed, capacity, or cost efficiency.
The front panel can also be configured with an optional Mini DisplayPort video port, which can be used for quick local monitoring and diagnostics without needing to access the rear of the rack. Up to two optional USB 3.0 ports are also available; one is designated explicitly for connecting to the Lenovo XClarity Controller (XCC). This connectivity simplifies management tasks, such as uploading firmware updates or running diagnostics directly from a USB device.
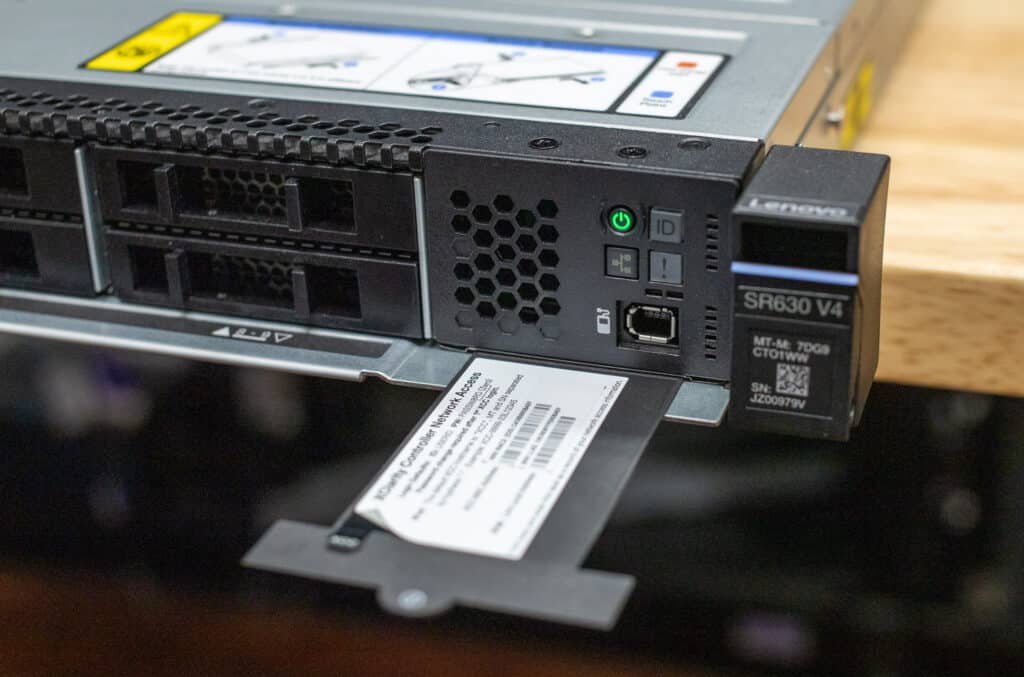
Lenovo has included an external diagnostics port on our system, which can be very helpful for on-site IT staff troubleshooting hardware issues (such as system health and failures). This can speed up problem resolution and minimize downtime. It also has a pull-out information tag to quickly access essential system details like serial numbers, configurations, and network information.
The front operator panel indicators and controls provide the usual at-a-glance information about system status and activity, including power and reset buttons and LED indicators for drive status and health.
Rear Panel
The rear panel includes hot-swap power supplies (800W to 2000W) located on each side of the system, which provide redundancy and can be replaced without powering down the system. The Dual OCP 3.0 slots support PCIe Gen 5 x16 for advanced networking, allowing high-bandwidth adapters like dual-port 200GbE cards. The panel also includes a video port, two USB 3.0 ports, and a dedicated XClarity Controller (XCC) management port for local and remote system management. LED indicators offer quick visual status updates for system health.
The rear panel includes a mix of low-profile and full-height PCIe slots for expansion, letting users add GPUs, storage controllers, or other adapters. Storage options include 2.5-inch hot-swap drives and M.2 hot-swap drives, providing flexible configurations for boot devices or additional storage. The back panel is also available in four air-cooled and two water-cooled configurations.
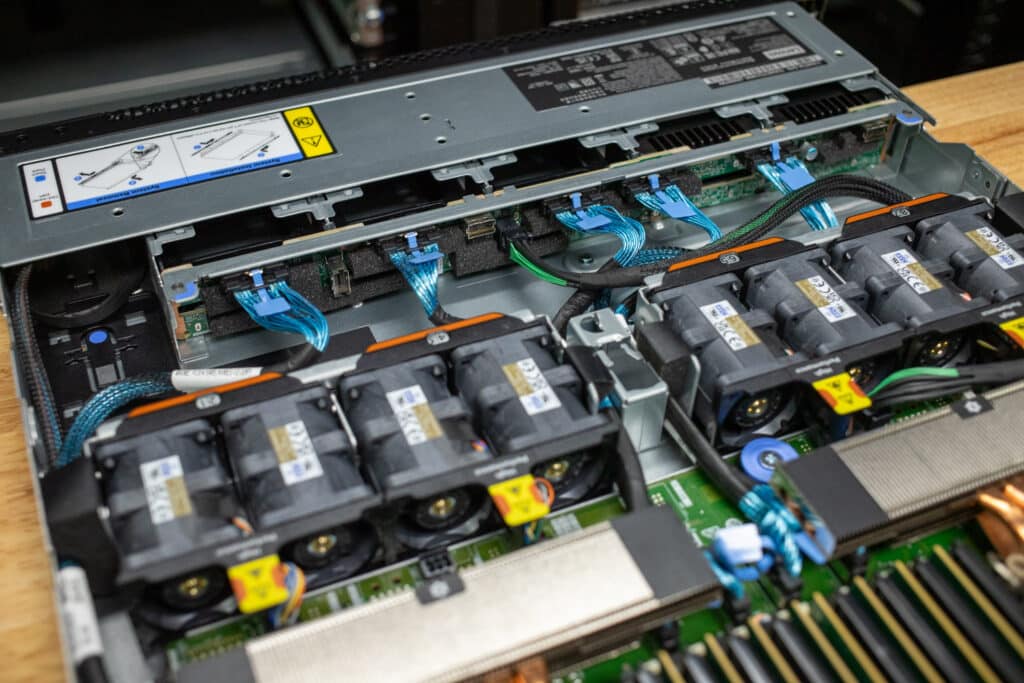
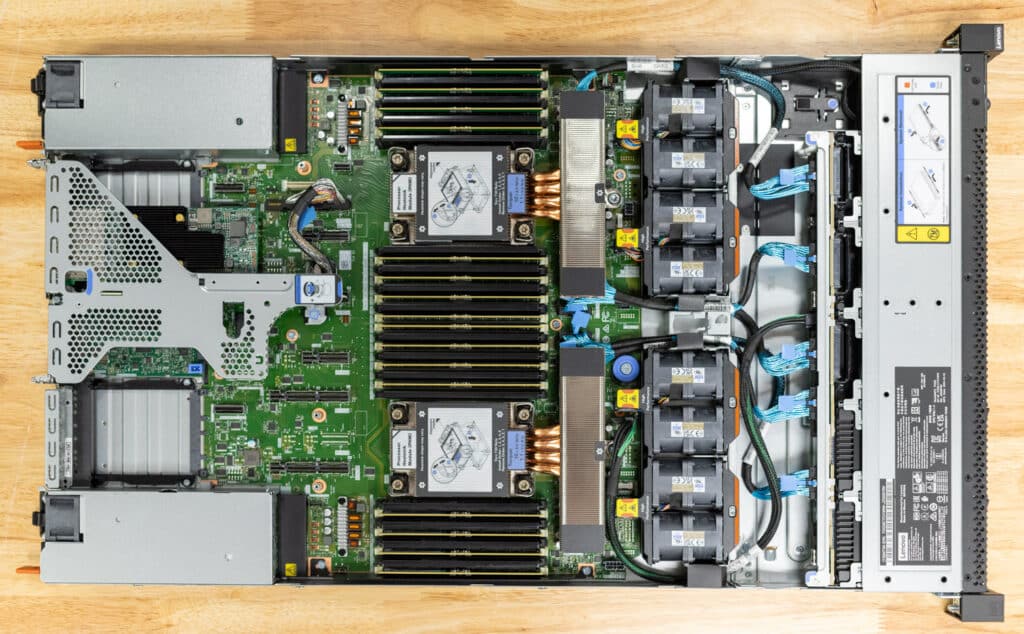
Internal
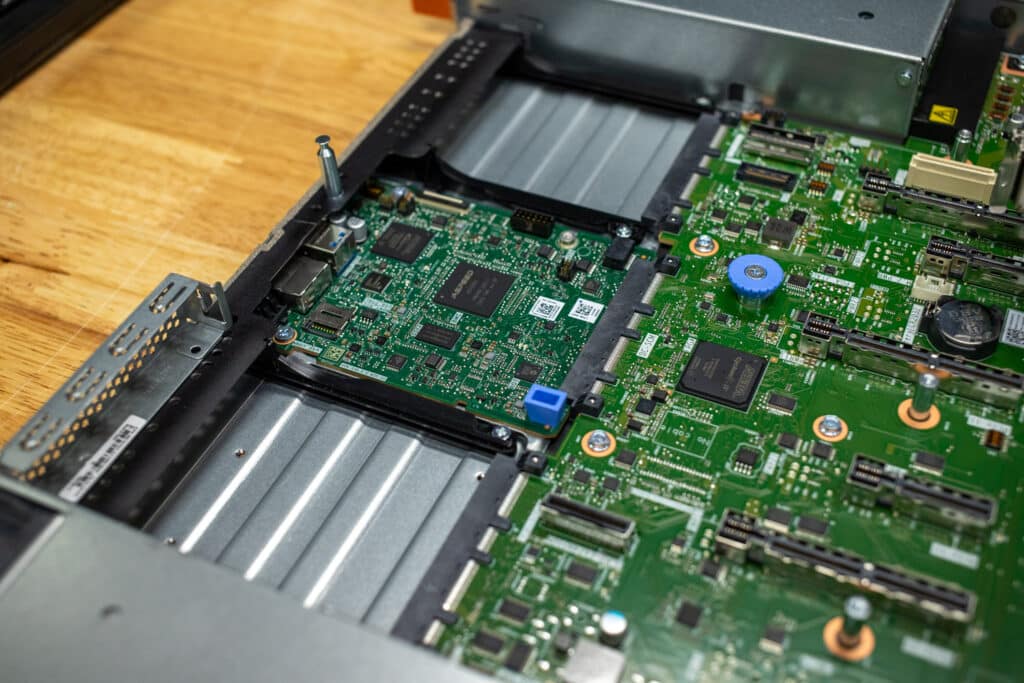
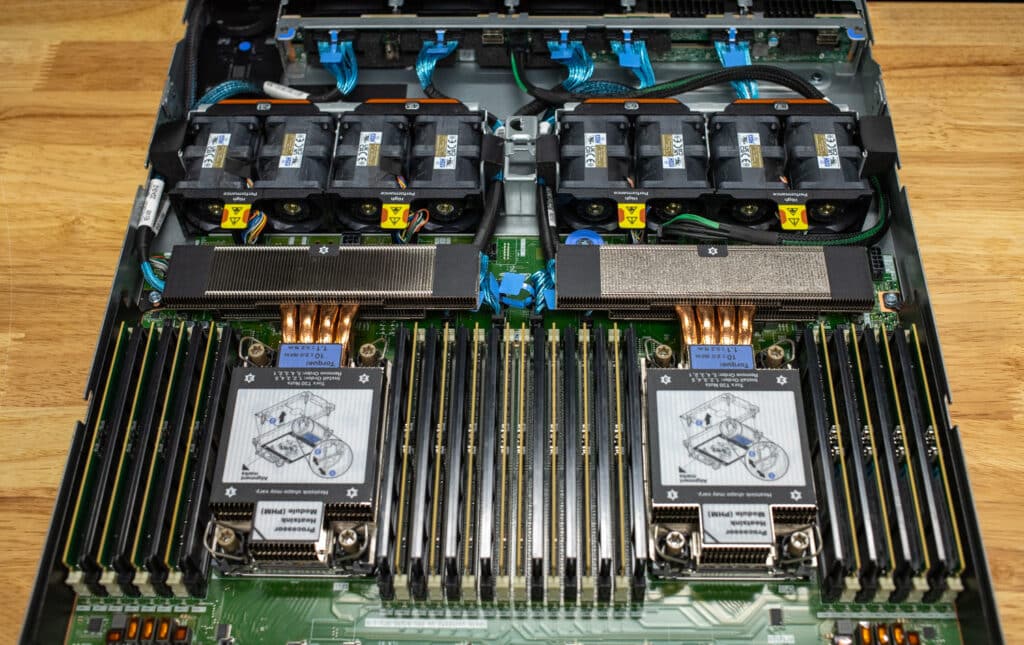
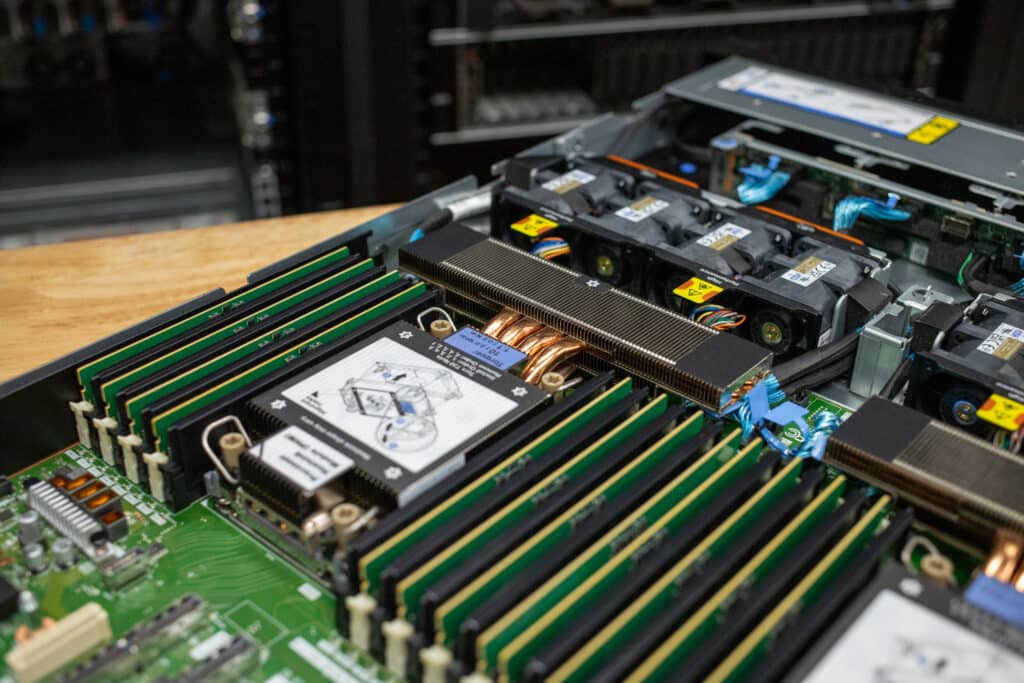
When you open the Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4, you’ll see the dual CPUs surrounded by their respective DIMM slots. This chassis offers 16 DIMMs per CPU or 32 total, allowing for up to 2TB of RAM installed.
From the front, you’ll notice up to eight hot-swap fans lined up in a row, channeling airflow across the critical components and keeping everything cool under pressure. Our system has directly attached NVMe SSDs, which are cabled directly to the motherboard.
This direct-attached NVMe offers the highest available NVMe performance, although, for RAID, users must choose between software or hardware options like Graid.
In the rear, the PCIe slots are ready to house GPUs or other expansion cards, while the OCP slots add another layer of versatility for specialized networking needs. Hot-swap power supplies are easy to access and replace, minimizing downtime during maintenance.
XClarity Controller 3
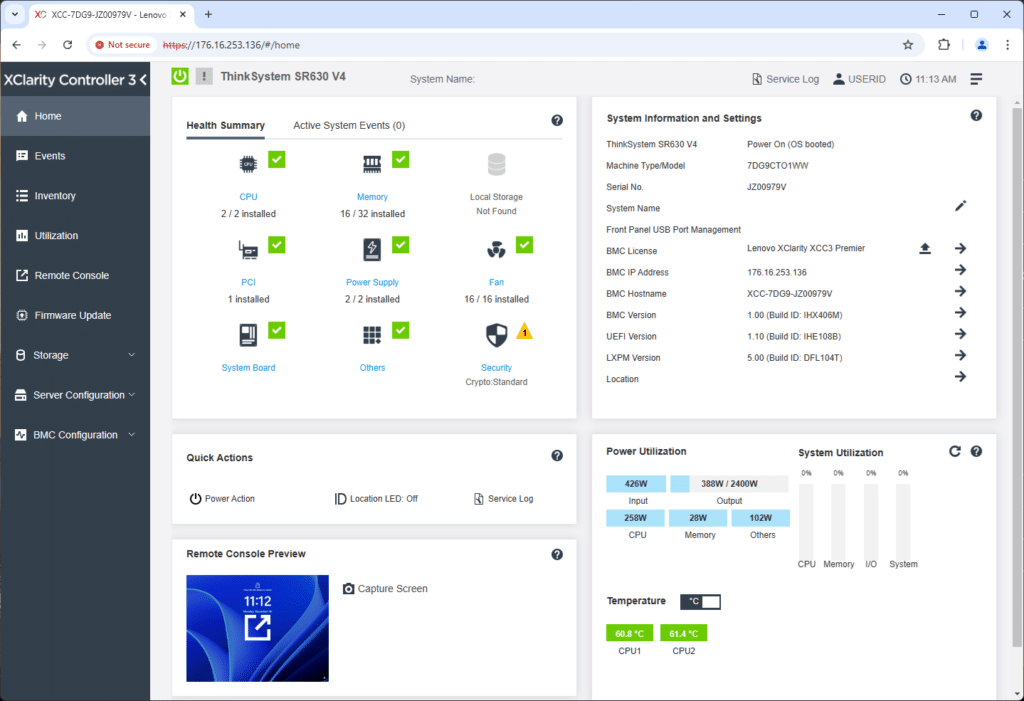
The Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 is equipped with XClarity Controller 3 (XCC3) for remote and lifecycle management. It offers out-of-band management capabilities through a dedicated LAN port, allowing users to configure and deploy new hardware, interface with the system if primary networks are down, perform firmware management activities, and perform countless other tasks.
Users can get a quick overview of all the main components and warnings from the main landing screen. System health, active events, and power are the key areas here.
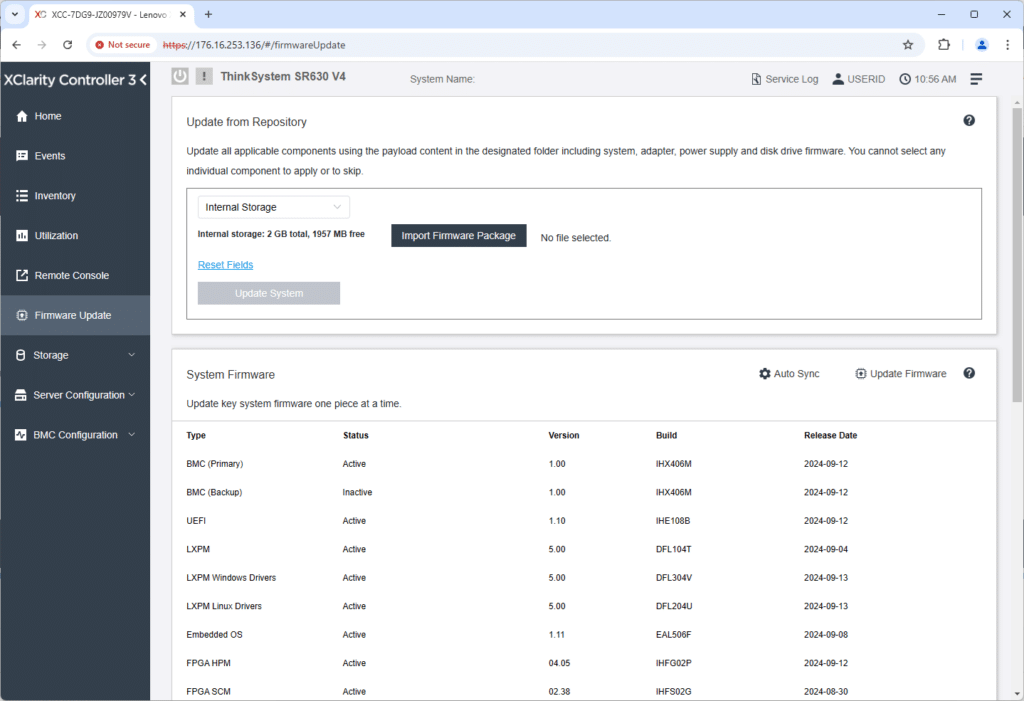
You can see how the platform handles updates by drilling into a couple of areas, such as Firmware Update. You import a firmware package to local storage inside the XClarity controller and click update system to start the update process for the firmware payload uploaded.
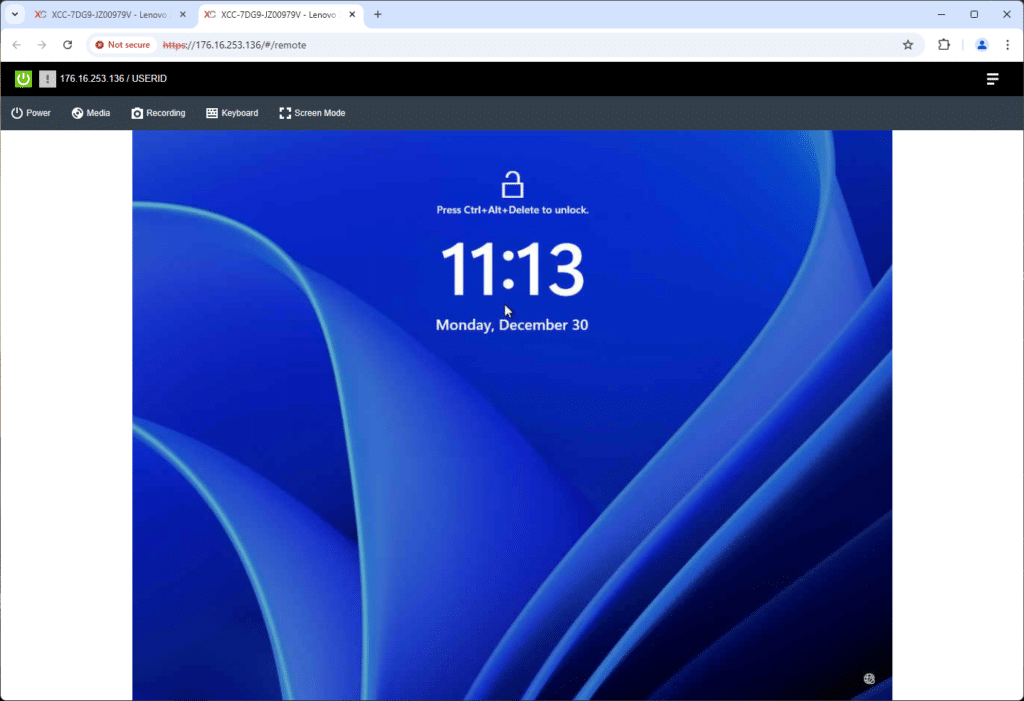
Remote Control is another common function that Lenovo XClarity handles well through an HTML5 web interface. This allows a wide range of client systems to manage the platform, including mobile platforms. While an iPad may not be the primary support mechanism, at times, you need to use whatever is nearby.
Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 Performance
This section examines benchmark results from y-cruncher, Cinebench, Blackmagic, 7-Zip, and Geekbench. We compared the dual-CPU Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 with the recently reviewed single-processor Supermicro Hyper 1U SYS-112H-TN. Both systems are powered by the Intel Xeon 6780E, which allows us to see how the 6780E scales from single- or dual-processor configurations.
In addition to the Supermicro, we added an older Intel Ice Lake Server, which was provided when the Ice Lake Xeon 8380 CPUs were first released. This highlights how the E-core models are positioned as a cost-effective upgrade for legacy platforms that prioritize efficiency over raw processing power. This compares the dual-processor SR630 V4 and Intel Ice Lake platform to the single-processor Supermicro Hyper 1U to illustrate the difference in performance.
Here are the configurations for each system.
Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 Configuration
- CPU: 2 x Intel Xeon 6780E (144-core)
- RAM: 512GB DDR5
- SSD: Samsung MZWL6960HFJA-00AW7
- Operating System: Server 2025
Supermicro Hyper 1U SYS-112H-TN Configuration
- CPU: Intel Xeon 6780E (144-core)
- RAM: 512GB DDR5
- SSD: Micron 7450 NVMe Datacenter SSD
- Operating System: Server 2022
Intel Ice Lake Server
- CPU: 2 x Intel Xeon 8380 (80-core)
- RAM: 512GB DDR5
- SSD:
- Operating System: Server 2025
Blender OptiX
First up is the Blender test, an open-source 3D modeling application. This benchmark was run using the Blender Benchmark utility. The score is samples per minute, with higher being better.
The Blender OptiX benchmarks reveal intriguing insights across the tested systems. The Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 excelled with Blender 4.2.0, delivering 1,432 samples per minute in the Monster scene, while the Intel Ice Lake Server achieved 569 and the Supermicro Hyper 1U 112H-TN (running Blender 4.0) achieved 781. Lenovo reported 914 samples in the Junkshop scene, with the Intel Ice Lake Server’s 403 and Supermicro’s 514. The Classroom scene showed Lenovo with 657 samples, Ice Lake with 280, and Supermicro with 371.
| Blender CPU | Supermicro Hyper 1U 112H-TN (1x Xeon 6780E, 512GB DDR5)
Blender 4.0 |
Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 (2 x Intel Xeon 6780E, 512GB)
Blender 4.2 |
Intel Ice Lake Server (2 x Intel Xeon 8380, 512GB)Blender 4.2 |
| Monster | 781.42 | 1432.09 | 569.10 |
| Junkshop | 514.658 | 914.75 | 403.96 |
| Classroom | 370.52 | 656.68 | 280.86 |
Geekbench 6
Geekbench 6 is a cross-platform benchmark that measures overall system performance. The Geekbench Browser allows you to compare any system to it.
Lenovo’s single-core performance scored 1,173, while the dual-processor Supermicro logged 1,154, highlighting its potential for tasks that rely on individual core efficiency. In the multi-core test, Supermicro reported 15,167 and Lenovo 13,868. Not all applications fared well with the increased core counts. Geekbench had trouble scaling from 144 cores to 288 cores on the dual-socket Lenovo SR630 V4 platform. The older Ice Lake CPUs exhibited higher single- and multi-core scores, reaching 1,668 and 17,409, respectively.
| Geekbench 6 (Higher is better) |
Supermicro Hyper 1U 112H-TN (Xeon 6780E, 512GB DDR5) | Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 (2 x Intel Xeon 6780E, 512GB) | Intel Ice Lake Server (2 x Intel Xeon 8380, 512GB) |
| CPU Single-Core | 1,154 | 1,173 | 1,668 |
| CPU Multi-Core | 15,167 | 13,868 | 17,409 |
Cinebench R23
The Cinebench R23 benchmark tool evaluates a system’s CPU performance by rendering a complex 3D scene using the Cinema 4D engine. It measures single-core and multi-core performance, providing a comprehensive view of the CPU’s capabilities in handling 3D rendering tasks.
The table below shows the Supermicro and Lenovo systems recorded strong results. The Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 outperformed in multi-core and single-core, scoring 99,266 and 894 points, respectively. The Supermicro Hyper 1U 112H-TN recorded 92,516 and 888 points. The additional CPU had some benefits in this benchmark, but the numbers did not double, going from one to two processors. The Ice Lake CPUs recorded 74,020, with limited scaling compared to Lenovo’s dual Xeon 6780Es.
| Cinebench R23 | Supermicro Hyper 1U 112H-TN (Xeon 6780E, 512GB DDR5) | Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 (2 x Intel Xeon 6780E, 512GB) | Intel Ice Lake Server (2 x Intel Xeon 8380, 512GB) |
| CPU Multi Core | 92,516 | 99,266 pts | 74,020 pts |
| CPU Single Core | 888 pts | 894 pts | 1,059 pts |
| MP Ratio | 104.20 x | 111.00 x | 69.87 x |
Cinebench 2024
Cinebench 2024 extends R23’s benchmark capabilities by adding GPU performance evaluation. It continues to test CPU performance but also includes tests that measure the GPU’s ability to handle rendering tasks.
The results of the 2024 version of Cinebench told a similar story. Here, the Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 with its dual 6780E CPUs reflected the advantage over the single-socket Supermicro Hyper 1U 112H-TN in multi-core CPU performance with a score of 2,884 points. The Supermicro reported 2,565 points. The Intel Ice Lake 8380 CPUs demonstrated its power with a multi-core score of 4,131. For single-core tests, the Intel Ice Lake 8380 scored 61 points.
| Cinebench R23 | Supermicro Hyper 1U 112H-TN (Xeon 6780E, 512GB DDR5) | Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 (2 x Intel Xeon 6780E, 512GB) | Intel Ice Lake Server (2 x Intel Xeon 8380, 512GB) |
| CPU Multi Core | 2,565 pts | 2,884 pts | 4,131 pts |
| CPU Single Core | 53 pts | 53 pts | 61 pts |
| MP Ratio | 48.38 x | 54.43 x | 68.22 x |
y-cruncher
y-cruncher is a popular benchmarking and stress-testing application that launched back in 2009. This test is multi-threaded and scalable, computing Pi and other constants up to the trillions of digits. Faster is better in this test. This software has been fantastic at testing high-core count platforms and showing compute advantages between single and dual-socket platforms.
In the y-cruncher benchmarks, the dual-socket ThinkSystem SR360 V4 took 5.997 seconds to calculate Pi to 1 billion digits. The single Intel Xeon 6780E took 8.757 seconds. To calculate 50 billion digits, a single CPU needed 674.299 seconds, compared to dual CPUs, calculating it in 476.826 seconds. While not every workload responds well to the high-core counts of the new e-core CPUs, y-cruncher had no trouble leveraging them. The older Intel Ice Lake Server completed the Pi calculation to 1 billion digits in 7.074 seconds in the first 1 Billion digit test while hitting 617.828 seconds in 50 billion digits.
| y-cruncher (0.8.5.9) (lower is better) | Supermicro Hyper 1U 112H-TN (Xeon 6780E, 512GB DDR5) | Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 (2 x Intel Xeon 6780E, 512GB) | Intel Ice Lake Server (2 x Intel Xeon 8380, 512GB) |
| 1 Billion | 8.757 seconds | 5.997 seconds | 7.074 seconds |
| 2.5 Billion | 24.928 seconds | 17.573 seconds | 19.203 seconds |
| 5 Billion | 53.489 seconds | 37.793 seconds | 42.300 seconds |
| 10 Billion | 113.727 seconds | 81.046 seconds | 93.886 seconds |
| 25 Billion | 308.218 seconds | 220.025 seconds | 272.679 seconds |
| 50 Billion | 674.299 seconds | 476.826 seconds | 617.828 seconds |
Blackmagic RAW Speed Test
The Blackmagic RAW Speed Test is a performance benchmarking tool designed to measure a system’s capabilities in handling video playback and editing using the Blackmagic RAW codec. It evaluates how well a system can decode and play back high-resolution video files, providing frame rates for both CPU- and GPU-based processing.
The Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 performed slightly better than the Supermicro and Ice Lake systems, scoring 120 FPS in 8K CPU, indicating a top pick for video playback and editing tasks. The Supermicro Hyper 1U 112H-TN had 116 FPS in 8K CPU performance. While the dual-socket Lenovo performed better, it wasn’t massive, considering the dual-socket configuration with 116 FPS (8K CPU) and 0 FPS (8K GPU). The Intel Ice Lake Server was right there with the Lenovo and Supermicro with 116 FPS in the 8K CPU benchmark. However, it did not record a GPU score due to the absence of a dedicated GPU.
7-Zip
The popular 7-Zip utility’s built-in memory benchmark measures the performance of a system’s CPU and memory during compression and decompression tasks, indicating how well the system can handle data-intensive operations.
In compression tasks, the Supermicro system performed slightly better than the SR630 in CPU usage and resulting ratings, with a total compression rating of 245.823 GIPS and Lenovo’s 224.313 GIPS. This suggests a slight advantage when managing heavily threaded compression workloads. Lenovo’d decompression tasks showed a higher resulting rating of 288.457 GIPS, while Supermicro’s rating indicated 269.373 GIPS. This translates to better performance for workloads that require reading and extracting data. The Intel Ice Lake Server demonstrated a balanced performance, with a compression rating of 235.437 GIPS and a decompression rating of 253.692 GIPS.
The systems performed nearly identically when comparing overall performance, with total ratings of 257.598 GIPS for the single-socket Supermicro and 256.385 GIPS for the dual-socket Lenovo. The older Ice Lake Xeon hit 244.565 GIPS. All three systems are highly capable.
| 7-Zip Compression | Supermicro Hyper 1U 112H-TN (Xeon 6780E, 512GB DDR5) | Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4(Intel Xeon 6780E, 512GB) | Intel Ice Lake Server (2 x Intel Xeon 8380, 512GB) |
| Compressing | |||
| Current CPU Usage | 5287% | 5064% | 5835% |
| Current Rating/Usage | 4.647 GIPS | 4.341 GIPS | 4.030 GIPS |
| Current Rating | 245.699 GIPS | 219.840 GIPS | 235.143 GIPS |
| Resulting CPU Usage | 5296% | 5156% | 5839 |
| Resulting Rating/Usage | 4.642 GIPS | 4.350 GIPS | 4.032 GIPS |
| Resulting Rating | 245.823 GIPS | 224.313 GIPS | 235.437 GIPS |
| Decompressing | |||
| Current CPU Usage | 6236% | 6184% | 6230% |
| Current Rating/Usage | 4.261 GIPS | 4.688 GIPS | 4.050 GIPS |
| Current Rating | 265.709 GIPS | 289.879 GIPS | 252.326 GIPS |
| Resulting CPU Usage | 6236% | 6205% | 6245% |
| Resulting Rating/Usage | 4.341 GIPS | 4.649 GIPS | 4.062 GIPS |
| Resulting Rating | 269.373 GIPS | 288.457 GIPS | 253.692 GIPS |
| Total Rating | |||
| Total CPU Usage | 5751% | 5681% | 6042% |
| Total Rating/Usage | 4.491 GIPS | 4.500 GIPS | 4.047 GIPS |
| Total Rating | 257.598 GIPS | 256.385 GIPS | 244.565 GIPS |
Conclusion
The Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V4 is a versatile 1U rack server that, although not a significant upgrade over its predecessor, still marks a reliable step forward in the evolution of Lenovo’s mainline enterprise systems. With support for Intel Xeon 6700E-series processors, it doubles core density compared to its predecessor, offering improved scalability for demanding workloads. Enhanced DDR5 memory speeds of up to 6400 MHz and planned support for emerging technologies like Compute Express Link (CXL) and MCRDIMMs show that Lenovo intends to keep this server line equipped for future demands.
The SR630 V4’s shift toward NVMe storage and flexible drive configurations also means it prioritizes performance and scalability in data-heavy workloads. Moreover, the dual OCP 3.0 slots supporting PCIe 5.0 enable advanced networking options, including hot-swap components and enhanced cooling systems, streamlining maintenance and operational efficiency.
Regarding its performance in our benchmark tests, the SR630 V4 demonstrated solid results, excelling in multi-threaded workloads such as Cinebench R23 and Y-Cruncher. The way the new Intel Sierra Forest E-core Xeon CPUs fit into the space is for businesses looking to upgrade existing platforms for higher efficiency. Not all workloads require higher performance, but they could take in new improvements such as density and reduced power consumption.
That said, while E-core efficiency may not fully meet the demands of workloads requiring high single-thread performance, Lenovo has planned support for P-core processors. Additional drive configurations are also available, supporting a broad range of enterprise applications.
Engage with StorageReview
Newsletter | YouTube | Podcast iTunes/Spotify | Instagram | Twitter | TikTok | RSS Feed