This week, VMware went into more detail describing the new Distributed Resource Scheduling (DRS) algorithm, improved in the latest VMware vSphere, version 7. VMware now uses an advanced DRS logic and a new DRS UI in the vSphere Client. With these enhancements, VMware DRS focuses on a better solution to support modern workloads.
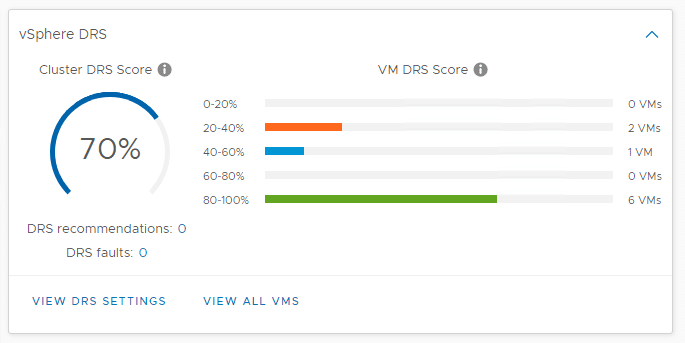
VMware released Distributed Resource Scheduling (DRS) in 2006, with an algorithm that, in the past, focused on the cluster state. The cluster was checking every 5 minutes ESXi host resources and then rebalancing, if needed, based on the resources consumed by the ESXi hosts. VMware says that the new DRS logic takes a very different approach. Now, it computes a VM DRS score on each host and moves the VM to the host that provides the highest. The VM DRS score is focused on the execution efficiency of a virtual machine and not in its health score.
Alongside the VM DRS score, VMware also shows the Cluster DRS Score in the UI, which is calculated using an aggregation of all the VM scores in the cluster. The vSphere cluster summary overview provides insights on what is happening from a DRS perspective. More information about the VM DRS score is available in the new UI, which is also one of the critical improvements of this new version.
VMware also added additional unique capabilities to the new DRS logic: Assignable Hardware and Scalable Shares.
- Assignable Hardware: When a VM configured with hardware accelerators is first powered on, it needs to be placed on an appropriate host in the cluster. The Assignable Hardware framework integrates with DRS to do that. PCIe devices with the new Dynamic DirectPath I/O or NVIDIA vGPU profiles are supported in vSphere 7 as part of this initial placement.
- Scalable Shares: Enabling Scalable Shares allows resource pools to have dynamic & relative entitlements. When using resource pools, one can regularly see a situation where resource pools, configured with higher share levels would not necessarily guarantee more resources for their workloads. Scalable shares aim to solve that issue. An improvement like this is also important for vSphere with Kubernetes, as the vSphere Pod Service needs this to ensure performance.




 Amazon
Amazon