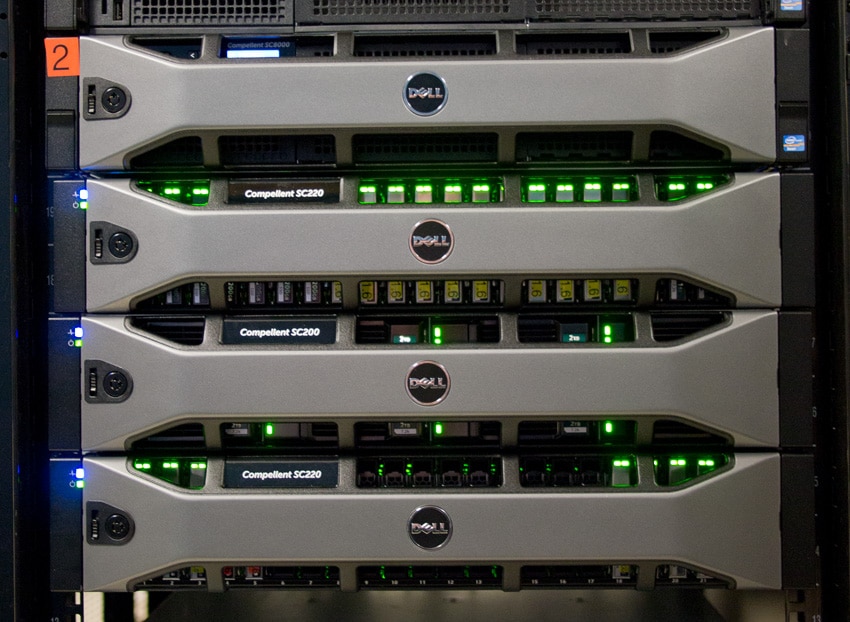
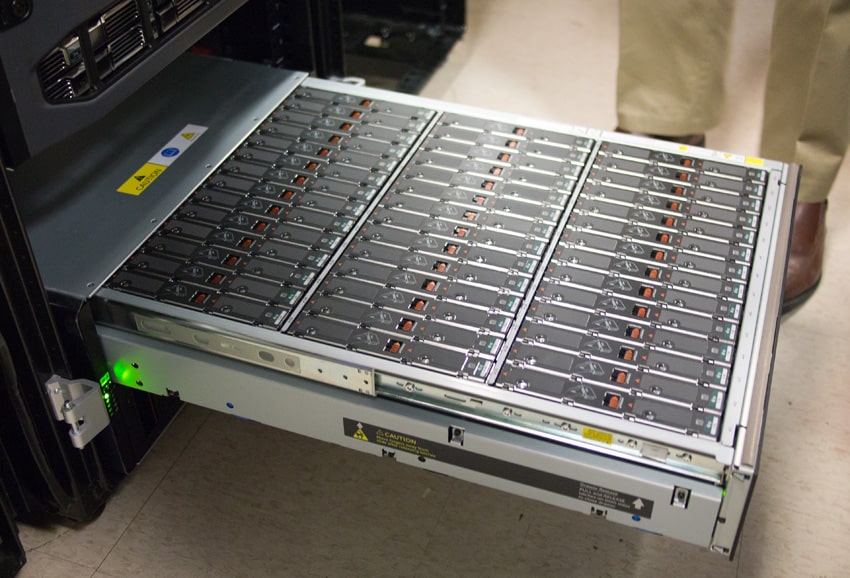
StorageReview recently spent a few days in Dell’s facilities in Nashua, New Hampshire to take a close look at Dell’s Compellent storage platform. Compellent is an all flash or hybrid system for large-scale enterprise storage with multiple tiers that can accommodate different drive types, speeds and interfaces which delivers automated tiering based on analysis of data access requirements. In this overview we’ll break down Compellent’s key tiering technology which is dubbed “Data Progression” and highlight other key features and configuration options that give Compellent its flexibility and performance.

Our last deep dive with Dell was a hands-on orientation to EqualLogic in preparation for reviewing their hybrid arrays (PS6110XS review, PS6210XS preview). This time we focused on Compellent, a Dell offering designed to handle mainstream storage needs at scale. Dell offers a Compellent SC8000 head unit that can be paired with various expansion options including the ultra-dense SC280, which allows customers to scale capacity by 336TB intervals per 5U shelf. Compellent hardware configurations can be customized to fit based on customer needs, but the platform is built on a core of shared functionality to give Compellent a consistent overall management experience.
Until now, the most common Compellent configurations have utilized SLC flash, 10K/15K HDDs, and 7K HDDs across three storage tiers. Dell has strongly emphasized new flash functionality in Storage Center 6.4 that lets Dell essentially swap in enterprise MLC SSDs for the 10K/15K HDD tier. The benefits of MLC flash include gains in capacity, reduction in OPEX, and increased performance for the middle tier. Compellent’s support for an MLC flash tier in conjunction with its Data Progression tiering technology constitutes a key advantage for Compellent in the enterprise storage space.
Compellent Fluid Data Architecture and Data Progression
Data Progression is an automated tiering technology that optimizes the location of data, both on a schedule and on demand as prompted by a storage profile. Compellent’s tiering profiles streamline policy administration by assigning tier attributes based on the profile. Storage Center 6.4 added two new profiles: Flash-optimized and cost-optimized storage profiles. The Flash-optimized profile directs all writes to SLC NAND Tier 1 storage (SLC SSDs in RAID 10,). On-demand data progression then moves replay and read-intensive data to the MLC NAND Tier 2 where it benefits from MLC’s read performance.
Flash-optimized data progression moves data across tiers in the background whenever it is identified as having a new pattern of utilization. To understand how Data Progression works, we’ll start with an overview of Compellent Fluid Data Architecture and how the system breaks down drives into the individual pages of data that ultimately become volumes that are addressed by the system. Compellent Fluid Data Architecture offers three page sizes: 512KB, 2MB, and 4MB with a default size of 2MB. Data is optimized by data progression on a per page basis, meaning that files can be striped across drives for improved access times and to perform tiering optimizations in parallel.
Individual pages are given an internal designation of Accessible or Historical (replay). Data Progression incorporates this accessibility information in the metadata used to determine the class of storage a page should use. Historical pages are read-only pages (set by Data Instant Replay) and are eligible to move to the lowest tier immediately. Compellent’s Data Instant Replay uses a continuous snapshot approach which tracks incremental changes to protected data. Remote Instant Replay uses a similar approach between local and remote sites to replicate incremental changes over Fiber Channel or IP connections. Accessible pages can currently be read or written by the server and may be assigned a different tier depending on how the data is being utilized.
Compellent also offers various levels of RAID which are applied depending on the redundancy level that has been set for the tier. By default, tiers with drive sizes of 900GB or greater are set to dual redundancy, but single redundancy is also available. Each tier can be configured with its own redundancy level, which can be modified later on the fly. Single redundancy enables RAID10, RAID 5-5 (4+1), RAID 5-9 (8+1), and dual redundancy enables RAID10DM, RAID6-6 (4+2), RAID 6-10 (8+2).
Compellent SC8000 Controller
The SC8000 is the 2U rack server at the center of the latest generation of Compellent solutions, with each server featuring dual six-core, 2.5GHz Intel Xeon E5-2640 CPUs with 32GB or 128GB of memory (16GB or 64GB per controller) in order to support up to 960 drives in the array. The SC8000 offers simultaneous iSCSI, Fibre Channel and Fibre Channel over Ethernet front-end interconnects. The chassis offers six PCIe expansion slots and an Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller (iDRAC7 Enterprise) port for monitoring.
The SC8000 can be integrated with SAS and Fibre Channel expansion shelves, currently including the SC280, SC220, and the SC200. The SC8000 utilizes dual, redundant 750W 80 plus Platinum certified power supplies. We are particularly interested in configurations that leverage Compellent’s new Flash tiering capabilities, including Dell’s flash-optimized Compellent solution which pairs the SC8000 with a SC220 disk shelf that is populated with six 400GB write-intensive SLC SSDs and six 1.6TB read-intensive MLC SSDs. An all-flash option fills the remaining twelve SC220 bays with six-packs of SLC and MLC SSDs, while hybrid-flash configurations mix SSDs and 1TB 7.2K RPM HDDs.
Compellent Expansion Shelves
The SC280 is noteworthy among Dell Compellent expansion shelves, packing up to 84 x 4TB SAS HDDs into a 5U, two-drawer enclosure for a total of 336TB of storage. This density allows a single 48U rack with two controllers to reach up to 2PB of raw capacity when fully loaded with SC280 units. The SC280 utilizes dual hot-swappable power supplies, five hot-swappable fans, and redundant hot-swappable 6Gb SAS I/O modules.
Dell also offers the SC200, a 2U 6Gb SAS shelf which supports up to 12 x 3.5-inch drives, including 7K and 15K HDDs and 200GB and 400GB SSDs. The SC220 is a 2U 6Gb SAS shelf that supports up to 24 x 2.5-inch drives including 7K, 10K, and 15K HDDs and 200GB, 400GB, and 1.6TB SSDs.
Compellent FS8600 NAS
The Compellent FS8600 is a NAS filer that can be added to a Compellent SAN in front of the SC8000 controller to provide a Fluid File v3 NAS unified file storage environment. The FS8600 leverages Dell’s FludFS to support a scale-out file architecture with up to 2PB in a single namespace, and provides policy-based dedupe, compression, and other functionality you’d expect from an enterprise NAS platform. According to Dell, with four FS86000 units working in tandem, a Compellent system can scale performance to 494,000 SPECsfs file OPS and 9.2GB/sec throughput.
Management
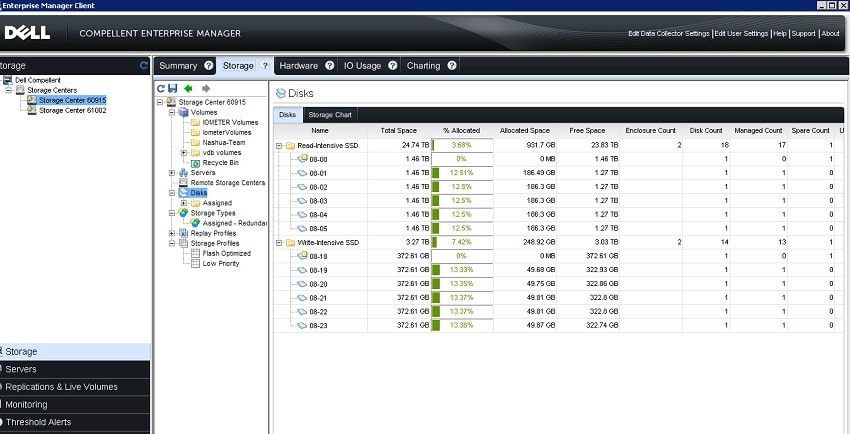
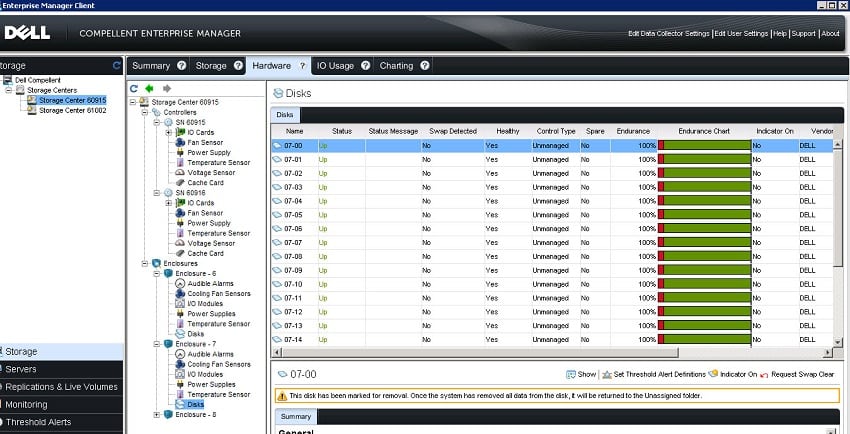
Dell Compellent Storage Center has a GUI designed to be accessible, and emphasizes ease of use with a relatively gentle learning curve. Wizards are offered for common allocation, configuration, and administration functions, while the software’s Support Assist capabilities offer remote, diagnostic, and monitoring tools with alert and notification services. Compellent Storage Center monitoring tools can provide details about wear on each SSD in the array.
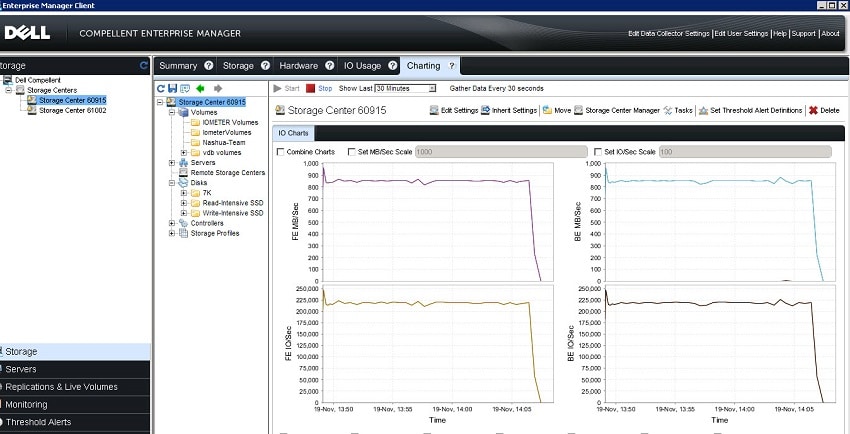
Enterprise Manager is a more comprehensive monitoring and management solution for local and remote Compellent Storage Center systems and allows for administration of multiple Compellent systems though a single console view. Enterprise Manager facilitates the configuration and verification of remote replication processes, monitors storage capacity and disk utilization, and generates usage and performance reports.
With the latest updates to the Storage Center operating system, Dell Compellent Enterprise Manager and Storage Center user interfaces also report sub-millisecond latencies for flash storage.
Dell Compellent offers a satisfying variety of platform integrations, including VMware to manage storage and virtual machines together with a vSphere plug-in, a vCenter SRM adapter, and VAAI plug-in support. The Storage Center Command Set for Windows PowerShell provides a scripting interface, while Replay Manager provides automated backup and restore for Microsoft Exchange, SQL Server, and Hyper-V.
Summary
Dell Compellent makes an interesting argument for all-flash performance tiers with their recent updates; swap out lower capacity and more power consuming 10K or 15K HDDs with a newly optimized MLC storage tier. The best part is you get more performance in that middle tier too, all for roughly the same price as the high speed HDDs. For mainstream enterprise storage, the concept is resonating. Dell expects a significant increase in Compellent shipments configured with the new MLC tier.
The conversation isn’t just about flash though, Compellent’s real magic is in its data progression and tier management, getting the most of the flash inside in addition to the high-capacity platter drives. Factor in development of expansion shelves like the SC280, which features great density thanks to spring loaded HDD insertion mechanism, and it’s clear Dell sees great upside for the Compellent family. Expect to see more as StorageReview continues to work with Dell Storage to bring usability and performance testing results to our audience.
Discuss This Story