It’s no secret Cloud computing has revolutionized the way we store, process, and access data. The cloud has enabled businesses and individuals to tap into vast computing resources on demand. However, the current landscape is dominated by a few centralized providers, raising concerns about monopolistic practices, data sovereignty, and vendor lock-in. Enter Akash Network, a pioneering decentralized cloud computing platform built on blockchain technology, poised to disrupt the status quo and democratize the cloud computing ecosystem.
What is Akash Network?
Akash Network is a decentralized peer-to-peer marketplace for cloud computing resources built on the Cosmos blockchain ecosystem. It represents a paradigm shift in the cloud computing industry by providing a more open, transparent, and decentralized alternative to traditional centralized cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
At the heart of Akash Network lies the use of blockchain technology and a native cryptocurrency called AKT to facilitate secure and transparent transactions between providers (those who contribute computing resources) and tenants (those who rent computing resources). The platform is underpinned by decentralization, transparency, and security principles, enabling a more efficient, cost-effective, and democratized way of accessing and utilizing cloud computing resources.
Akash Tokens
The Akash Network’s decentralized architecture eliminates the need for a centralized authority or intermediary. This empowers individuals and organizations to participate in the network as providers and tenants. The democratization of cloud computing resources has the potential to disrupt existing centralized models and promote greater competition, innovation, and accessibility.
How Does Akash Network Work?
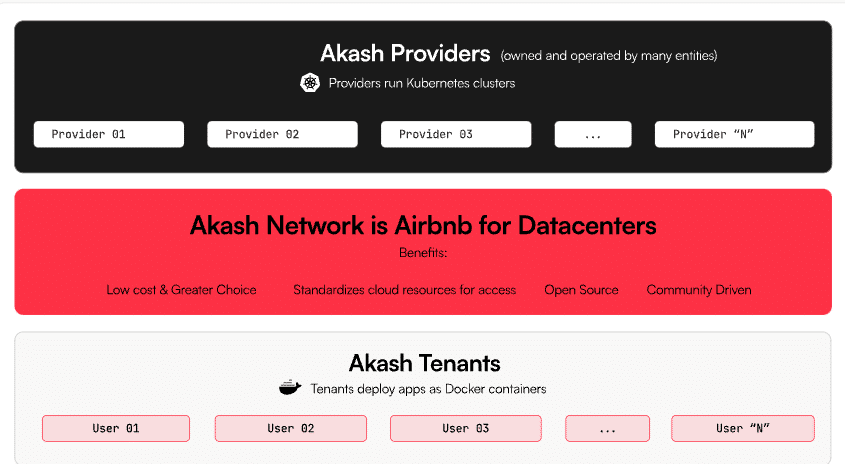
Akash Network operates as a two-sided marketplace, seamlessly connecting providers with tenants. The platform revolves around Deployments, which fully describe the resources a tenant requests from the network. Deployments contain Groups, which are resources meant to be leased together from a single provider.
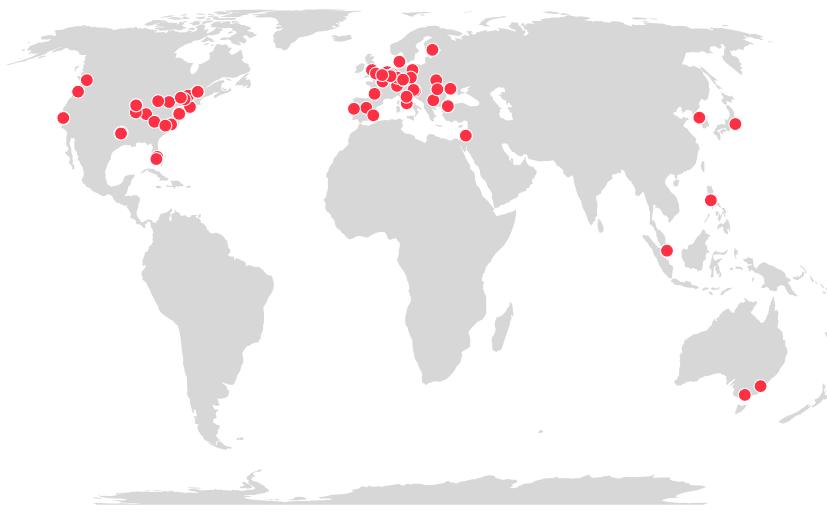
Akash Global Nodes
The process of deploying applications or workloads on Akash Network typically involves the following steps:
- Providers list their available computing resources on the network, specifying the hardware, pricing, and other relevant details.
- Tenants define their application or workload requirements in a deployment. Requirements include resources such as the desired GPU, CPU, RAM, storage, network bandwidth, and other specific configurations.
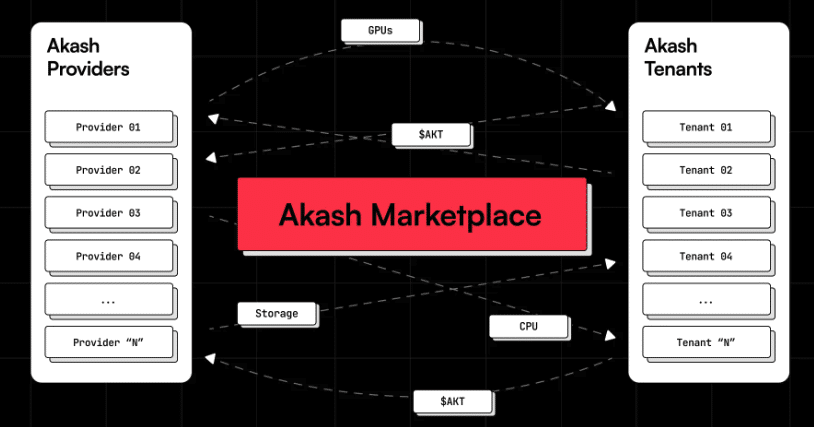
- The Akash Network employs a decentralized matching algorithm corresponding to the tenants’ requirements. The result delivers suitable providers’ offerings, facilitating resource leasing through a secure and transparent bidding process.
- Once a match is made, the Akash Network uses a reverse auction model. Tenants set the price and terms of their deployment, and providers bid on the deployments. The bidding process involves providers placing a refundable bid deposit.
- After the bidding period, a winning bid is chosen for the order, and a lease is created between the tenant and the winning provider.
- The tenant then submits a manifest to the provider, instructing how to execute the workloads.
- The provider executes the workloads per the manifest, allowing the tenant’s application to run on the leased resources.
Deployers and Bidders
As noted, Akash operates a unique “Reverse Auction” system where network deployers specify the price they are willing to pay for the resources they need, and providers compete to fulfill the request. This approach consistently leads to lower costs and more options and allows for self-sovereign control. Akash is an open-source, community-driven platform powered by an L1 blockchain and the AKT utility token.
At present, Akash is collaborating with approximately 70 providers globally. Provider details can be found on this provider link. Deployers can view which bidders and providers they could potentially work with in specific geographies. Any provider can bid on a deployment, and the decision of whether a provider appears in the bid list is governed by the pricing script associated with the provider. Each provider determines how they want to price the resources they offer and sets these prices in the pricing script.
While Akash does not track the number of bid requests, it does monitor active leases, which are leases with active applications and workloads running on the network. Currently, the number of active leases is close to 800. Details for active leases can be found here.
Akash Network leverages technologies like containerization and blockchain to ensure a seamless and secure deployment and execution of applications and workloads. Containerization technologies like Docker allow for easy packaging, deployment, and management of applications, providing portability and scalability across different providers’ computing environments. This empowers tenants to easily move their workloads between different providers, avoiding vendor lock-in and enabling a truly decentralized and flexible cloud computing experience.
Payments and Escrow Accounts
Leases on Akash Network are paid from the tenant (deployment owner) to the provider through a deposit and withdrawal mechanism using the AKT cryptocurrency. Tenants must maintain a sufficient deposit balance to keep their leases active since providers can withdraw owed funds from this deposit. Providers can close the lease if the deposit reaches zero, effectively terminating the tenant’s workload.
To facilitate efficient and secure payments, Akash utilizes escrow accounts, a mechanism that allows time-based payments from one account to another without requiring every block of micropayments. Escrow accounts also hold bid deposits, which are refunded to providers when their bids are closed.
The use of escrow accounts addresses two primary challenges in the Akash Network:
- Akash leases are priced in blocks, meaning the tenant’s payment to the provider is due every new block. Performance and security considerations prohibit the naive approach of transferring tokens on every block.
- Bidding on an order should not be free, as it would raise performance and security concerns. Akash requires a deposit for every bid, which is returned to the bidder when the bid is closed.
By leveraging escrow accounts and the AKT cryptocurrency, Akash Network enables a secure, transparent, and auditable payment system for cloud computing resources, incentivizing providers to contribute their resources to the network while ensuring fair compensation.
Audited Attributes and Selective Deployment
One of Akash Network’s unique features is the ability for tenants to select which providers can run their applications. This is achieved through Audited Attributes, which allow users deploying applications to assign specific attributes to providers via on-chain transactions.
Audited Attributes enable tenants to set criteria such as geographic location, hardware specifications, or compliance requirements, ensuring their applications are deployed on providers that meet their specific needs. This level of control and transparency is particularly valuable for industries with stringent regulatory requirements or data sovereignty concerns.
The Power of Decentralization
The decentralized nature of Akash Network offers several advantages over traditional centralized cloud computing platforms:
- Censorship Resistance: With no central authority controlling the network, Akash Network is resistant to censorship, ensuring that applications and workloads can run without interference.
- Resilience and Fault Tolerance: The distributed architecture of Akash Network eliminates single points of failure, making it more resilient to outages or disruptions.
- Data Sovereignty: Tenants can choose to deploy their applications on providers that meet their data sovereignty requirements, ensuring compliance with local regulations and maintaining control over their data.
- Cost Efficiency: By leveraging underutilized computing resources from a decentralized pool of providers, Akash Network can offer more cost-effective solutions than centralized cloud providers.
Use Cases and Applications
The decentralized and flexible nature of Akash Network opens up a wide range of potential use cases across various industries. Some notable applications include:
- Decentralized Web Services: Developers can deploy and host decentralized web applications, APIs, and microservices on the Akash Network, ensuring censorship resistance and resilience.
- Blockchain Infrastructure: Akash Network can provide a secure and decentralized infrastructure for running blockchain nodes, enabling greater decentralization and fault tolerance for blockchain networks.
- Edge Computing: The distributed nature of Akash Network makes it well-suited for deploying edge computing applications, bringing computing resources closer to the data source for improved performance and reduced latency.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC): Akash Network can be leveraged to run computationally intensive workloads, such as scientific simulations, machine learning models, and data analysis pipelines, by aggregating computing resources from multiple providers.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Developers can build decentralized and resilient CDNs for efficient content delivery by leveraging Akash Network’s global distribution of providers.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While Akash Network presents a compelling vision for decentralized cloud computing, it also faces several challenges that must be addressed for widespread adoption:
- Adoption and Network Effects: As a relatively new platform, Akash Network needs to attract a critical mass of providers and tenants to build a robust and liquid marketplace for computing resources.
- Regulatory Landscape: Akash Network’s decentralized nature may raise regulatory concerns related to data privacy, security, and compliance, particularly in industries with stringent regulations.
- Performance and Scalability: As the network grows, Akash Network must ensure its underlying infrastructure and protocols can handle increasing demand and workloads while maintaining performance and efficiency.
- Interoperability: Seamless integration with existing cloud computing ecosystems and tools will be crucial for facilitating the migration of workloads to the Akash Network.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of Akash Network’s decentralized cloud computing model are significant. The need for open, transparent, and decentralized alternatives will likely grow as the world increasingly relies on cloud computing resources. Akash Network’s innovative approach, powered by blockchain technology and a native cryptocurrency, positions it as a trailblazer in this emerging space.
Back to the Future
Looking to the future, the success of Akash Network will depend on its ability to build a vibrant ecosystem of providers and tenants, foster collaboration with existing cloud computing players, and address the challenges of scalability, regulation, and interoperability.
Provider Infrastructure Limits Flexibility
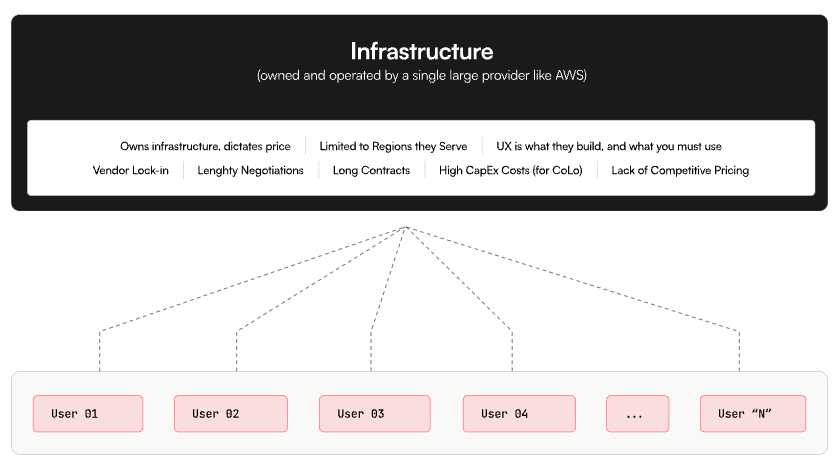
As the world becomes increasingly reliant on cloud computing resources, the need for open, transparent, and decentralized alternatives is likely to grow. Akash Network’s innovative approach, powered by blockchain technology and a native cryptocurrency, positions it as a trailblazer in this emerging space.
With its focus on decentralization, transparency, and democratization of cloud computing resources, Akash Network has the potential to reshape the industry’s landscape. By empowering individuals and organizations to contribute and access computing resources securely and trustless, Akash Network could unlock new levels of innovation, efficiency, and accessibility in cloud computing.
Akash Decentralized Infrastructure
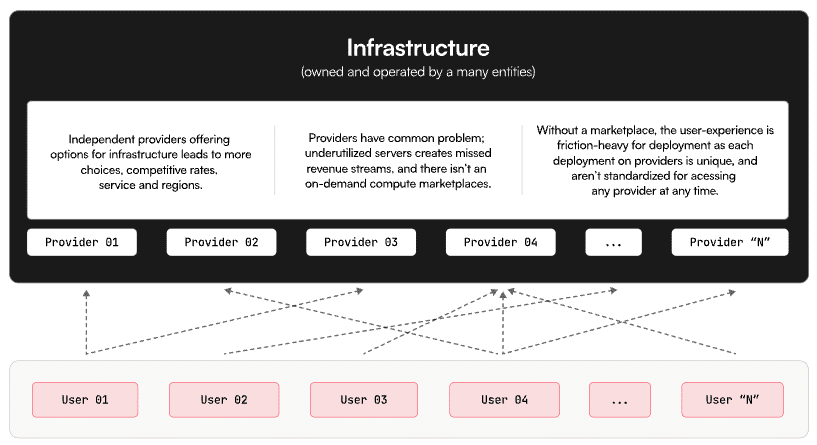
Moreover, the platform’s embrace of cutting-edge technologies like containerization and blockchain ensures that it remains at the forefront of technological advancements, adapting to evolving trends and requirements in the ever-changing digital landscape.
Conclusion
As Akash Network’s adoption grows, it may inspire and pave the way for other decentralized cloud computing solutions, fostering a more diverse and competitive ecosystem that benefits providers and tenants. This increased competition could drive innovation, lower costs, and promote greater consumer choice, ultimately benefiting the broader technology industry and society.
While the journey towards a genuinely decentralized cloud computing future may be challenging, Akash Network’s pioneering efforts represent a significant step in that direction. Akash Network is poised to disrupt the status quo and usher in an era of transparent, resilient, and democratized cloud computing services by harnessing the power of blockchain technology and decentralized architectures.


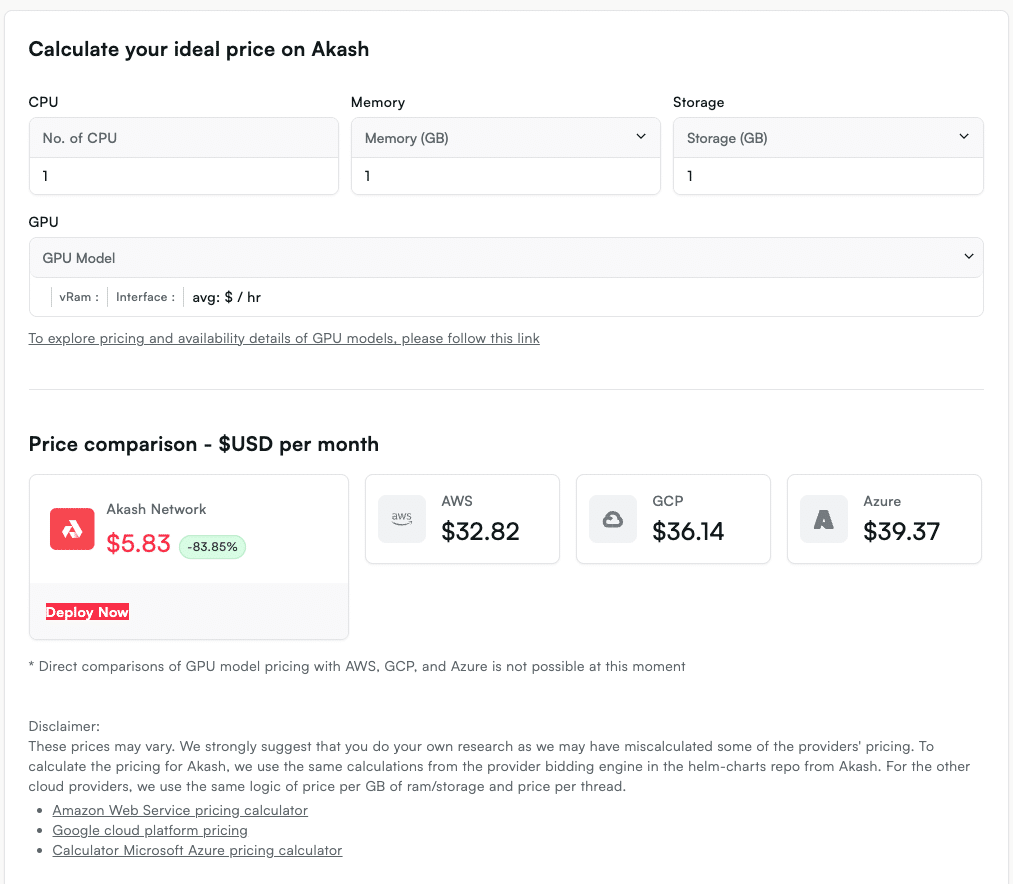


 Amazon
Amazon