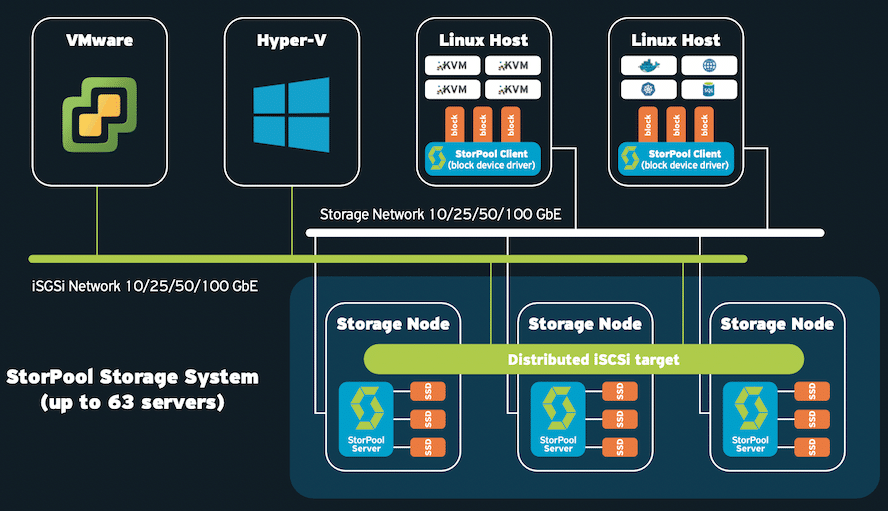
StorPool Storage v20 adds new capabilities including NVMe/TCP, StorPool on AWS support, and NFS File Storage. The StorPool Storage platform is designed for large-scale cloud infrastructures running workloads that require low latency and is highly reliable.
StorPool Storage v20 adds new capabilities including NVMe/TCP, StorPool on AWS support, and NFS File Storage. The StorPool Storage platform is designed for large-scale cloud infrastructures running workloads that require low latency and is highly reliable.
With StorPool Storage, customers can deploy high-performance, linearly-scalable primary storage systems on commodity hardware to serve large-scale cloud data storage and data management requirements.
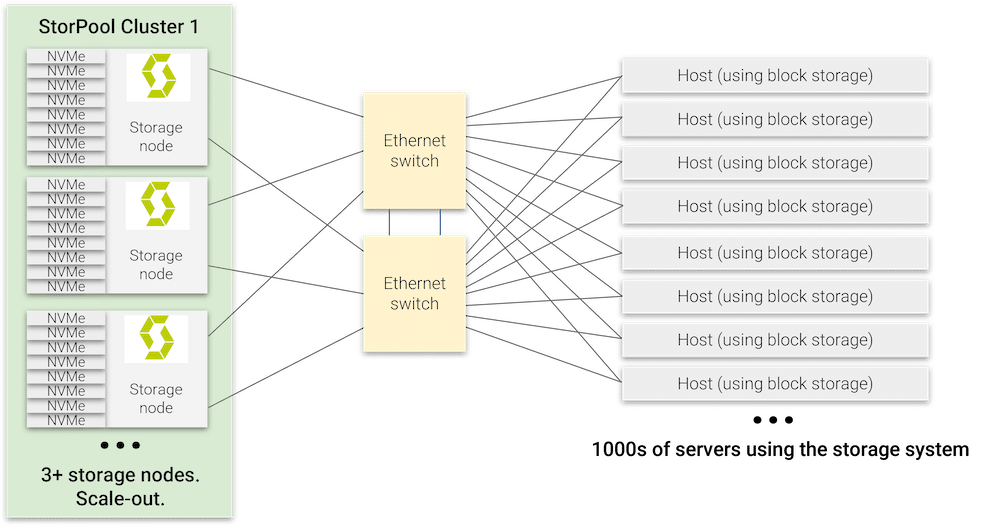
StorPool Storage v20
StorPool’s unique storage platform comes with 24/7/365 support, SLA, proactive monitoring, and issue resolution. It is a fully-managed storage solution that includes system design assistance, hardware functional tests, stress-test, hardware performance tests, and runs in customers’ data centers on customer-provided hardware.
NVMe/TCP Support
StorPool Storage v20 supports NVMe/TCP (NVMe over Fabrics, TCP transport). NVMe/TCP delivers high-performance, low-latency access to standalone NVMe SSD-based StorPool storage systems, using the standard NVMe/TCP initiators available in VMware vSphere, Linux-based hypervisors, container nodes, and bare-metal hosts.
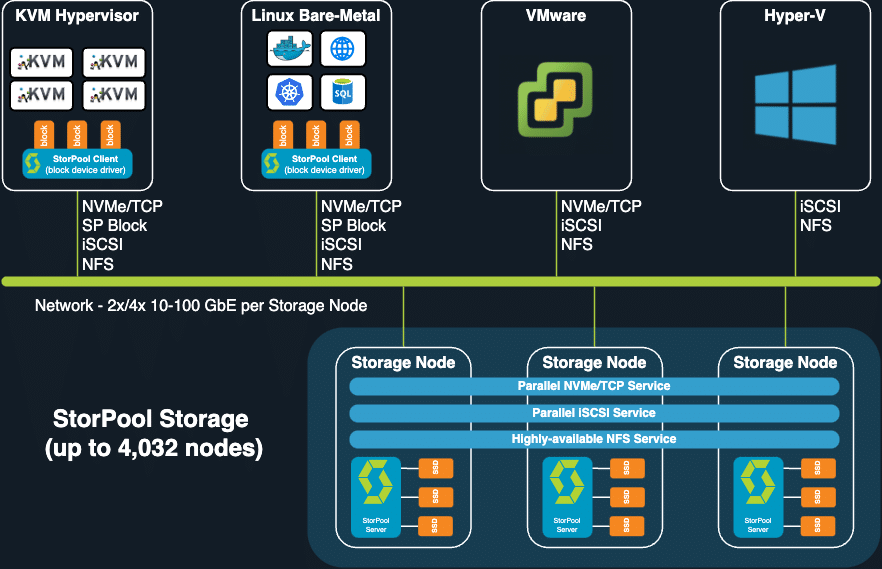 The StorPool NVMe/TCP implementation is software-only and does not require specialized hardware. Also, NVMe/TCP targets are highly available, so in the event of a node failure, StorPool fails over the targets on the failed storage node to a running node in the cluster.
The StorPool NVMe/TCP implementation is software-only and does not require specialized hardware. Also, NVMe/TCP targets are highly available, so in the event of a node failure, StorPool fails over the targets on the failed storage node to a running node in the cluster.
StorPool on AWS
StorPool on AWS promises low latency and high IOPS, delivered to single-instance workloads such as large transactional databases, SaaS applications, and heavily loaded e-commerce websites. With the new release, StorPool Storage can now be deployed on sets of three or more i3en.metal instances in AWS.
The solution delivers fast 1.3M+ balanced random read/write IOPS to EC2 r5n, and other compatible compute instances (m5n, c6i, r6i, etc.). StorPool frees customers from per-instance storage limitations and delivers this level of performance to any compatible instance type if network bandwidth is sufficient. StorPool utilizes less than a fifth of client CPU resources for storage operations, leaving more than 80 percent for user application(s) and database(s).
StorPool on AWS receives the same fully-managed service offering as on-premises customers. StorPool designs, deploys, tunes, monitors, and maintains each StorPool storage system on AWS.
NFS File Storage on StorPool
StorPool has introduced support for running NFS Servers inside StorPool storage clusters for specific use cases. NFS services delivered with StorPool are suitable for throughput-intensive file workloads shared among internal and external end-users with applications focused on video rendering and editing and heavily loaded web applications.
NFS services can also address moderate-load use cases such as configuration files, scripts, images, and email hosting and support cloud platform operations like secondary storage for Apache CloudStack, and NFS storage for OpenStack Glance. NFS file storage on StorPool is unsuitable for IOPS-intensive file workloads like virtual disks for virtual machines.
Deploying NFS Servers on StorPool storage nodes leverages the ability of StorPool Storage to run hyper-converged with other workloads and the low resource consumption of StorPool software components. Running in virtual machines backed by StorPool volumes and managed by the StorPool operations team, NFS Servers supports multiple file shares. The cumulative provisioned storage of all shares exposed from each NFS Server can be up to 50 TB. NFS service data is distributed across all nodes in the cluster, and StorPool maintains data and service integrity in case of hardware failures.
You can find more details on StorPool Storage v20 here.
Engage with StorageReview
Newsletter | YouTube | Podcast iTunes/Spotify | Instagram | Twitter | Facebook | RSS Feed