Micron has announced the availability of the Micron 7400 NVMe SSD, highlighted by its PCIe Gen4 interface and comprehensive security features. Available in a range of form factors, the Micron 7400 is ideal for demanding data center workloads and helping to drive the transition to next-generation server architectures.
Micron has announced the availability of the Micron 7400 NVMe SSD, highlighted by its PCIe Gen4 interface and comprehensive security features. Available in a range of form factors, the Micron 7400 is ideal for demanding data center workloads and helping to drive the transition to next-generation server architectures.
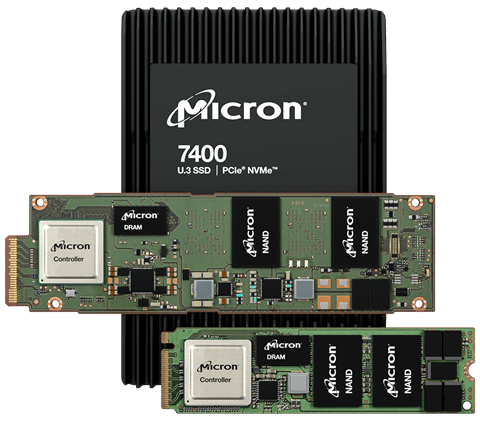
Micron 7400 Form Factors
Data centers are always evolving due to the exponential growth of data and how many applications now demand high-performance storage solutions, such as SQL and NoSQL databases, block and object stores, VDI and server virtualization, and cloud storage.
This is where the new Micron 7400 comes in, which is one of the broader enterprise SSD offerings we’ve seen. The line consists of several three drive types, which consist of different form-factor sizes and capacity models.
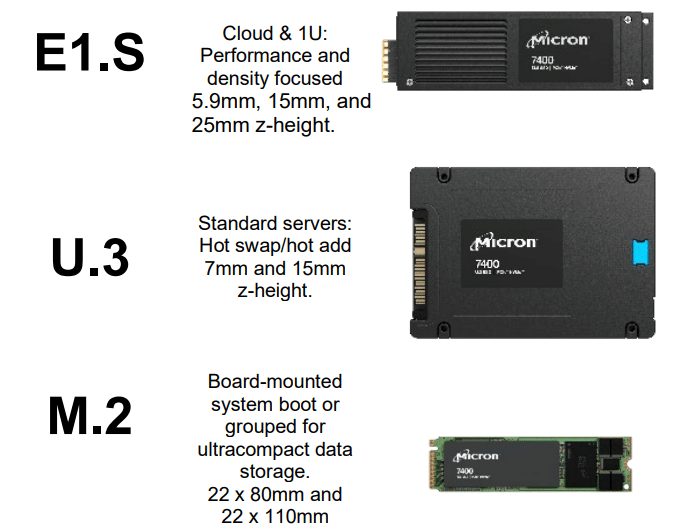
- U.3: available in (7mm and 15mm sizes), which is available in capacities ranging from 800GB to 7.68TB. This is the market’s only PCIe Gen4 U.3 form factor in both 7mm and 15mm sizes. The U.3 form factor adds support for NVMe, SAS, and SAS host controllers, which means simpler field support.
- M.2 (22 x 80mm and 22 x 110mm sizes), which are available in capacities ranging from 400GB to 3.84TB. This is the only PCIe Gen4 M.2 22 x 80mm drive (specifically designed for server boot use) that features power loss protection. M.2 also has the benefit of existing industry adoption, in addition to being the smallest form factor with low power draws.
- E1.S (E1.S: 5.9mm, 15mm, and 25mm sizes), which is available in capacities ranging from 800GB to 3.84TB
This comprehensive line of data center SSDs certainly will help enterprises face the always growing/evolving capacity, power, and thermal requirements of data center environments.
The most interesting option of the bunch is the new E1.S Enterprise and Data Center SSD Form Factor (EDSFF). We wrote a detailed article about how the E1.S ruler is finally going mainstream, and what it means to enterprises going forward. The new E1.S form factor (specifically the 15mm variant) will bring incredible performance numbers with its 25W+ capabilities when using the upcoming PCIe Gen5 SSDs. But for now, it means greater density, flash-optimized performance, and improved power and (integrated) cooling options. As a result, IT will be able to fit more SSDs in the same chassis while maintaining performance and temperature levels.
Micron 7400 SSD Security
The Micron 7400 SSD offers a range of standards-based features, including TCG-Opal 2.01 and IEEE-1667, as well as new in-flight and at-rest data protection capabilities:
| Secure Execution Environment | Includes dedicated security processing hardware with physical isolation for security-related function isolation |
| Asymmetric Roots of Trust | Enables authenticated revocation of root keys (in immutable ROM) |
| Strong Asymmetric Key Support | Uses standard, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)-approved algorithms with 208- bit/3072-bit RSA keys |
| RSA Delegation Key Support | Enables customers to maintain ownership of RSA keys |
| Secure Boot | Helps ensure firmware integrity on the running platform |
| Key-Based Firmware Update | Validates firmware using public key-based authentication prior to firmware update |
| Key-Based Privileged Access | Protects against unauthorized privileged SSD function execution with public key-based authorization |
Micron 7400 SSD Performance
Micron indicates that the 7400 SSD line more than doubles IOPs per watt and throughput when compared to their previous generation. They are also backward compatibility with PCIe Gen3 systems, so customers who still use the last-gen interface can transition to Gen4 platforms when they are ready.
As for the specifics of their performance, all potential numbers vary quite a bit depending on the capacity and size model. The Micron 7400 line also comes in two different family types: PRO, which offers 1 DWPD (drive write per day; or MAX, which offers 3 DWPD. The MAX also excels in use cases where random write performance and endurance are vital.
Here is a rundown of the highest transfer rates you can expect them to reach:
- The U.3 form factor offers up to 6.6GB/s and 5.4GB/s in sequential read and write, while random performance is quoted to deliver up to 1 million IOPS read and 363K IOPS write.
- For the E1.S form factor, the 7400 is expected to reach sequential speeds up to 6.6GB/s read and 3.5GB/s write, while random read and write IOPS is quoted at up to 800K and 347K, respectively.
- The M.2 offering is quoted with read and write sequential performance at 4.4GB/s and 2.2GB/s, respectively. Random performance is expected to reach up to 650K read and 206K write.
The Micron 7400 supports 128 namespaces (i.e., isolated logical blocks of NAND that are separately accessible for noninterfering I/O and multitenancy), allowing it to increase scalability for virtualized environments such as hyperconverged infrastructure and software-defined storage. In comparison, the Micron 7300 supports just one.
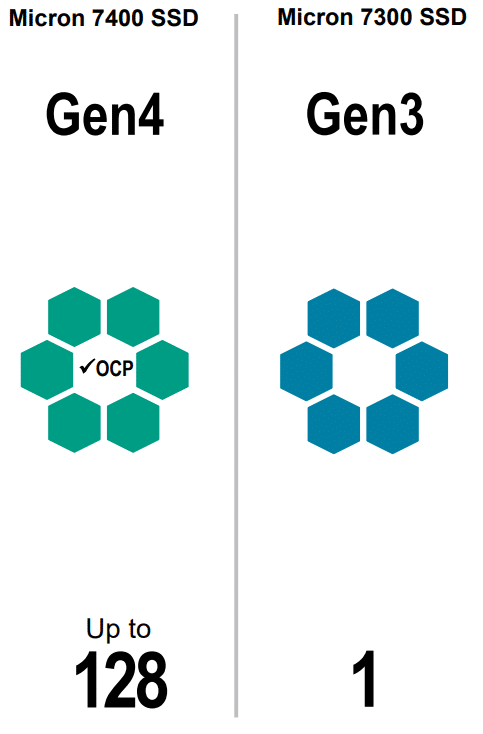
In addition, it also supports Open Compute Project (OCP) deployments for qualified environments.
Micron 7400 SSD Specifications
| U.3
|
7400 PRO: U.3
Read-Intensive, 1 Drive Write per Day |
7400 MAX: U.3
Mixed-Use, 3 Drive Writes per Day |
|||||||
| Capacity | 960GB | 1.92TB | 3.84TB | 7.68TB | 800GB | 1.6TB | 3.2TB | 6.4TB | |
|
Performance
|
Seq. Read (MB/s) | 6,500 | 6,500 | 6,600 | 6,600 | 6,500 | 6,500 | 6,600 | 6,600 |
| Seq. Write (MB/s) | 1,000 | 2,200 | 3,500 | 5,40010 | 1,000 | 2,200 | 3,500 | 5,40010 | |
| Rand. Read (IOPS) | 240,000 | 430,000 | 800,000 | 1,000,000 | 240,000 | 430,000 | 800,000 | 1,000,000 | |
| Rand. Write (IOPS) | 60,000 | 95,000 | 150,000 | 190,000 | 122,000 | 224,000 | 347,000 | 363,000 | |
| 70/30 Rand. Read/Write (IOPS) | 105,000 | 174,000 | 275,000 | 400,000 | 159,000 | 276,000 | 455,000 | 610,000 | |
| Latency (TYP, µs) | 75 (read)
15 (write) |
75 (read)
15 (write) |
75 (read)
15 (write) |
75 (read)
15 (write) |
75 (read)
15 (write) |
75 (read)
15 (write) |
75 (read)
15 (write) |
75 (read)
15 (write) |
|
| Endurance (Total bytes written in PB) | 1,700
6,700 |
3,500
14,400 |
7,000
25,700 |
14,000
48,900 |
4,300
8,000 |
8,700
16,400 |
17,500
31,800 |
35,000
62,800 |
|
| E1.S
|
7400 PRO: E1.S
Read-Intensive, 1 Drive Write per Day |
7400 MAX: E1.S
Mixed-Use, 3 Drive Writes per Day |
|||||||
| Capacity | 960GB | 1.92TB | 3.84TB | 800GB | 1.6TB | 3.2TB | |||
|
Performance
|
Seq. Read (MB/s) | 6,500 | 6,500 | 6,600 | 6,500 | 6,500 | 6,600 | ||
| Seq. Write (MB/s) | 1,000 | 2,200 | 3,500 | 1,000 | 2,200 | 3,500 | |||
| Rand. Read (IOPS) | 240,000 | 430,000 | 800,000 | 240,000 | 430,000 | 800,000 | |||
| Rand. Write (IOPS) | 60,000 | 95,000 | 150,000 | 122,000 | 224,000 | 347,000 | |||
| 70/30 Rand. Read/Write (IOPS) | 105,000 | 174,000 | 275,000 | 159,000 | 276,000 | 455,000 | |||
| Latency (TYP, µs) | 75 (read)
15 (write) |
75 (read)
15 (write) |
75 (read)
15 (write) |
75 (read)
15 (write) |
75 (read)
15 (write) |
75 (read)
15 (write) |
|||
| Endurance (Total bytes written in PB) |
1,700
6,700 |
3,500
14,400 |
7,000
25,700 |
4,300
8,000 |
8,700
16,400 |
17,500
31,800 |
|||
| M.2
|
7400 PRO: M.2
Read-Intensive, 1 Drive Write per Day |
7400 MAX: M.2
Mixed-Use, 3 Drive Writes per Day |
|||||||
| Capacity | 480GB | 960GB | 1.92TB | 3.84TB | 400GB | 800GB | 1.6TB | 3.2TB | |
|
Performance |
Seq. Read (MB/s) | 4,400 | 4,400 | 4,400 | 4,400 | 4,400 | 4,400 | 4,400 | 4,400 |
| Seq. Write (MB/s) | 530 | 1,000 | 2,000 | 2,200 | 530 | 1,000 | 2,000 | 2,200 | |
| Rand. Read (IOPS) | 120,000 | 230,000 | 420,000 | 650,000 | 120,000 | 230,000 | 420,000 | 650,000 | |
| Rand. Write (IOPS) | 25,000 | 60,000 | 85,000 | 105,000 | 55,000 | 118,000 | 172,000 | 206,000 | |
| 70/30 Rand. Read/Write (IOPS) | 45,000 | 105,000 | 160,000 | 240,000 | 75,000 | 153,000 | 261,000 | 360,000 | |
| Latency (TYP, µs) | 85 (read)
40 (write) |
85 (read)
15 (write) |
85 (read)
15 (write) |
85 (read)
15 (write) |
85 (read)
15 (write) |
85 (read)
15 (write) |
85 (read)
15 (write) |
85 (read)
15 (write) |
|
| Endurance (Total bytes written in PB) |
800
3,800 |
1,700
6,700 |
3,500
14,400 |
7,000
25,700 |
2,100
4,100 |
4,300
8,000 |
8,700
16,400 |
17,500
31,800 |
|
| Micron 7400 SSD: Common Features | |||||||||
|
Basic Attributes |
Interface | PCIe Gen4 1×4 NVMe (v1.4) | |||||||
| Form Factors | U.3 (7mm, 15mm), E1.S (5.9mm, 15mm, 25mm), M.2 (22 x 80mm, 22 x 110mm) | ||||||||
| NAND | Micron 96-layer 3D TLC NAND | ||||||||
| Typ. Latency | Read: M.2: 85µs, U.3, E1.S: 75µs; Write: 25µs | ||||||||
|
Reliability |
MTTF | 2 million device hours | |||||||
| UBER | <1 sector per 1017 bits read | ||||||||
| Warranty | 5 years | ||||||||
| Environmental Characteristics | Power | Sequential read (maximum of all capacities by form factor): U.3: 13.6W / E1.S: 11.5W / M.2: 8.25W Sequential write (maximum of all capacities by form factor): U.3: 22W / E1.S: 12W / M.2: 8.25W | |||||||
| Operating Temp. | 0-70°C | ||||||||
Micron 7400 SSD Availability
The Micron 7400 SSD is available now.
Engage with StorageReview
Newsletter | YouTube | Podcast iTunes/Spotify | Instagram | Twitter | Facebook | RSS Feed
