Today VMware Inc. released the latest version of their very popular hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) software, VMware vSAN 7. The latest version comes with several enhancements, with one of the major focuses being on simplifying infrastructure management through the reduction of tools required. vSAN 7 unifies block and file storage, reducing the need for third party solutions. And now vSAN supports containers through VMware Cloud Foundation.
Today VMware Inc. released the latest version of their very popular hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) software, VMware vSAN 7. The latest version comes with several enhancements, with one of the major focuses being on simplifying infrastructure management through the reduction of tools required. vSAN 7 unifies block and file storage, reducing the need for third party solutions. And now vSAN supports containers through VMware Cloud Foundation.
HCI has seen an increasing adoption over the last few years in businesses of various sizes in multiple industries. While it is widely popular, VMware sees many areas where HCI can be modernized to deliver results faster. The company looked at the three areas outlined above and rolled the improvements into VMware vSAN 7 to modernize their, and the industry’s leading, HCI solution.
VMware On Simplifying Infrastructure Management
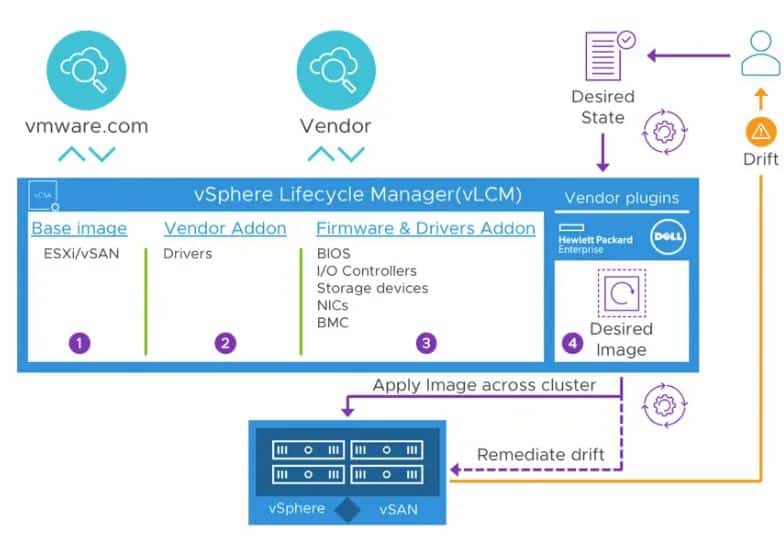
Admins may need several tools and specialized skills to maintain infrastructure and lifecycle management. Before vSAN 7 users needed vSphere Update Manager (VUM) for software and drivers and server vendor-provided utility for firmware updates. Now, users can leverage vSphere Lifecycle Manager (vLCM) a unified way to update software and firmware management that is native to vSphere. According to the company, vLCM is built off a desired-state model that provides lifecycle management for the hypervisor and the full stack of drivers and firmware for the servers powering the data center. In order to reduce the effort of monitoring compliance, vLCM can be used to apply an image, monitor the compliance, and remediate the cluster if there is a drift. vLCM should introduce a new level of simplicity to lifecycle management at scale.
Native File Service Improvements In VMware vSAN 7
On the same vein of simplification, vSAN 7 is introducing new native files services that again will reduce the need for third party solutions. The latest version now supports NFS v3 and v4.1 and therefore the use cases leveraging them. The enhanced file services can be provisioned and managed through the vCenter UI.
Native Support For Kubernetes
vSAN is looking to build off of cloud-native storage capabilities first introduced in vSAN 6.7 Update 3. Now, it supports native file services as persistent volumes for Kubernetes clusters. These new persistent volumes are stated to support the use of encryption and snapshots. Containerized workloads are now able to be deployed on vSAN datastores through vSpereh Add-on for Kubernetes (formerly Project Pacific).
Other enhancements in VMware vSAN 7 include:
- Immediate repair operation after a vSAN Witness Host is replaced – vSAN 7 enhances the replacement and resynchronizing logic of a vSAN Witness Host for Stretched Cluster and 2-node topologies. When a vSAN Witness Host appliance is impacted or needs to be replaced, it can be easily done using a “Replace Witness” button in vCenter. After the replacement, vSAN invokes an immediate repair operation, quickly reinstating the vSAN Witness Host to a consistent state. This enhancement helps mitigate a transient vulnerability to site-level protection by expediting vSAN Witness Host restoration.
- Stretched Cluster I/O redirect based on an imbalance of capacity across sites – A vSAN Stretched Cluster topology provides the resilience of VM and data in the event of a site outage. The agility of vSAN enables administrators to fine-tune configuration parameters for individual VMs with different protection levels or affinities. As a result, there could be an imbalance of available capacity at one site versus the other. vSAN 7 introduces new intelligence to minimize impact due to capacity strained conditions. If there is an imbalance, vSAN checks multiple parameters based on which it limits the IO to the capacity-constrained site and redirects active IO to the healthy site. These mitigation steps occur non-disruptively to the operation of the VM. This optimization is an excellent example of introducing more intelligence to vSAN to ensure predictable operation under a wide variety of conditions.
- Accurate VM level space reporting across vCenter UI for vSAN powered VMs – VMware vSAN 7 introduces a new level of consistency in VM level capacity reporting in vCenter for vSAN powered VMs. The initial design of vCenter accommodated for VM-level capacity reporting similar to how traditional storage operates. These improvements will help reconcile the reporting differences that may have been found between vSAN centric areas of vCenter and traditional VM reporting areas such as at the cluster and host view.
- Improved Memory reporting for ongoing optimization – A new time-based memory consumption metric is exposed in the UI and through API to provide deeper insight into resource consumption. With the robust architecture of vSAN, as the environment evolves (through scale-up or scale-out), time-based metrics help correlate the change in memory consumption with hardware and software configuration changes made in the cluster. This helps systematically assess the impact of configuration changes and continually optimize the design.
- Visibility of vSphere Replication objects in vSAN capacity views – VMware vSphere Replication is a hypervisor-based, asynchronous replication solution for vSphere VMs. It provides a simple and effective mechanism to protect and recover VMs. vSphere replication is included with vSphere Essentials Plus Kit and higher license editions. vSAN 7 introduces a significant improvement for environments using vSphere Replication. Administrators will now be able to easily identify vSphere Replication related object data at the VM object level, as well in the cluster-level capacity views. This awareness for vSphere Replication data goes a long way toward helping an administrator determine resources used for asynchronous replication needs.
- Support for larger capacity devices – vSAN demonstrates great agility to meet the evolving storage needs. vSAN 7 supports newer and larger density storage devices. vSAN’s support of higher density storage devices can bring inherent improvements to customer environments, such as improved deduplication and compression ratios and a lower cost per terabyte. The support for higher density drives presents a benefit unique to vSAN’s architecture: Incrementally adding or replacing existing disk groups with new disk groups consisting of much higher density drives without any additional licensing cost.
- Native support for planned and unplanned maintenance with NVMe hotplug – vSphere 7 introduces one feature that meets or exceeds the capability associated with older SAS and SATA devices: Hotplug support for NVMe devices in vSphere and vSAN. This introduces a new level of flexibility and serviceability to hosts populated with NVMe devices, improving uptime by simplifying maintenance tasks around adding, removing, and relocating storage devices in hosts. Modern hosts can potentially have dozens of NVMe devices, and the benefits of hotplug most help environments large and small.
- Removal of Eager Zero Thick (EZT) requirement for shared disk in vSAN – This release also introduces improved flexibility for VM applications using shared virtual disks, such as Oracle RAC. VMware vSAN 7 eliminates the prerequisite that shared virtual disks with multi-writer flags must use the eager zero thick format. This streamlined set of requirements improves simplicity and efficiency.
Engage with StorageReview
Newsletter | YouTube | Podcast iTunes/Spotify | Instagram | Twitter | Facebook | RSS Feed