Enterprise software developer Proxmox Server Solutions GmbH, better known to us as Proxmox, has released version 7.2 of its server virtualization management platform, Proxmox Virtual Environment. The new version of the hypervisor is based on Debian 11.3 (Bullseye) but uses a newer Linux kernel 5.15.30 and includes updates to the latest versions of leading open-source technologies for virtual environments, like QEMU 6.2.0, LXC 4.0.12, and ZFS 2.1.4.
Enterprise software developer Proxmox Server Solutions GmbH, better known to us as Proxmox, has released version 7.2 of its server virtualization management platform, Proxmox Virtual Environment. The new version of the hypervisor is based on Debian 11.3 (Bullseye) but uses a newer Linux kernel 5.15.30 and includes updates to the latest versions of leading open-source technologies for virtual environments, like QEMU 6.2.0, LXC 4.0.12, and ZFS 2.1.4.

Proxmox VE, the open-source project, has a worldwide user base with more than 600,000 hosts. The virtualization platform has been translated into over 26 languages. More than 88,000 active community members in the support forum engage with and help each other. Using Proxmox VE as an alternative to proprietary virtualization management solutions, enterprises can centralize and modernize their IT infrastructure and turn it into a cost-effective and flexible software-defined data center based on the latest open-source technologies.
We like Proxmox VE and did a full review in July 2021. We installed it on several systems with success. Had some hiccups with hardware on a couple of servers, but overall it was simple to install and did what we wanted an OS to do. Check out the PVE 7.0 review.
Proxmox Virtual Environment is free and open-source software, published under the GNU Affero General Public License, v3. The ISO contains the complete feature-set and can be installed on bare metal. The virtualization platform from Proxmox comes stocked with all the essential management tools and an easy-to-use, web-based user interface. This allows for simple, out-of-the-box host management through the command line or a standard web browser.
For enterprise users, Proxmox Server Solutions GmbH offers a subscription-based support model relied upon by thousands of enterprise customers. The subscription service provides access to an Enterprise Repository, with regular updates via the web interface and technical support directly from the developers.
Proxmox VE supports Ceph Pacific 16.2.7 and offers continued support for Ceph Octopus 15.2.16 until mid-2022.
What’s new in Proxmox Virtual Environment 7.2
Backup/Restore:
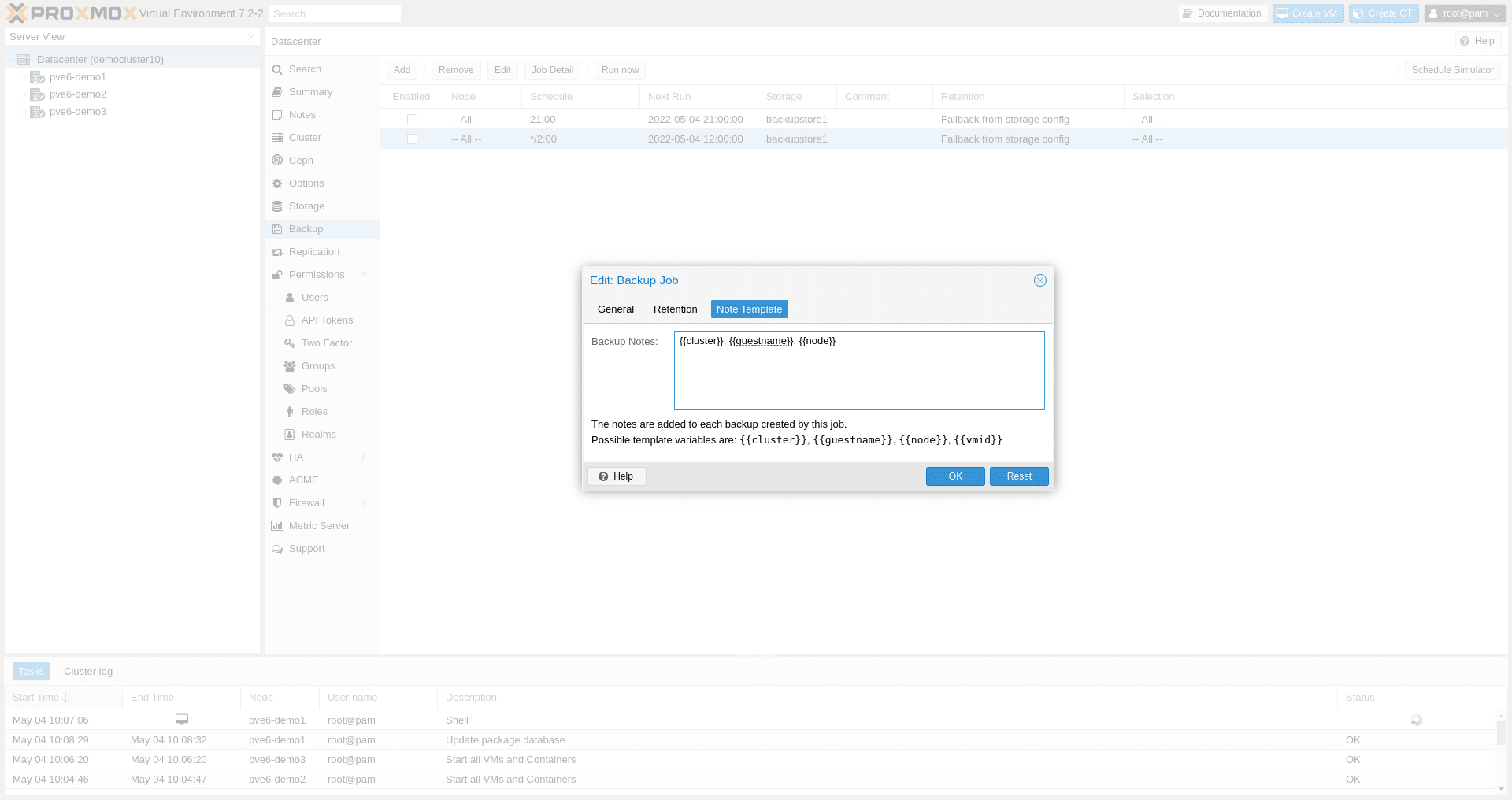
Notes templates: Meta-information can be added via a notes template for backup jobs to better distinguish and search for backups. This template is evaluated when the job is executed and added to any resulting backup. Notes templates can contain template variables like {{guestname}} or {{cluster}}.
To benefit from the Rust code of Proxmox Backup Server, the Proxmox developers use perlmod, a Rust crate that allows exporting Rust modules as Perl packages. perlmod is used by Proxmox to transfer data between Rust and Perl, thus implementing parts of Proxmox VE and Proxmox Mail Gateway in Rust.
The next-event scheduling code was updated via this Perl-to-Rust-binding (perlmod) and now uses the same code as Proxmox Backup Server. Users can specify the existing weekday, time, and time range, but also a specific date and time (e.g., *-12-31 23:50; New Year’s Eve, 10 minutes before midnight every year), date ranges (e.g., Sat *-1..7 15:00; first Saturday every month at 15:00), or repeating ranges (e.g., Sat *-1..7 */30; first Saturday every month, every half hour). Some basic restore settings, for example, guest name or memory, can now be overwritten in the enhanced backup-restore dialog in the web interface.
A new ‘job-init’ hook step was added to the backup process. It can be used to prepare the backup storage, for example, by starting the storage server.
High Availability Manager
The number of configurable services that can be handled per single node has increased by improving the local resource manager (pve-ha-lrm) scheduler, which launches workers. This helps in large deployments, as the services at the end of the queue are also checked to ensure that they are still in the target state.
Introducing a skip-round command to the integrated HA simulator in Proxmox VE makes it easier to test races in scheduling (on the different nodes).
Cluster: With the creation of new VMs or containers, version 7.2 provides the configuration of the desired range from which the new VMIDs are proposed via the web interface. The lower and upper boundaries can be set in the Datacenter -> Options panel. Setting lower equal to upper disables auto-suggestion completely, meaning the administrator must manually enter an ID.
Ceph: Proxmox VE supports Ceph Pacific 16.2.7 and Ceph Octopus 15.2.16 with continued support until mid-2022. This version also supports creating and destroying erasure-coded pools, which can be added as Proxmox VE storage entries and help reduce the amount of disk space required. A new option in the GUI allows for passing the keyring secrets of external Ceph clusters when adding an RBD or CephFS storage to Proxmox VE.
Web interface: Further enhancements in the web interface allow for safe reassignment of a VM disk or CT volume to another guest on the same node; the reassigned disk/volume can be attached at a different bus/mount point on the destination guest. This can help in upgrades, restructuring, or after disaster recovery.
Management: Many improvements in Proxmox VE 7.2 enable even more convenient administration of the system. For example, a particular kernel version can be selected to boot persistently from a running system through ‘proxmox-boot tool kernel pin’. The selection can be used either indefinitely or just for the next boot, and this eliminates the need to watch the boot process to select the desired kernel version on the bootloader screen.
Further Enhancements and Bug Fixes
In the installation ISO, ZFS installs can be configured to use various compression algorithms (e.g., zstd, gzip, etc.). Additionally, the memtest86+ package, a tool aimed at memory failure detection, has been updated to the completely rewritten 6.0b.
Further improvements have been added to virtual machines (KVM/QEMU); one to highlight is support for the accelerated virtio-gl (VirGL) display driver. For VirtIO and VirGL display types, SPICE is enabled by default. Changing the graphics card to VirGL can significantly increase frames per second (FPS) in modern Linux distributions. For Proxmox containers (LXC), many templates have also been refreshed or newly added, such as the NixOS container template.
The Proxmox VE Android app now provides a simple dark theme and enables it if the system settings are configured to use dark designs. The mobile app also provides an inline console by relaying noVNC for VMs, and xterm.js for containers, and the Proxmox VE node shell in the GUI.
To prevent a network outage during the transition from ifupdown to ifupdown2, the ifupdown package was modified not to stop networking upon its removal.
Availability
Proxmox Virtual Environment is free and open-source software, published under the GNU Affero General Public License, v3. The ISO contains the complete feature-set and can be installed on bare metal. Proxmox VE 7.2 is available for download.
Engage with StorageReview
Newsletter | YouTube | Podcast iTunes/Spotify | Instagram | Twitter | Facebook | TikTok | RSS Feed