It’s CPU Season again; the market has been abuzz with anticipation, and AMD has not disappointed. Today, the AMD Threadripper 7000 WX-Series was launched, setting new standards in the high-end desktop and workstation market segment. Aimed at professionals who require extreme multi-threading capabilities and high-frequency performance, this series is a testament to AMD’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of computing.
It’s CPU Season again; the market has been abuzz with anticipation, and AMD has not disappointed. Today, the AMD Threadripper 7000 WX-Series was launched, setting new standards in the high-end desktop and workstation market segment. Aimed at professionals who require extreme multi-threading capabilities and high-frequency performance, this series is a testament to AMD’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of computing.
Read our companion piece on the Dell Precision 7875 Tower.

AMD Threadripper 7000 WX-Series CPU SKU Models
| AMD 7000 WX-Series | Cores/Threads | Frequency (Boost*/Base) | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7995WX | 96 / 192 | Up to 5.1 / 2.5 GHz | 350W |
| 7985WX | 64 / 128 | Up to 5.1 / 3.2 GHz | 350W |
| 7975WX | 32 / 64 | Up to 5.3 / 4.0 GHz | 350W |
| 7965WX | 24 / 48 | Up to 5.3 / 4.2 GHz | 350W |
| 7955WX | 16 / 32 | Up to 5.3 / 4.5 GHz | 350W |
| 7945WX | 12 / 24 | Up to 5.3 / 4.7 GHz | 350W |
AMD Threadripper 7000 WX-Series Performance
The new Threadripper 7000 WX-Series comes with up to 96 cores and 192 threads in the 7995WX model, offering unparalleled multi-threaded performance. With boost frequencies reaching up to 5.3 GHz, these processors are not just about core count; they’re also designed for speed.
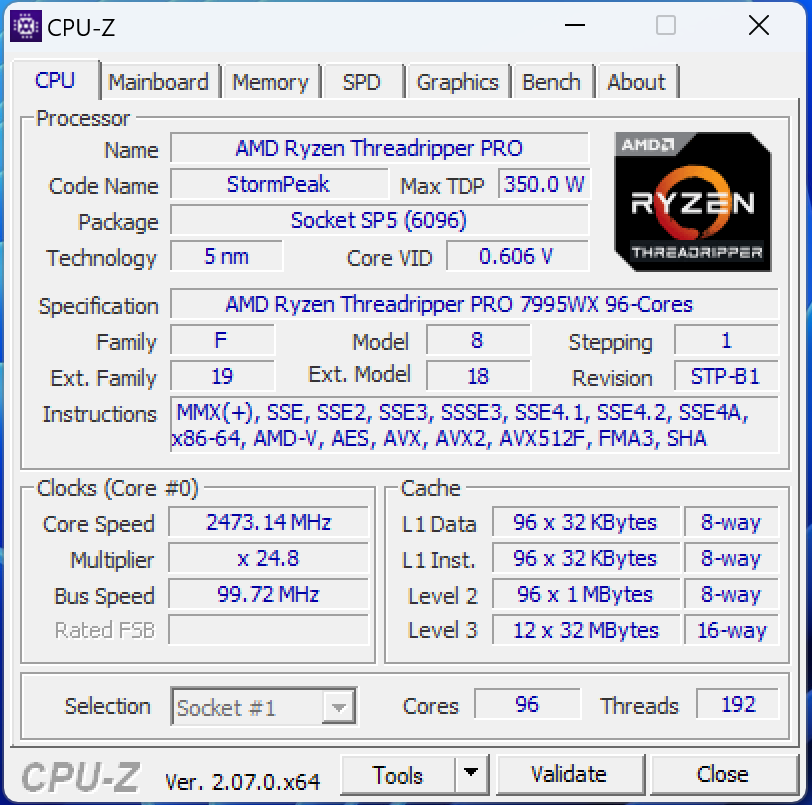
Threadripper 7995WX CpuZ
Thanks to Dell, we were granted remote access to the Dell Precision 7875 system in the Dell Customer Solutions Center (CSC) lab. We connected through the system’s built-in Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) and a commercial desktop capture application commonly used for low-latency game streaming.
Both methods introduce some performance overhead, affecting CPU workloads. Specifically, we observed a 3-5 percent drop in performance on CPU-bound tasks. These metrics were determined by comparing results from Dell’s internal tests with our own experiences.
We’re comparing performance results to our recent Tyan Server/Workstation Build with 96-core AMD Genoa-X CPU and the same Genoa-X in a more traditional server platform.
Geekbench 6
Geekbench 6 is a cross-platform benchmark that measures overall system performance. Higher scores are better.
You can find comparisons to any system you want in the Geekbench Browser.
| Geekbench 6 | Precision 7875 (AMD 7995WX (96 cores) | TYAN Transport HX FT65T-B8050 | AMD 1p/96c Genoa-X system |
| CPU Benchmark – Single-Core | 2,762 | 2,097 | 2,093 |
| CPU Benchmark – Multi-Core | 22,886 | 21,077 | 21,329 |
In the Geekbench 6 benchmarks, the 7995WX delivered great performance in both single-core and multi-core CPU benchmarks. With a single-core CPU score of 2,762, it outperforms the TYAN Transport HX FT65T-B8050’s 2,097 and surpasses the AMD 1p/96c Genoa-X’s 2.093. Its multi-core CPU score is impressive at 22,886, just edging out the TYAN’s 21,077 and AMD 1p/96c Genoa-X’s 21,329.
Geekbench 5
We also ran Geekbench5 to grab another comparison point where the Precision 7875 and 96-core Threadripper 7995WX retake the top spot.
| Geekbench 5 | Precision 7875 (AMD 7995WX (96 cores) 2x NVIDIA RTX 6000 Ada, 512GB DDR5 RAM) | TYAN Transport HX FT65T-B8050 (AMD Genoa-X 9684X, NVIDIA A6000) |
| CPU Benchmark – Single-Core | 2,007 | 1500 |
| CPU Benchmark – Multi-Core | 55,854 | 55,338 |
Cinebench R23
Maxon’s Cinebench R23 is a CPU rendering benchmark that utilizes all CPU cores and threads. We ran it for both multi- and single-core tests. Higher scores are better.
Here, the Precision 7875 continued its leading performance.
| Cinebench R23 | Precision 7875 (AMD 7995WX (96 cores) 2x NVIDIA RTX 6000 Ada, 512GB DDR5 RAM) | TYAN Transport HX FT65T-B8050 (AMD Genoa-X 9684X, NVIDIA A6000) | AMD 1p/96c Genoa-X system |
| CPU (Multi-Core) | 102,600 Points | 94,754 Points | 93,720 Points |
| CPU (Single-Core) | 1,826 Points | 1,299 Points | 1,301 Points |
| MP Ratio | N/A | 72.96x | 72.04x |
y-cruncher
y-cruncher is a multi-threaded and scalable program that can compute Pi and other mathematical constants to trillions of digits. Since its launch in 2009, y-cruncher has become a popular benchmarking and stress-testing application for overclockers and hardware enthusiasts. Faster is better in this test.
As this is a CPU and memory-bound test, the Precision 7875 outpaces the HX FT65T-B8050’s AMD Genoa-X 9684X and the Dell Precision 7960’s Xeon w9-3495X.
| y-cruncher (Total Computation time) | Precision 7875 (AMD 7995WX (96 cores) 2x NVIDIA RTX 6000 Ada, 512GB DDR5 RAM) | TYAN Transport HX FT65T-B8050 (AMD Genoa-X 9684X, NVIDIA A6000) | Dell Precision 7960 (Xeon w9-3495X, RTX 6000 Ada) |
| 1 billion digits | 9.696 seconds | 10.233 Seconds | 12.788 Seconds |
| 2.5 billion digits | 19.707 seconds | 20.543 Seconds | 34.459 Seconds |
| 10 billion digits | 71.463 seconds | 72.568 Seconds | 157.770 Seconds |
Multi-threading at High Speed
If you are in the business of content creation, 3D rendering, or any high-performance computing, you will appreciate the vast number of cores and threads. For instance, the 7995WX, with its 96 cores, can handle complex tasks with a level of efficiency that was previously unimaginable.
In our testing, the workstation we evaluated stands as a notably proficient platform engineered for professionals needing raw computational horsepower, versatility, and cutting-edge technology. Although our remote tests were constrained, they pointed to exceptional performance for the CPU. The Threadripper 7995WX will be an excellent choice for tackling complex, compute-intensive projects like 3D rendering, simulations, machine learning, and video editing.
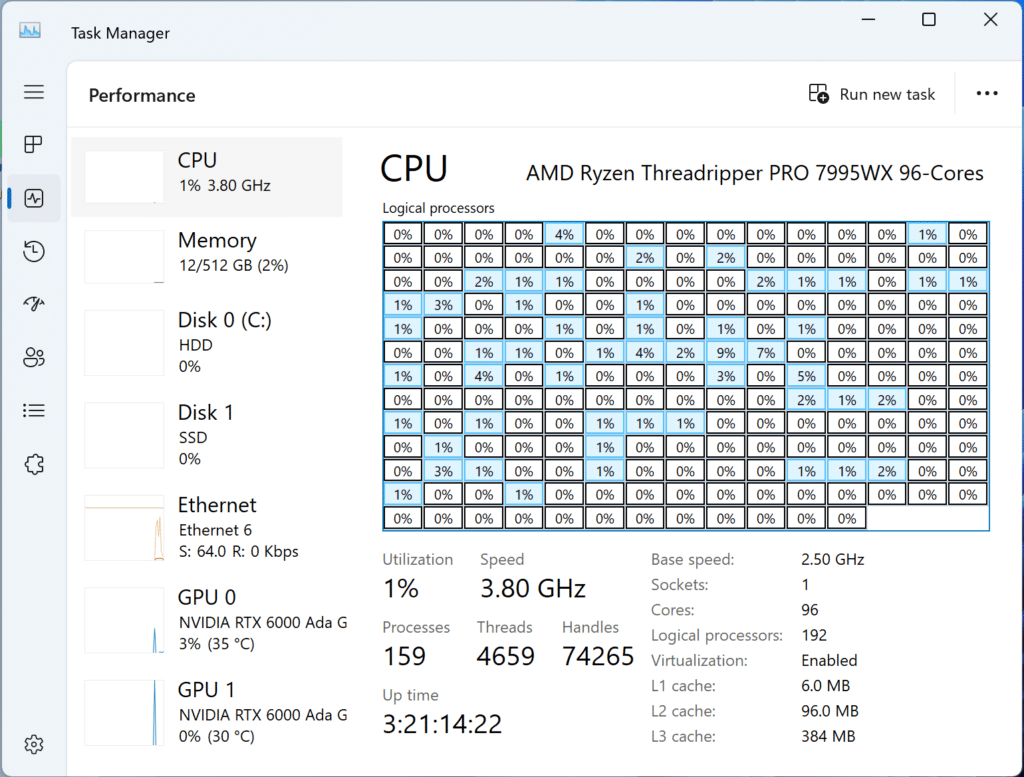
Threadripper PRO 7995WX 96 core Task Manager
The high-frequency performance is equally impressive. With base frequencies starting from 2.5 GHz in the 7995WX and going up to 4.7 GHz in the 7945WX, users can expect swift and responsive performance across the board. The boost frequencies add the cherry on top, ensuring the processor can efficiently handle peak workloads.
All of the PCIe Lanes
Including 128 PCIe Gen5 lanes in AMD’s new Ryzen Threadripper PRO 7000 WX-Series is a significant milestone, particularly for workstations designed for HPC, AI/ML training, and data-intensive workflows. PCIe lanes are the fundamental communication pathways between the CPU and hardware components like GPUs, SSDs, and network cards. As more and more devices move to the PCIe bus, like storage, having a high number of Gen5 lanes enables more power to be put into the workstation.
With 128 lanes, users have unprecedented flexibility to add multiple high-speed storage drives, high-performance GPUs for AI and graphics rendering, and even specialized hardware accelerators without creating a bottleneck in data flow.
That’s a lot of PCIe!
AMD CPU Comparison: 5000 WX-Series vs 7000 WX-Series
All the models in the 7000 WX-Series come with a TDP of 350W, up from the 280W of the 5000 WX Series. While this might seem high, it is a necessary trade-off for the performance gains. Adequate cooling solutions and a well-ventilated chassis will be essential for optimum performance. As AMD and Intel CPUs continue to push the envelope of package power, considerations must be made to dissipate the heat under sustained workloads.
| Generation | Model | Cores/Threads | Frequency (Boost*/Base) | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5000 WX-Series | 5995WX | 64 / 128 | Up to 4.5 / 2.7 GHz | 280W |
| 5975WX | 32 / 64 | Up to 4.5 / 3.6 GHz | 280W | |
| 5965WX | 24 / 48 | Up to 4.5 / 3.8 GHz | 280W | |
| 5955WX | 16 / 32 | Up to 4.5 / 4.0 GHz | 280W | |
| 5945WX | 12 / 24 | Up to 4.5 / 4.1 GHz | 280W | |
| 7000 WX-Series | 7995WX | 96 / 192 | Up to 5.1 / 2.5 GHz | 350W |
| 7985WX | 64 / 128 | Up to 5.1 / 3.2 GHz | 350W | |
| 7975WX | 32 / 64 | Up to 5.3 / 4.0 GHz | 350W | |
| 7965WX | 24 / 48 | Up to 5.3 / 4.2 GHz | 350W | |
| 7955WX | 16 / 32 | Up to 5.3 / 4.5 GHz | 350W | |
| 7945WX | 12 / 24 | Up to 5.3 / 4.7 GHz | 350W |
AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7000
AMD also announced the Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series targeted at the high-end desktop market.
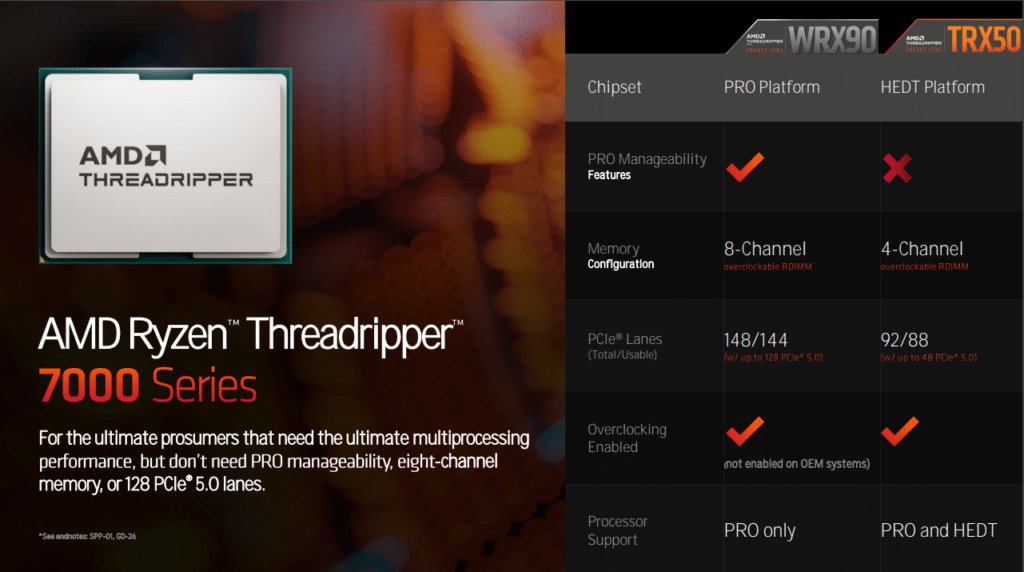
AMD has unveiled its powerful Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series, targeting ultimate prosumers needing robust multiprocessing performance. While both the WRX90 (PRO platform) and TRX50 (HEDT platform) are supported, there are key distinctions between the two platforms, including:
- Chipset Differences:
- WRX90: Designed as a PRO platform, boasting PRO manageability features exclusive to this chipset.
- TRX50: Tailored as a HEDT platform, it lacks the PRO manageability features.
- Memory Configuration:
- WRX90: Offers 8-channel overclockable RDIMM support, ensuring faster memory access.
- TRX50: Features 4-channel overclockable RDIMM support.
- PCIe® Lanes:
- WRX90: Provides a generous 148 total PCIe 5.0 lanes, with 144 usable lanes (supporting up to 128 PCIe 5.0 devices).
- TRX50: Has 92 total PCIe 5.0 lanes, with 88 usable (supporting up to 48 PCIe 5.0 devices).
- Overclocking:
- Both chipsets support overclocking, though it’s noteworthy that OEM systems on the WRX90 platform will not have this feature enabled.
In essence, the Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series reinforces AMD’s commitment to delivering cutting-edge performance to high-demand users, with the WRX90 chipset aimed towards professional users who require advanced manageability features. With the capability of the AMD TRX50 Chipset to accommodate PRO CPUs, constructing a top-tier desktop boasting 96 processing threads becomes a feasible endeavor.
Architecture Overview
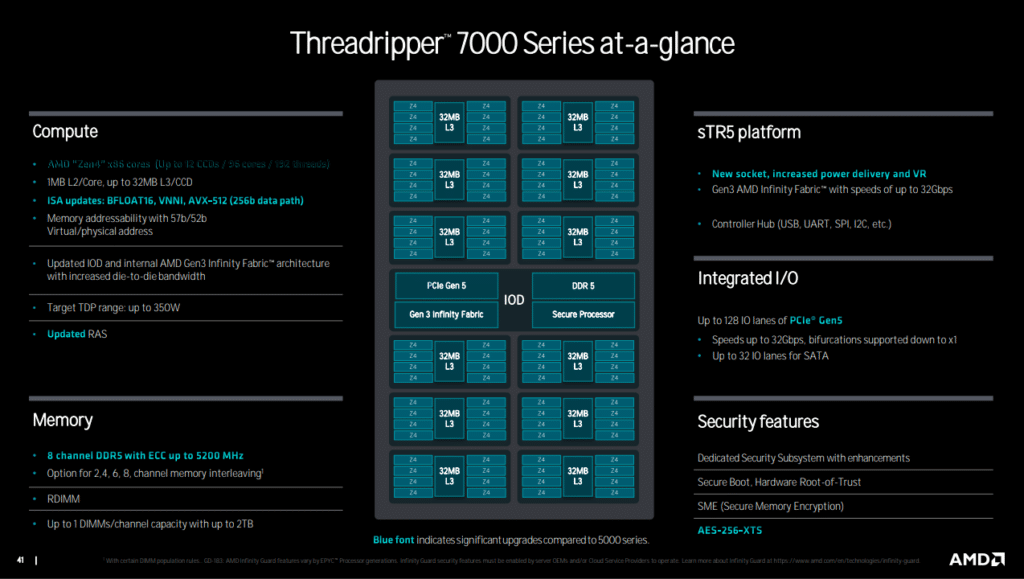
The updated core architecture is impressive, beginning with significant enhancements to Branch Prediction. This feature has been improved to enable more accurate and quicker decision-making by the CPU, which contributes to smoother, faster performance across various tasks.
Another improvement is the enlargement of the Op-Cache and Instruction Retire Queue. This expansion allows quicker instruction execution and retirement, speeding up the overall workflow. Coupled with a larger Integer and Floating-Point (Int/FP) register file, these improvements contribute to more efficient data processing capabilities.
The architecture includes deeper buffers throughout the core for more optimal data flow and reduced latency. Additionally, Load/Store operations have been optimized for better memory access performance, improving the speed at which the CPU can handle data.
Regarding energy efficiency, the Threadripper 7000 series now supports more power-efficient AVX-512 instructions in the Floating-Point Unit. This inclusion makes it possible to perform complex mathematical computations with lower energy consumption, a critical consideration in today’s eco-conscious environment.
As for the cache hierarchy, the Threadripper 7000 series has a fast private 1MB L2 cache. This larger cache allows quicker data retrieval, reducing the CPU’s wait time. The architecture also supports more outstanding misses from L2 to L3 per core and from L3 to memory, improving the system’s tolerance for cache misses and enhancing performance.
The architecture takes a baseline from the “Zen 3” design, with an L3 cache shared among all the complex’s eight cores. This design choice aids in better resource allocation. L3 is filled from L2 victims, meaning that data evicted from the L2 cache moves to the L3 cache. Additionally, L2 tags are duplicated in L3, aiding in probe filtering and enabling faster cache transfers. These cache improvements collectively lead to a more responsive and efficient system.
Memory Capabilities
The memory architecture of the Threadripper 7000 series comes with robust capabilities, supporting 8-channel DDR5 memory with speeds up to DDR-5200. This allows for a peak theoretical bandwidth of 266GB/s, calculated using the formula 8 channels × 8 Bytes × 5.2 GT/s. It’s a highly versatile memory configuration with one DIMM per channel capability and support for Registered DIMMs (RDIMMs). Capacity options are flexible, scaling up to 2TB for WRX90 and 1TB for TRX50 on the Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series. The architecture also includes a read UECC retry capability for enhanced reliability.
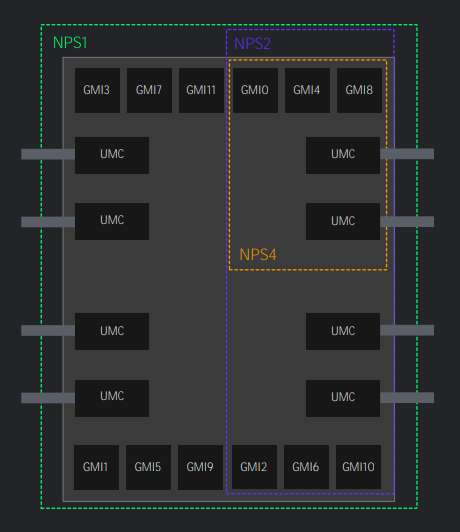
What’s particularly interesting is that this memory setup offers high bandwidth and efficiency in both dual-rank and single-rank configurations on the Threadripper 7000 series. This allows optimal DRAM capacity and total cost of ownership (TCO) optimization. Moreover, various interleaving options (2-ch, 4-ch, 6-ch, 8-ch) offer a tradeoff between latency and bandwidth, meeting different system requirements. Systems, by default, are configured as NPS1 but can be customized for additional optimization with multiple memory nodes per socket (NPS).
I/O Capabilities
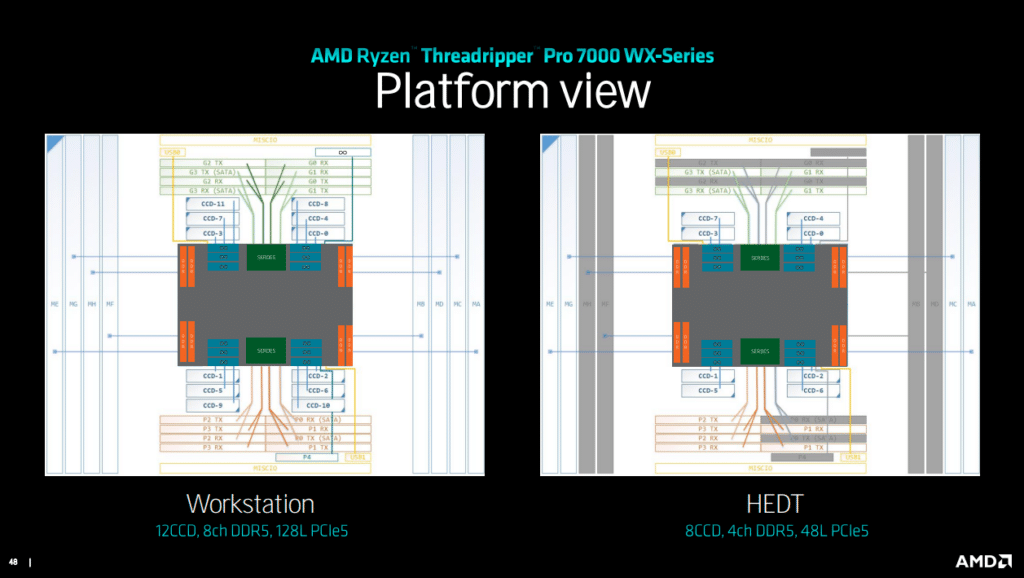
The Threadripper 7000 series shows promise in its I/O capabilities as well. The design allows for die-to-die connectivity with up to 12 CCDs, featuring a refined IOD/CCD and package co-design. The improved Die-to-Die chiplet interface offers power efficiency, consuming less than 2pJ per bit with additional usage-based power reductions. Bandwidth capabilities are impressive, going up to 36Gbps and featuring up to 2x probe throughput compared to the 5000 Series.
Further enhancing its I/O capabilities, the Threadripper 7000 series supports up to 128 lanes per socket with PCIe Gen5 and eight bonus lanes of Gen3. This leads to very high I/O connectivity and offers over 90 percent higher peak (per slot) I/O bandwidth than the 5000 Series. This comes in addition to a combination of PCIe and SATA SERDES, allowing for up to nine PCIe devices per x16, for example, x8 + 8×1 configurations.
Conclusion
The AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7000 WX-Series is a powerful entrant to the HEDT market. With an impressive range of specs and the performance metrics to back it up, it sets new benchmarks for what a desktop processor can achieve. Combining these with the memory and I/O features, the Threadripper 7000 series presents an extraordinarily versatile and powerful platform capable of handling a broad range of high-performance computing tasks. Whether you’re into high-performance computing, content creation, or 3D rendering, these processors are built to deliver, and the new CPUs from AMD have you covered.
It’s worth mentioning that the performance of the AMD 7995WX outperformed the 96-core Genoa server-class processor in our tests. This outcome is expected, considering the 7995WX is explicitly designed for workstation applications and benefits from refinements over the server-class Genoa part. These refinements optimize it for the unique demands of high-end professional use cases. We are highly optimistic about the capabilities of this new CPU from AMD and look forward to a more comprehensive evaluation once we have a system in our lab. With systems coming from the usual suspects like Dell, HP and Lenovo, it shouldn’t be long until we can get a deeper hands-on look at these CPUs.
Dell Precision 7875 Tower Blog
AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7000 Series
Engage with StorageReview
Newsletter | YouTube | Podcast iTunes/Spotify | Instagram | Twitter | TikTok | RSS Feed