Western Digital (WD) has announced the OptiNAND flash-enhanced drive architecture at the company’s HDD Reimagine event held today. This new technology optimizes and integrates HDDs with integrated NAND (iNAND). This new class of embedded flash drives, allows customers to meet the exponential growth in data creation, both today and in the future. Let’s be clear though, this is not a new play on hybrid hard drives – OptiNAND is much more nuanced.
Western Digital (WD) has announced the OptiNAND flash-enhanced drive architecture at the company’s HDD Reimagine event held today. This new technology optimizes and integrates HDDs with integrated NAND (iNAND). This new class of embedded flash drives, allows customers to meet the exponential growth in data creation, both today and in the future. Let’s be clear though, this is not a new play on hybrid hard drives – OptiNAND is much more nuanced.
What is WD OptiNAND?
In the most simple terms, WD OptiNAND is a platform that combines iNAND, controller and firmware as an SoC delivered on the PCB of a hard drive. The iNAND is a 64-layer dynamic flash (BICS3) package that manages the hard drive’s metadata. iNAND technology can enable both SLC for write-heavy operations and TLC for read-heavy operations in the same device. WD says these flash-enhanced drives will offer improved capacity, performance, and reliability. This is why hyperscalers have great interest in WD’s new tech for their cold data and archive tiers.
It’s also critical to point at that these are very much not hybrid hard drives. The hybrid concept paired flash with hard drives to attempt to get to a place where end-users and storage systems could have the performance benefits of flash and the capacity and cost per terabyte benefits of a hard drive. These drives were a complete mess though. They were expensive, performed poorly, and had very limited operating system support. As such, understanding that OptiNAND is not a hybrid hard drive technology is important. All data is read from and written to the HDD platters.
How Does WD OptiNAND Work?
OptiNAND requires a hard drive platform that supports its integration. So this will be a going forward type of integration and can work on SMR or CMR drives. OptiNAND is initially being delivered as a 64GB payload on WD’s 20TB class HDDs that are currently sampling with cloud providers and other large customers.
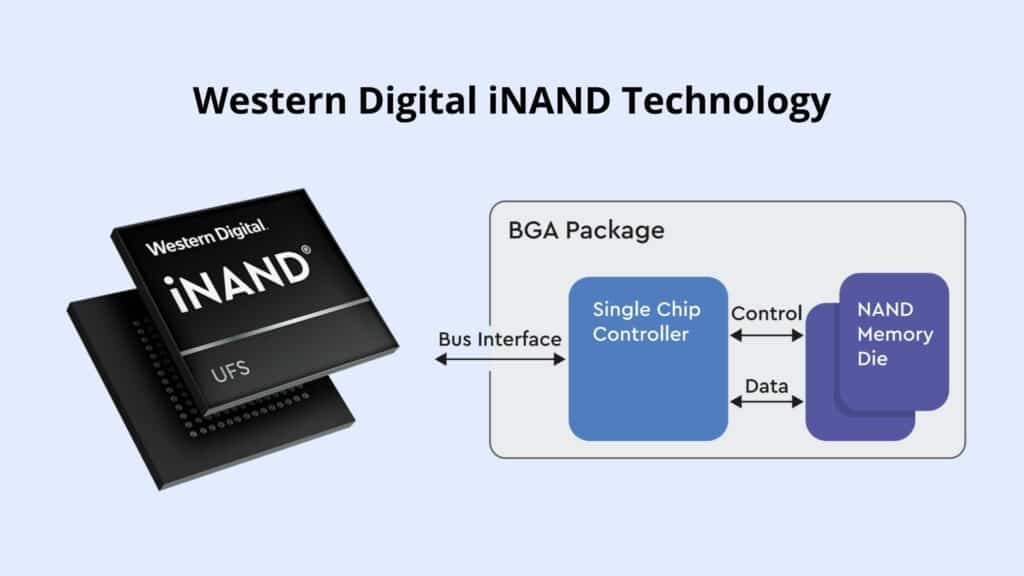
If you know hard drive tech, then the immediate response to this may be something like, “Aren’t HDDs already using DRAM for metadata?” Well yes, but in relation to having 64GB of iNAND, an 18TB HDD’s DRAM is only 512MB of cache. Of course, DRAM is also much more expensive than NAND, so scaling into larger capacities becomes unpractical.
Flash is also interesting from a persistence standpoint. DRAM gets flushed on power loss, but NAND is non-volatile and can continue to keep metadata information without having to re-hydrate after a boot sequence, be removed from the system for some reason, or any other event where power drops. WD’s figures are that OptiNAND drives can secure more than 100MB of write cache data in the event of an unplanned power loss, a 50X improvement over standard drives that can flush about 2MB.
There’s a performance angle here as well. Hard drive latency is improved with optimizations to drive firmware focused on requiring fewer adjacent track interference (ATI) refreshes and reducing the need for write cache flushes in write cache-enabled mode. Also, retrieving metadata from the drive interferes with host operations and performance. OptiNAND offers a more efficient data flow. The platform will also offer WD engineers more flexibility in the future, to develop entirely new functionality that lets the drives operate more quickly.
In addition to being more efficient, the metadata no longer needs to be stored on the hard drive media at all, freeing up a little more usable space for the end-user. There are other portions of data related to drive telemetry that also no longer need to reside on the HDD itself, thanks to the iNAND capacity. Some of the intelligence built into the platform also nets efficiency gains, which leads to more tracks per inch (TPI) and increased areal density.
Where Are We Today?
OptiNAND is real and shipping to big customers that have a heavy data need. While flash gets all the excitement, see our Ruler SSD podcast, it’s true that hard drives make up the lion’s share of bit storage in a data center. According to IDC, HDDs will represent 82% of the capacity sold to the enterprise market in 2025.

Drives using the new architecture will leverage technologies such as triple-stage actuator (TSA) and HelioSeal technology and will offer 2.2TB per platter to extend capacity gains on PMR technology. The currently sampling 20TB SKU is a 9 platter drive, which gets us close enough to that 20TB classification. This is just the start though, but the time this technology gets to general availability, it’s likely to show up in a 22TB or 24TB iteration.
It’s worth noting that OptiNAND isn’t exactly ready to revolutionize HDD capacity or performance today. This is an incremental step that helps WD milk out a little more from their hard drives. It is a platform however that gives WD the potential to extract more over time. In large-scale data centers, even a little bump in capacity, performance, and reliability make a material difference.
Engage with StorageReview
Newsletter | YouTube | LinkedIn | Instagram | Twitter | Facebook | TikTok | RSS Feed