In this edition of Before the Home Lab we'll look at installing Proxmox.
What is Proxmox VE?
Proxmox is the hypervisor for Proxmox Virtual Environment (PVE). PVE is an open-source server virtualization environment. PVE is a Debian-based Linux distribution with a modified Ubuntu LTS kernel and allows deployment and management of virtual machines and containers.
How to Install Proxmox VE
First thing we should do is go download Proxmox, head over to the page, get ready for another useless account… wait a minute, is that a download button that downloads stuff?

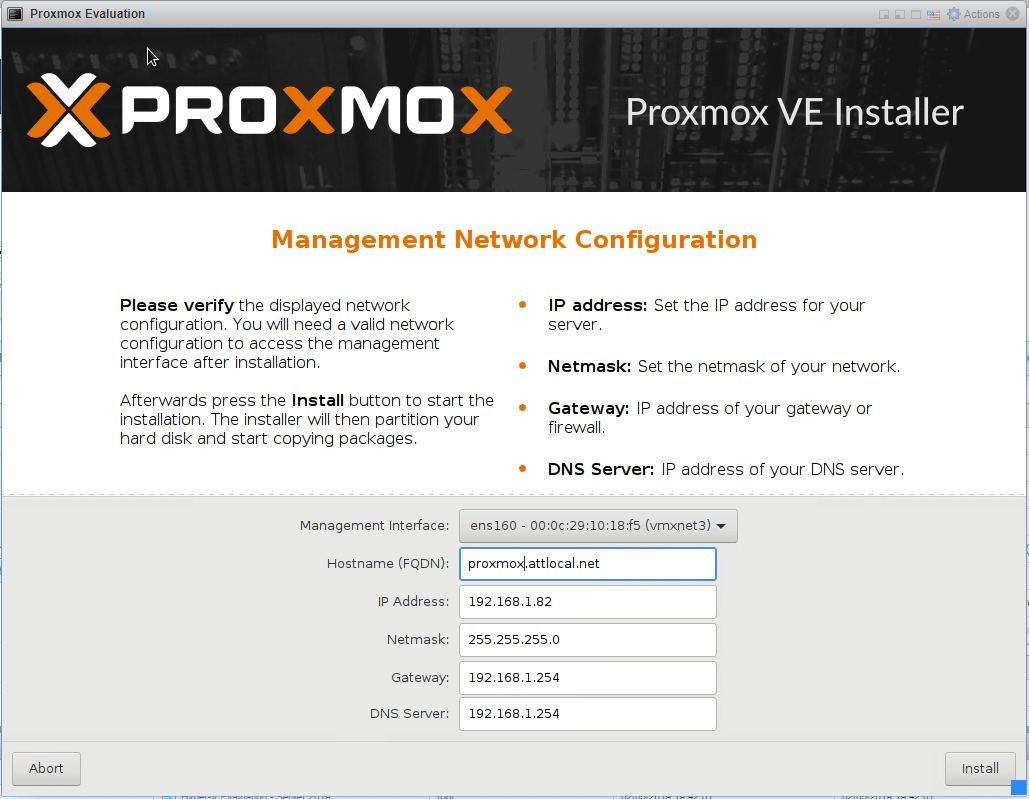
In a physical deployment, you’d make a bootable disk out of this ISO on a flash drive and then install it on your hardware on an SD card or USB drive. Since this is a virtual deployment, we’re going to move this ISO file directly into the main datastore on my ESXi test bed.
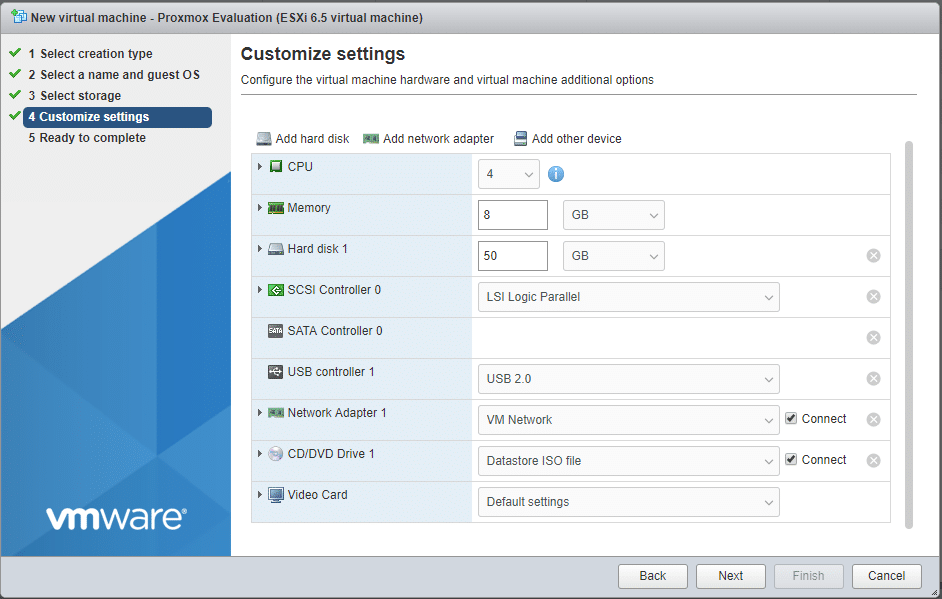
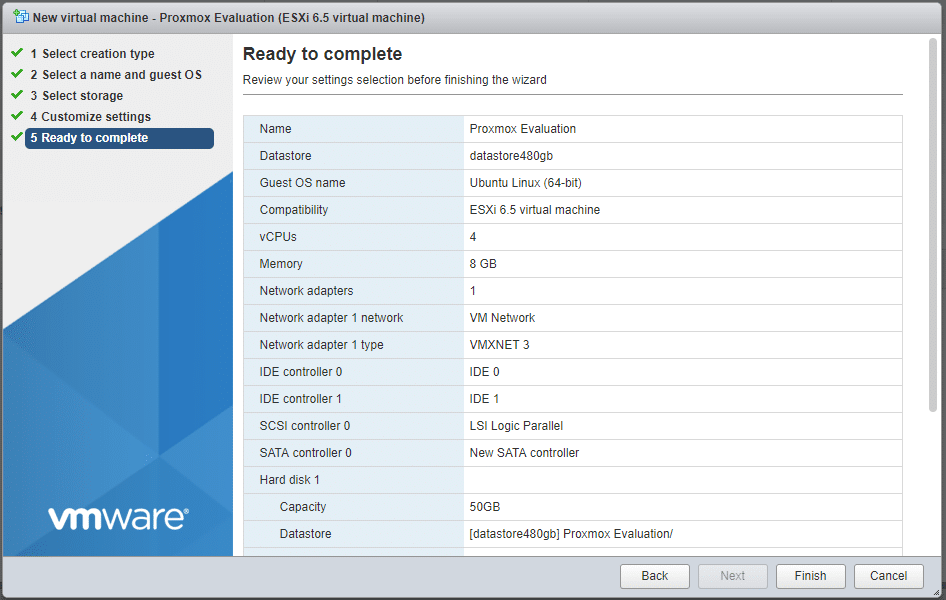
For reference, we added 50GB of thin-provisioned hard drive and an ISO file for Server 2016.
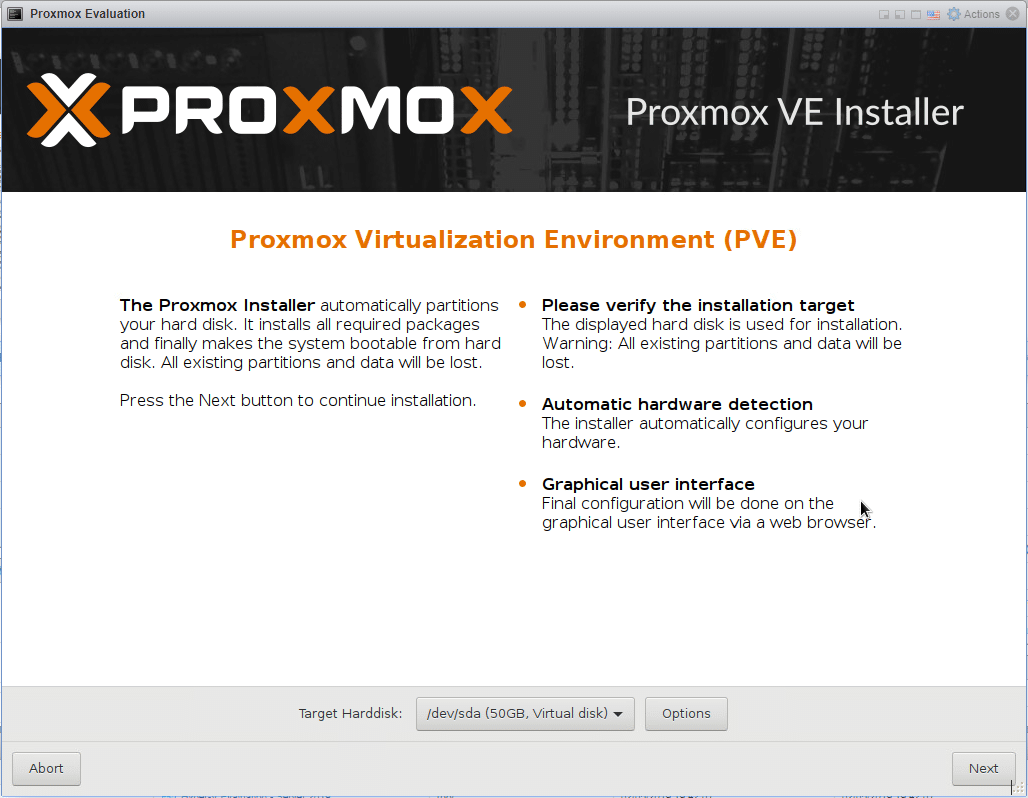
We can then start the VM and see the Proxmox installer.
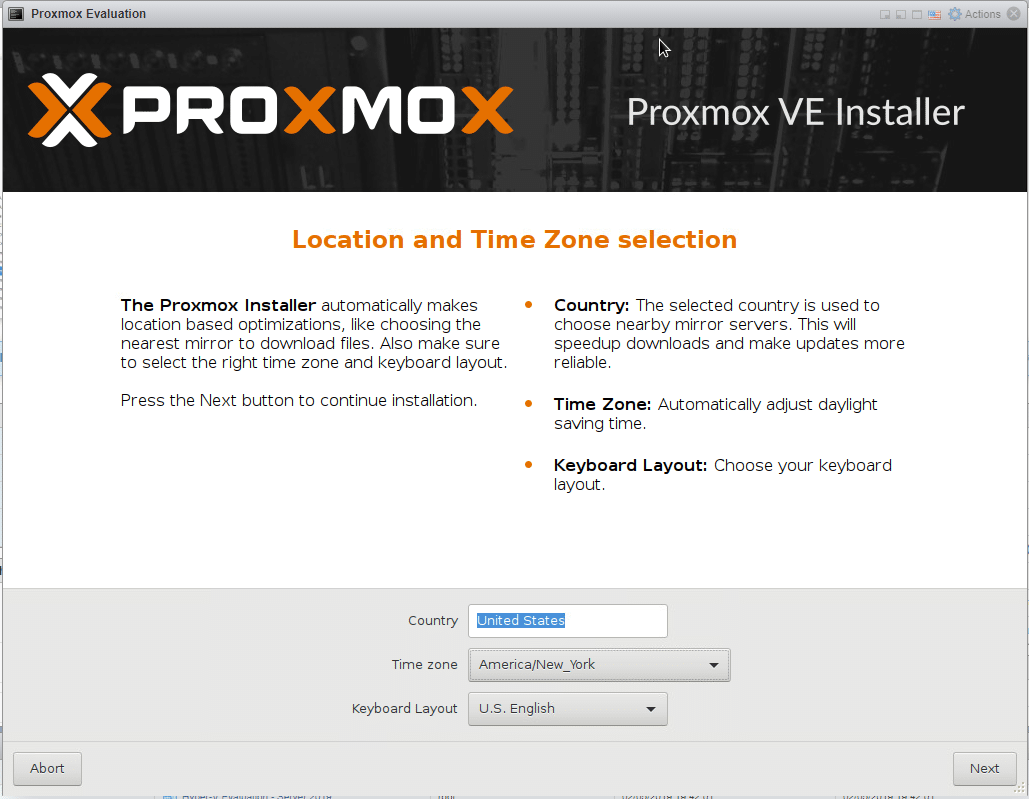
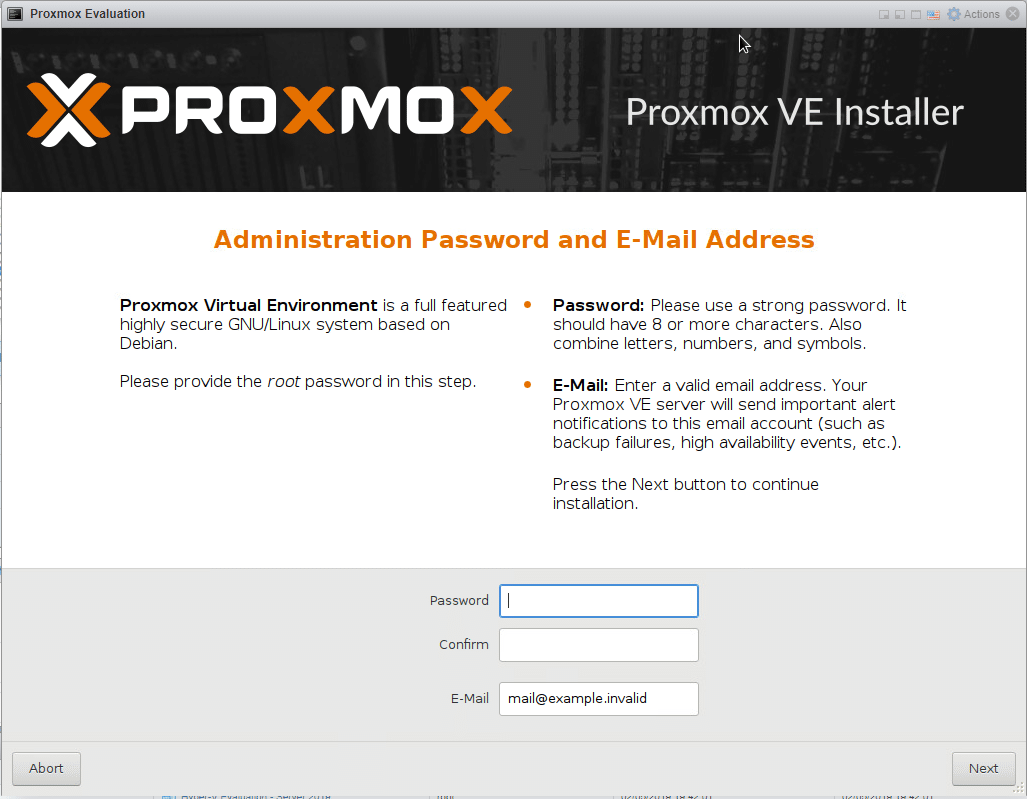
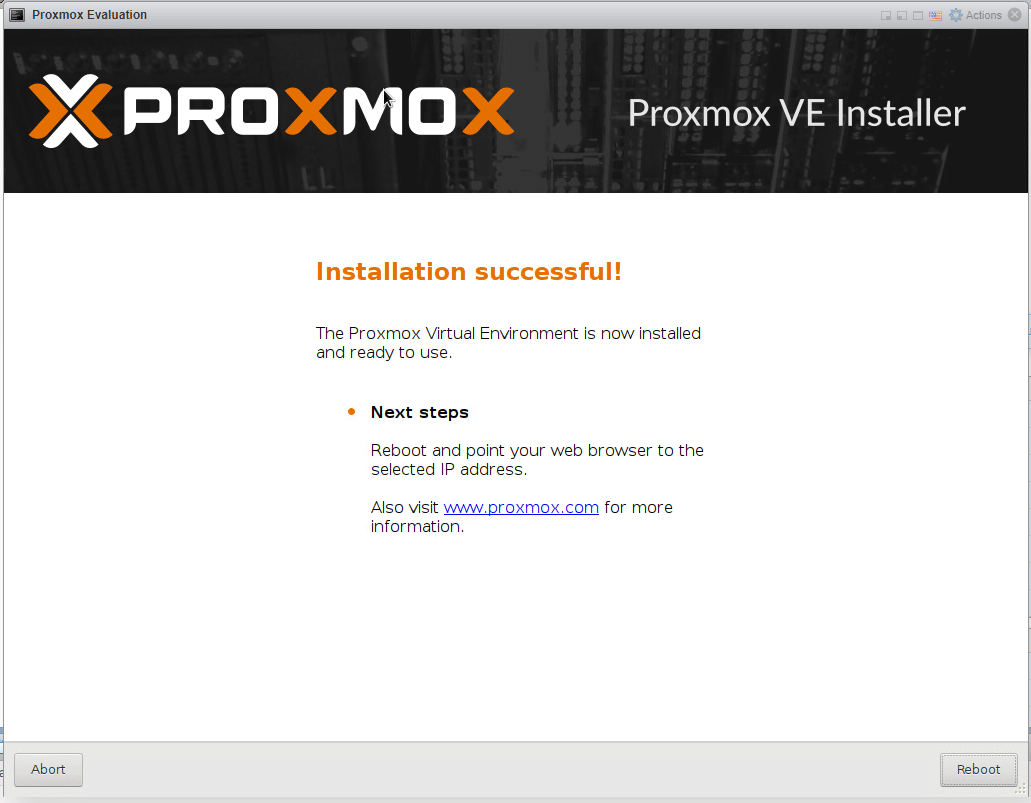
And away we go.
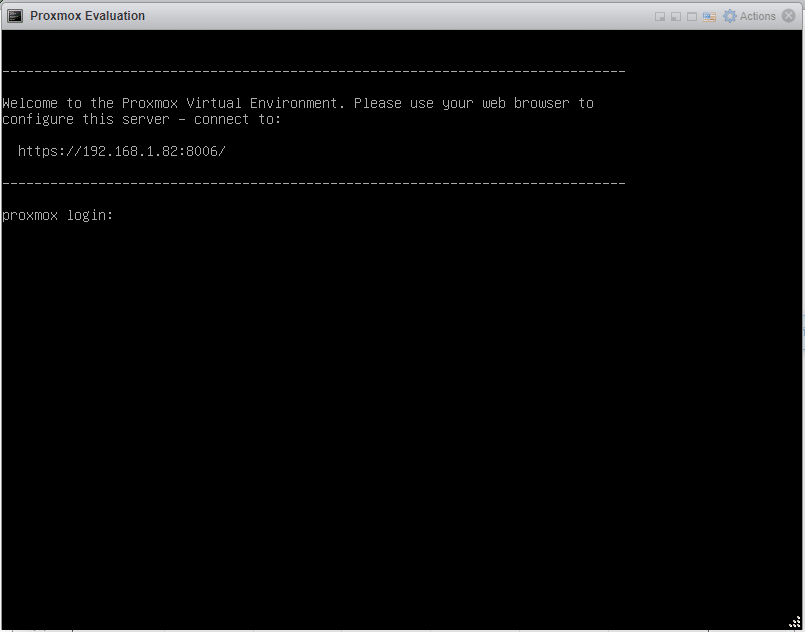
After reboot, we get a screen telling us to go to https://local-ip:8006/
Head over to the URL, bypass the security warning under Advanced.
Login to your new proxmox install
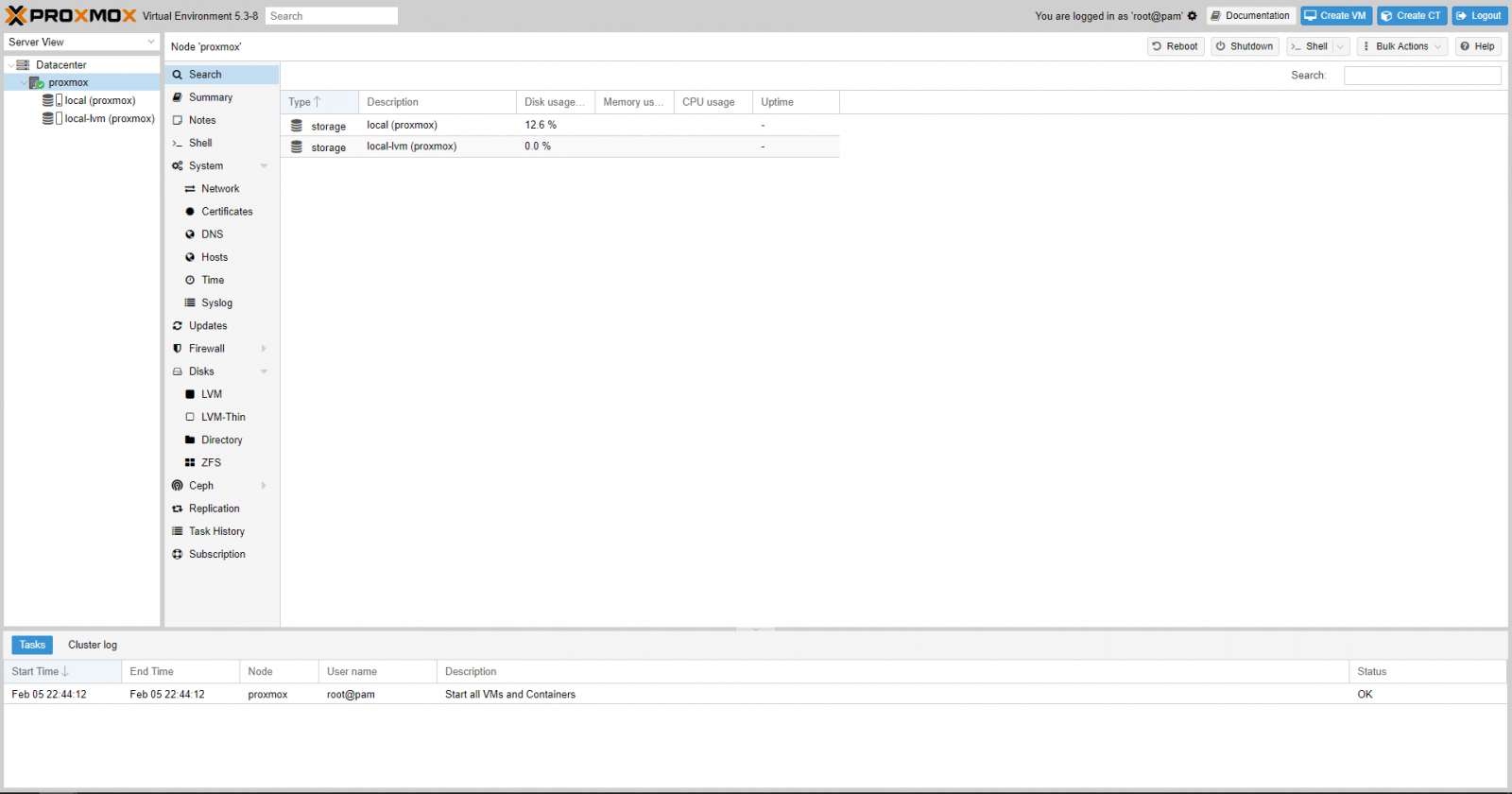
Ready to go. You might get a warning telling you there’s no subscription assigned, this can be safely ignored for evaluation.
In the next Before The Lab we'll look at installing oVirt.