Today, Aerospike announced that they are working on the fifth major release of their NoSQL database, Aerospike Database 5. Aerospike was founded in 2009 under the name Citrusleaf. In 2012 the company changed their name to match the name of their NoSQL database. Aerospike Database remains the company’s main product, despite being open-sourced under the AGPLv3.
Today, Aerospike announced that they are working on the fifth major release of their NoSQL database, Aerospike Database 5. Aerospike was founded in 2009 under the name Citrusleaf. In 2012 the company changed their name to match the name of their NoSQL database. Aerospike Database remains the company’s main product, despite being open-sourced under the AGPLv3.
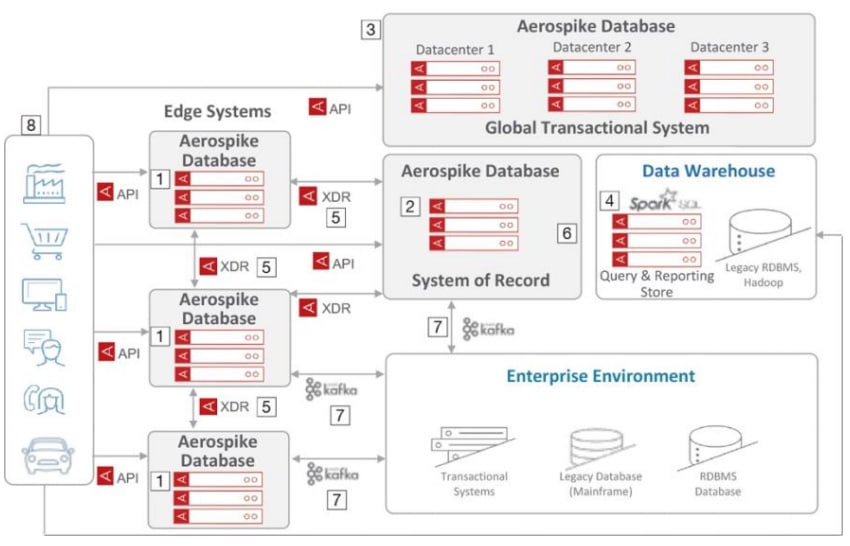
According to the company, the new release will feature significant performance improvements to Aerospike Cross Data Center Replication (XDR). Current versions of Aerospike Database already automatically route and augment data captured at the edge of the data center to wherever needed. Aerospike’s XDR feature even supports routing data to third party repositories, a rarity in a world where some days it seems like every vendor wants to lock you into their ecosystem.
Aerospike has been willing to share some details of their planned feature enhancements for the new version. According to the company, version 5 of Aerospike Database will deliver better management and control of asynchronous replication of data. Asynchronous replication of data is one of the things Aerospike XDR feature provides, so it looks like the company is focusing hard on improvements in that area for the upcoming release. A host of bug fixes have already gone into their codebase on GitHub, in preparation for the 5.0 version. In addition, they’ve also increased the number of addresses supported per-interface from twenty to one hundred.
One of the big features to Aerospike Database 5 is its multi-site clustering capabilities. With the configuration capability, nodes comprising a single Aerospike cluster are distributed across sites. The company claims that multi-site clustering supports always-on, strongly consistent, globally distributed transactions at scale. Features include:
- Strong Immediate Data Consistency – Aerospike Multi-Site Clustering brings the proven Jepsen validated Strong Consistency of the Aerospike Database to deployments across multiple sites. A commit-to-device may be performed at every phase to further enhance transactional durability.
- No Data Loss – With rack awareness and Strong Consistency, a single Aerospike cluster can be deployed across multiple geographically separated data centers with high resiliency, automated failovers, and no loss of data.
- Synchronous Active-Active Configuration – Aerospike Multi-Site Clustering is an Active-Active configuration where data is updated synchronously across the cluster providing a consistent data set. Applications can access the same updated records in real-time in different geographical regions.
- Strongest possible SLAs – Aerospike Multi-Site Clustering supports sub-millisecond reads and optimal writes of strongly consistent transactions. The speed of writes is dependent on network speed and geographical distance between the sites.
- High Availability and Resiliency – Aerospike provides high availability and a demonstrated uptime of five 9s, enabled by its cluster management and smart client technology. Synchronous replication of data across the cluster provides a globally consistent view of data.
- Conflict Avoidance, Not Conflict Resolution – with synchronous data replication and strong consistency, conflict detection and resolution is not required. In a failure scenario, Aerospike automatically transfers the management of write operations to another available data center, so application requests can still be processed. This is accomplished in a way that conflicting writes won’t occur and committed writes won’t be lost during site failures and when the cluster is subsequently restored to a fully healthy state.
- Immediate Failover – Aerospike utilizes automated cluster failure detection based on its internal roster and heartbeat mechanism. On failure of a cluster node or the network, Aerospike quickly recovers and reforms the cluster. Clients automatically connect to the new formation. The entire process is automated without any human Intervention or additional application code.
Aerospike Database 5 is slated for GA this month, the last two big releases were in December 2018, December 2019. The main new feature in the 4.8 release last December was adding support for storing record data in Intel Optane DC Persistent Memory (PMEM).
Engage with StorageReview
Newsletter | YouTube | Podcast iTunes/Spotify | Instagram | Twitter | Facebook | RSS Feed
