AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT Review: A 1440p powerhouse with solid gaming chops, but does it hold up against NVIDIA in AI and efficiency?
The AMD Radeon RX 9070 series edition cards launch today. AMD sent the ASUS Prime RX 9070 and RX 9070 XT variants of the cards to the lab for testing. These GPUs, built on the company’s cutting-edge RDNA 4 architecture and TSMC’s advanced 4nm process technology, target the sweet spot of price-to-performance for gamers seeking high-refresh 1440p gaming and entry-level 4K experiences. The 9070 series introduces impressive technological advancements while maintaining reasonable power consumption figures relative to their performance class.
Positioned in the upper mid-range tier, these GPUs blend gaming performance with AI acceleration, catering to gamers and creators. With 16GB of VRAM, enhanced ray tracing capabilities, and AMD’s latest AI-powered technologies like FidelityFX Super Resolution 4 and HYPR-RX, the RX 9070 series aims to deliver high performance while maintaining power efficiency.
The RX 9070 XT is the higher-end model, offering increased clock speeds and more graphics cores for demanding gaming workloads. ASUS’s PRIME design brings robust cooling and power delivery, ensuring consistent performance under heavy loads. Both GPUs are future-ready, with PCIe gen 5, DisplayPort 2.1 support, and AI accelerators for next-gen applications, making them an ideal choice for immersive gaming experiences.
AMD Radeon RX 9070 & RX 9070 XT Specifications
| Radeon RX 9070 XT vs. Radeon RX 9070 Specifications | ||
| Radeon RX 9070 XT | Radeon RX 9070 | |
| GPU Name | Navi 48 | Navi 48 |
| GPU Variant | Navi 48 XT | Navi 48 XL |
| Architecture | RDNA 4.0 | RDNA 4.0 |
| Foundry | TSMC | TSMC |
| Process Size | 4 nm | 4 nm |
| Transistors | 53,900 million | 53,900 million |
| Density | 151.0M / mm² | 151.0M / mm² |
| Die Size | 357 mm² | 357 mm² |
| Base Clock | 2400 MHz | 2070 MHz |
| Boost Clock | 2970 MHz | 2520 MHz |
| Memory Size | 16 GB | 16 GB |
| Memory Type | GDDR6 | GDDR6 |
| Shading Units | 4096 | 3584 |
| AI Accelerators | 128 | 112 |
| TMUs | 256 | 256 |
| ROPs | 128 | 128 |
| Compute Units | 64 | 56 |
| RT Cores | 64 | 56 |
| AMD Infinity Cache | 64 MB (3rd Gen) | 64 MB (3rd Gen) |
| Memory Bus | 256 bit | 256 bit |
| Bandwidth | 640 GB/s | 640 GB/s |
| Peak Pixel Fill-Rate | 190.1 GPixel/s | 161.3 GPixel/s |
| Peak Texture Fill-Rate | 730.3 GTexel/s | 564.5 GTexel/s |
| Peak Single Precision Throughput | 48.7 TFLOPS | 36.1 TFLOPS |
| Peak Half Precision Throughput | 97.3 TFLOPS | 72.3 TFLOPS |
| Peak INT8 AI TOPS Throughput | 779 TOPS | 578 TOPS |
| Peak INT4 AI TOPS Throughput | 1557 TOPS | 1156 TOPS |
| TDP | 304 W | 220 W |
| Suggested PSU | 750 W | 650 W |
| Outputs | 1x HDMI 2.1b, 3x DisplayPort 2.1a | 1x HDMI 2.1b, 3x DisplayPort 2.1a |
| PCIe Interface | PCIe 5.0 x 16 | PCIe 5.0 x 16 |
| Power Connectors | 3x 8-pin | 2x 8-pin |
| Launch Price | $599 USD | $549 USD |
What’s New with RDNA 4
AMD’s RDNA 4 architecture represents a significant evolution from previous generations, bringing substantial improvements across multiple domains. At the heart of these new GPUs lies the redesigned RDNA4 Compute Units, which deliver approximately 40% more performance per compute unit than RDNA 3. This efficiency gain comes from improved memory subsystems and more optimized data flow pathways throughout the GPU.
Ray tracing performance sees a dramatic uplift with AMD’s third-generation RT accelerators. Adding a second ray intersection engine effectively doubles the throughput for ray-box and ray-triangle testing operations, critical bottlenecks in previous generations. New dedicated ray transformation hardware further accelerates these workloads, while support for Oriented Bounding Boxes enables more efficient ray traversal with lower memory overhead.
Perhaps the most significant advancement comes in AI acceleration capabilities. The RX 9070 series features second-generation AI accelerators that deliver approximately 1,100 AI TOPS for the 9070 and over 1,500 AI TOPS for the 9070 XT when using INT4 calculations with sparsity. These dedicated AI units feature expanded math pipelines and support emerging AI data formats.
The new FSR4 technology is AMD’s answer to NVIDIA’s DLSS upscaling, leveraging the enhanced AI accelerators to deliver what AMD claims can be better-than-native image quality. Using machine learning-based upscaling algorithms specifically optimized for RDNA 4 hardware, FSR4 can increase performance while maintaining excellent image fidelity. AMD has designed the system to be backward compatible with the FSR 3.1 API, allowing developers to implement it easily into existing titles.
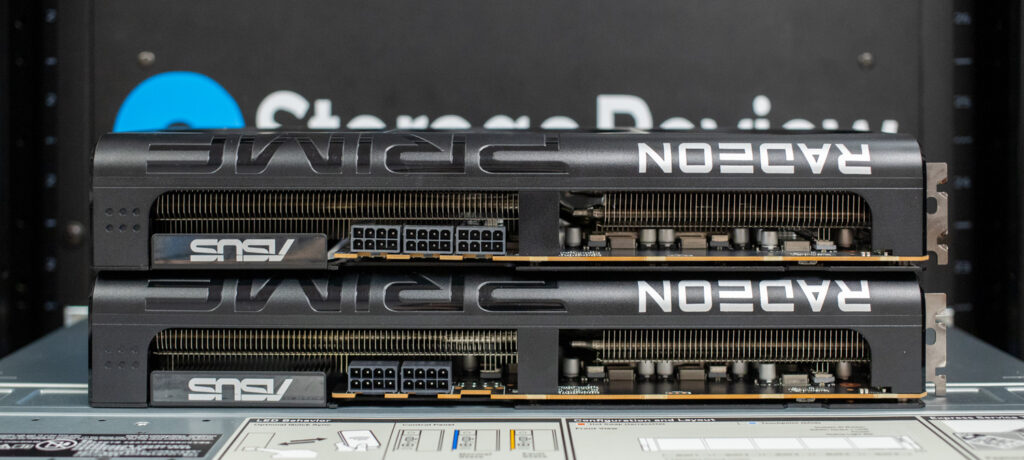
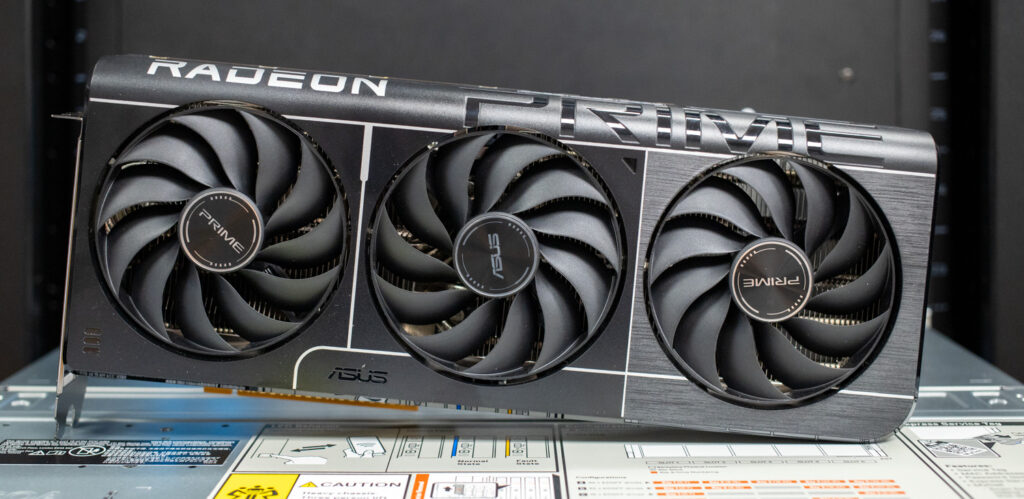
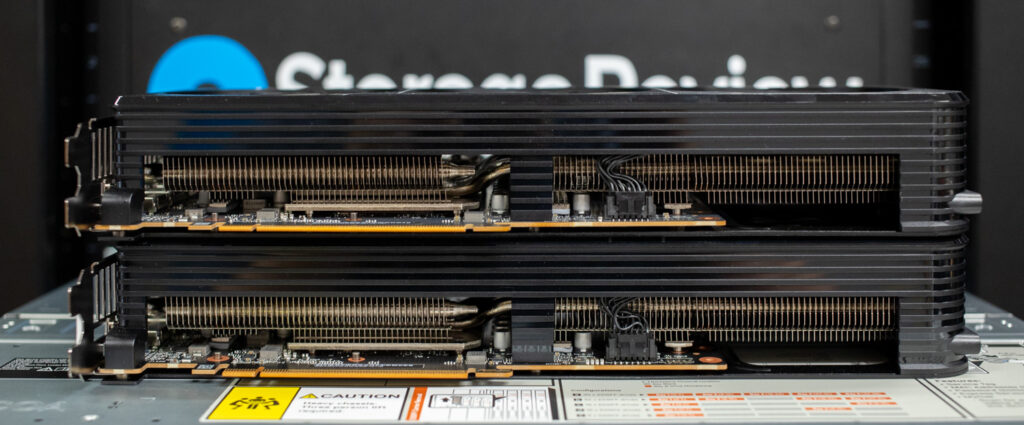
Build and Design ASUS Prime RX 9070 and RX 9070 XT
The build and design of the new ASUS Prime Radeon 9070 and 9070 XT cards closely resemble the ASUS Prime RTX 5070 Ti we previously reviewed. They differ on the power side — neither card requires a special 12-pin power cable, with the 9070 using standard 8-pin power with 2x 8-pin connectors and the 9070 XT using 3x 8-pin connectors. Both cards feature the 2.5 PCIe slot design height requirement.
For cooling, ASUS has implemented a triple Axial-tech fan design with dual ball bearings on the Radeon 9070 and 9070 XT to improve durability and maintain consistent airflow. The fans are paired with a large heatsink and heat pipes across the entire card, while a vented backplate and side cutouts help maximize heat dissipation. All three fans remain idle when GPU temperatures fall below 50°C, enabling silent operation during light workloads or less demanding gaming sessions. The fans automatically resume operation once temperatures surpass 55°C.
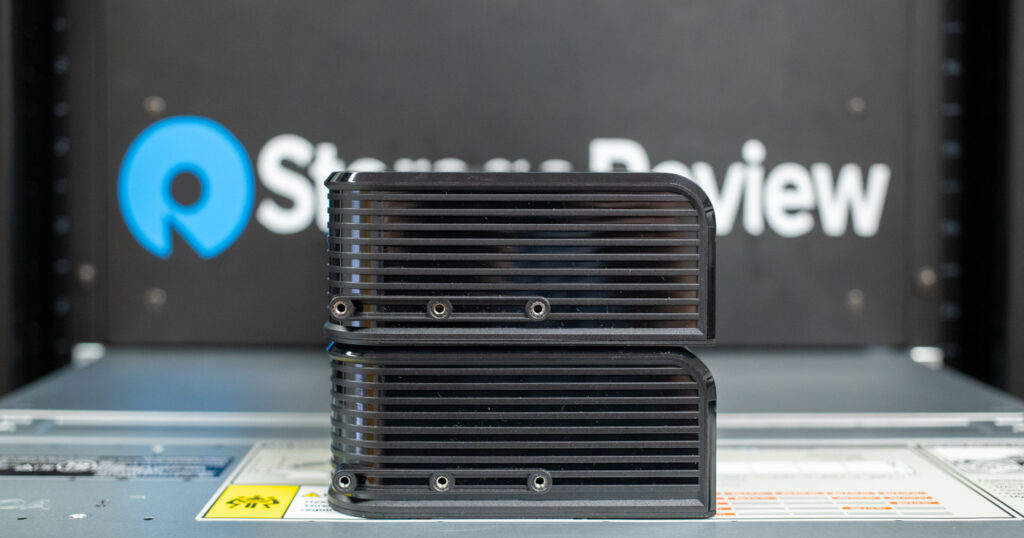
Looking at the bottom slot side of the cards, both models share an identical design for cooling, featuring the same heatsink, PCB layout, and shroud with venting cutouts to aid airflow.
On the end of both cards is an identical mounting point for an optional card stiffener to prevent card sag while installed in a case and provide added stability during transport.
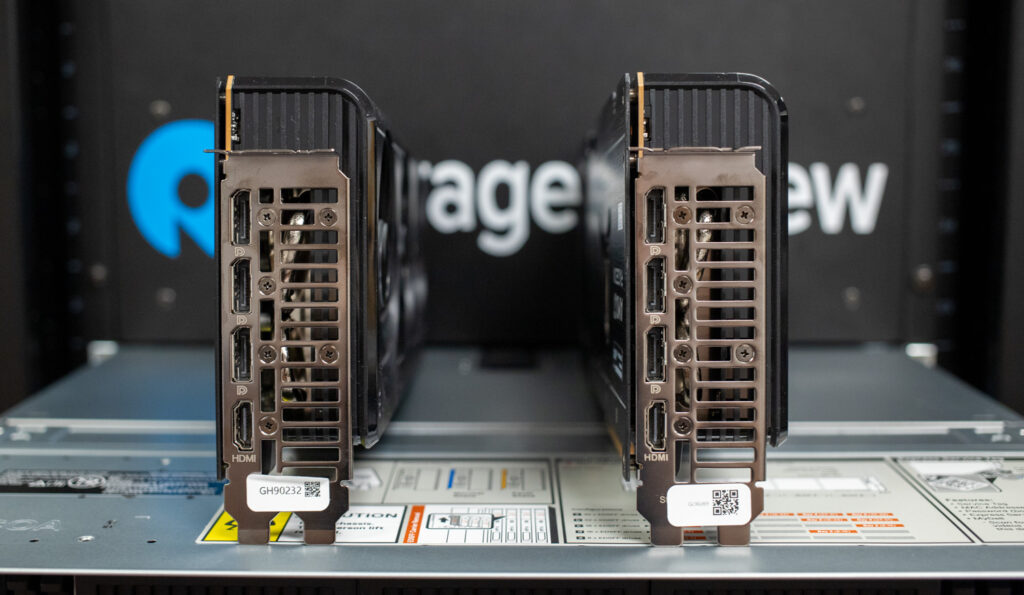
On the business end of both cards, we have display connectivity options, each featuring 1x HDMI 2.1b and 3x DisplayPort 2.1a ports. ASUS has also incorporated a 304 stainless-steel PCIe bracket design to ensure longevity and durability.
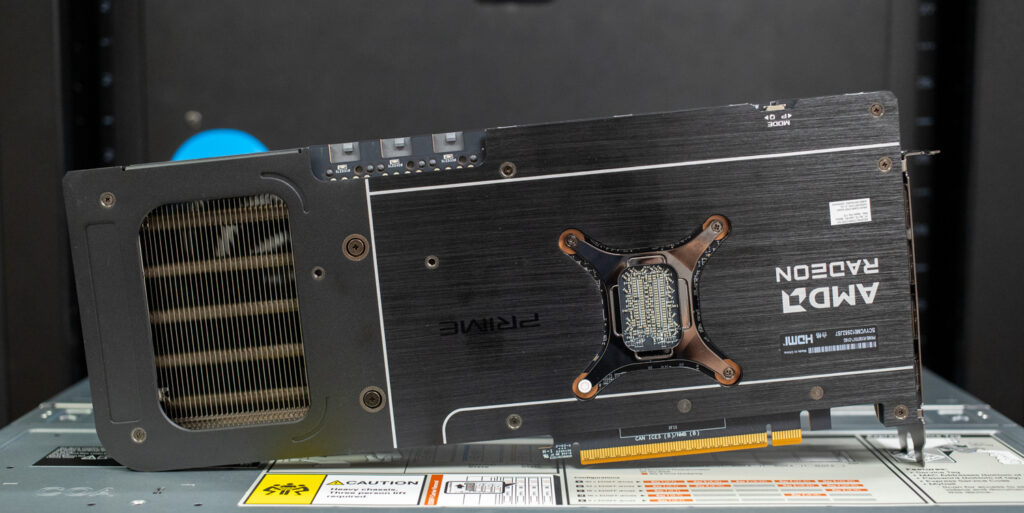
Other notable features of both cards include a switchable BIOS, controlled via a switch on the card, which toggles between “P” (performance) mode and “Q” (quiet) mode. Both units also incorporate a phase-change thermal pad designed to improve cooling performance and enhance the longevity of the thermal material in contact with the chip. Lastly, ASUS provides GPU Tweak III software for fine-tuning the card’s performance to meet specific requirements.
Benchmarking: ASUS Prime RX 9070 vs RX 9070 XT
To test the new Radeon cards from ASUS, we used our high-performance AMD Threadripper platform, featuring a 64-core CPU and a custom water cooling loop. This setup ensures the GPU operates at full capacity without CPU bottlenecks. For comparison, the ASUS Prime Radeon RX 9070 and RX 9070 XT were tested on this configuration, alongside the NVIDIA Founders RTX 4070 and the ASUS Prime NVIDIA RTX 5070 Ti.
Below is the complete system configuration.
StorageReview AMD Threadripper Test Platform
- Motherboard: ASUS Pro WS TRX50-SAGE WIFI
- CPU: AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X 64-Core
- RAM: 128GB DDR5 4800MT/s
- Storage: 2TB Samsung 980 Pro
- OS: Windows 11 Pro for Workstations
- Driver: AMD Adrenalin 25.3.1
UL Procyon: AI Text Generation
The Procyon AI Text Generation Benchmark simplifies AI LLM performance testing by offering a compact and consistent evaluation method. It allows for repeated testing across multiple LLM models while minimizing the complexity of large model sizes and variable factors. Developed with AI hardware leaders, it optimizes the use of local AI accelerators for more reliable and efficient performance assessments. The results measured below were tested using TensorRT on the NVIDIA models and ONNX for the AMD models.
| UL Procyon: AI Text Generation | AMD Radeon RX 9070 | AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 | ASUS PRIME NVIDIA RTX 5070 Ti | NVIDIA RTX 5070 |
| Phi Overall Score | 1,933 | 2,080 | 3,191 | 4,179 | 3,453 |
| Phi Output Time To First Token | 0.954 s | 0.855 s | 0.356 s | 0.290 s | 0.323 s |
| Phi Output Tokens Per Second | 139.187 tokens/s | 144.471 tokens/s | 141.575 tokens/s | 192.487 tokens/s | 150.435 tokens/s |
| Phi Overall Duration | 26.989 s | 25.587 s | 21.743 s | 15.771 s | 20.302 s |
| Mistral Overall Score | 2,040 | 2.231 s | 2,987 | 4,412 | 3,562 |
| Mistral Output Time To First Token | 1.109 s | 0.946 s | 0.508 s | 0.374s | 0.433 s |
| Mistral Output Tokens Per Second | 101.300 tokens/s | 103.348 tokens/s | 99.590 tokens/s | 160.167 tokens/s | 120.507 tokens/s |
| Mistral Overall Duration | 34.960 s | 33.350 s | 30.651 s | 19.480 s | 25.496 s |
| Llama3 Overall Score | 1,904 | 2,070 | 2,810 | 4,187 | 3,125 |
| Llama3 Output Time To First Token | 0.981 s | 0.845 s | 0.423 | 0.306 s | 0.379 s |
| Llama3 Output Tokens Per Second | 87.594 tokens/s | 89.102 tokens/s | 82.130 tokens/s | 131.583 tokens/s | 100.388 tokens/s |
| Llama3 Overall Duration | 38.273 s | 36.742 s | 36.147 s | 22.786 s | 29.720 s |
| Llama2 Overall Score | 2,047 | 2,298 | 2,658 | 4,284 | 3,125 |
| Llama2 Output Time To First Token | 1.926 s | 1.565 s | 0.947 s | 0.560 s | 0.785 s |
| Llama2 Output Tokens Per Second | 59.673 tokens/s | 61.127 tokens/s | 49.487 tokens/s | 75.905 tokens/s | 56.647 tokens/s |
| Llama2 Overall Duration | 59.100 s | 55.520 s | 61.300 s | 39.545 s | 53.234 s |
In the UL Procyon AI Text Generation test, the ASUS Prime NVIDIA RTX 5070 Ti leads with the highest overall scores across all models. It achieves 4,179 in Phi, 4,412 in Mistral, 4,187 in Llama3, and 4,284 in Llama2. The AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT follows closely, with scores of 2,080 in Phi, 2,231 in Mistral, 2,070 in Llama3, and 2,298 in Llama2. The NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 is next, scoring 3,191 in Phi, 2,987 in Mistral, 2,810 in Llama3, and 2,658 in Llama2. The AMD Radeon RX 9070 trails, with the lowest overall scores in all categories, achieving 1,933 in Phi, 2,040 in Mistral, 1,904 in Llama3, and 2,047 in Llama2.
UL Procyon: AI Image Generation
The Procyon AI Image Generation Benchmark consistently and accurately measures AI inference performance across various hardware, from low-power NPUs to high-end GPUs. It includes three tests: Stable Diffusion XL (FP16) for high-end GPUs, Stable Diffusion 1.5 (FP16) for moderately powerful GPUs, and Stable Diffusion 1.5 (INT8) for low-power devices. The benchmark uses the optimal inference engine for each system, ensuring fair and comparable results.
| UL Procyon: AI Image Generation (overall score: higher is better) | AMD Radeon RX 9070 | AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 | ASUS PRIME NVIDIA RTX 5070 Ti | NVIDIA RTX 5070 |
| Stable Diffusion 1.5 (FP16) — Overall Score | 2,280 | 2,598 | 2,400 | 3,755 | 2,937 |
| Stable Diffusion 1.5 (FP16) — Overall Time | 43.858 s | 38.481 s | 41.661s | 26.625 s | 34.038 s |
| Stable Diffusion 1.5 (FP16) — Image Generation Speed | 2.741 s/image | 2.405 s/image | 2.604 s/image | 1.664 s/image | 2.127 s/image |
| Stable Diffusion 1.5 (INT8) — Overall Score | N/A | N/A | 31,048 | 46,744 | 36,320 |
| Stable Diffusion 1.5 (INT8) — Overall Time | N/A | N/A | 8.052 s | 5.348 s | 6.883 s |
| Stable Diffusion 1.5 (INT8) — Image Generation Speed | N/A | N/A | 1.006 s/image | 0.669 s/image | 0.860 s/image |
| Stable Diffusion XL (FP16) — Overall Score | 1,805 | 2,010 | 1,940 | 3,352 | 2,473 |
| Stable Diffusion XL (FP16) — Overall Time | 332.400 s | 298.499 s | 309.269 s | 178.946 s | 242.606s |
| Stable Diffusion XL (FP16) — Image Generation Speed | 20.775 s/image | 18.656 s/image | 19.329 s/image | 11.184 s/image | 15.163 s/image |
In the AI Image Generation test, focusing on Stable Diffusion 1.5 (FP16) and Stable Diffusion XL (FP16), the AMD Radeon RX 9070 series performed solidly but was outpaced by NVIDIA. The RX 9070 scored 2,280, the RX 9070 XT reached 2,598, the NVIDIA RTX 4070 scored 2,400, and the ASUS Prime NVIDIA RTX 5070 Ti topped the chart with 3,755. The RX 9070 XT slightly outperformed the 4070 in the Stable Diffusion XL (FP16) test with a score of 2,010, though it still trailed behind the 5070 Ti’s 3,352. The Radeon cards also had slower image generation times than the 5070 Ti.
Luxmark
Luxmark is a GPU benchmark that uses LuxRender, an open-source ray tracing renderer, to evaluate a system’s performance in handling highly detailed 3D scenes. This benchmark is pertinent for assessing the graphical rendering prowess of servers and workstations, especially for visual effects and architectural visualization applications, where accurate light simulation is critical.
| Luxmark (higher is better) | AMD Radeon RX 9070 | AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 | ASUS PRIME NVIDIA RTX 5070 Ti | NVIDIA RTX 5070 |
| Food Score | 8,233 | 8,610 | 7,535 | 12,073 | 9,061 |
| Hall Score | 16,566 | 16,758 | 20,003 | 28,635 | 22,062 |
In the Luxmark tests, the ASUS Prime NVIDIA RTX 5070 Ti leads in both categories. It scores 12,073 in the Food test and 28,635 in the Hall test, showing a strong performance across the board. The AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT follows closely with 8,610 in the Food test and 16,758 in the Hall test, slightly outperforming the standard RX 9070. The RX 9070 achieves 8,233 in the Food test and 16,566 in the Hall test, while the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 finishes behind with 7,535 in the Food test and 20,003 in the Hall test. Overall, the RTX 5070 Ti is the clear leader, with the 4070 trailing in both tests.
Geekbench 6
Geekbench 6 is a cross-platform benchmark that measures overall system performance. The Geekbench Browser allows you to compare any system to it.
| Geekbench (higher is better) | AMD Radeon RX 9070 | AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 | ASUS PRIME NVIDIA RTX 5070 Ti | NVIDIA RTX 5070 |
| GPU OpenCL Score | 138,463 | 173,255 | 174,725 | 246,875 | 188,892 |
In the Geekbench GPU OpenCL test, the ASUS Prime NVIDIA RTX 5070 Ti leads with a strong score of 246,875, significantly outperforming the competition. The NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 follows with a score of 174,725, ahead of both AMD Radeon cards. The AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT comes in next with a score of 173,255, just slightly behind the RTX 4070. The standard RX 9070 trails with a score of 138,463, placing it last in this test.
3D Mark
3DMark Port Royal, Speed Way, and Steel Nomad are GPU benchmarks testing performance in different scenarios. Port Royal focuses on ray tracing, Speed Way evaluates performance in racing simulations, and Steel Nomad challenges GPUs with high-intensity, realistic graphics. They assess GPU capabilities in rendering, lighting, and dynamic scenes.
| 3DMark Test (higher is better) | AMD Radeon RX 9070 | AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 | ASUS PRIME NVIDIA RTX 5070 Ti | NVIDIA RTX 5070 |
| Port Royal | 15,760 | 17,989 | 11,074 | 19,290 | 14,026 |
| Speed Way | 5,791 | 6,237 | 4,477 | 7,709 | 5,869 |
| Steel Nomad | 5,992 | 6,977 | 3,748 | 6,458 | 5,019 |
In gaming-focused 3DMark benchmarks, the AMD Radeon RX 9070 and 9070 XT outperformed the NVIDIA RTX 5070, with the AMD Radeon RX 9070 averaging 17% higher and the RX 9070 XT 28% higher across tests. While the RTX 5070 holds its own in ray tracing, AMD’s cards present a stronger option for raw gaming performance.
Power Consumption: ASUS Prime Radeon RX 9070 XT
Power consumption is a significant component of any high or low-end computing platform. Each new generation of GPU consumes more power under load, meaning larger power supplies and ample airflow for cooling. However, there is another aspect to power regarding performance: faster GPUs might spike higher, but the duration of each workload decreases.
We tested the ASUS PRIME RX 9070 XT’s power draw, which has a 304W TDP rating. During the Procyon AI image-generation test, power consumption rose from 243W at idle to 849W under load, an increase of 606W. The average power draw under load was approximately 676W. This is much higher than the NVIDIA models during the same period, putting more load across the entire system.
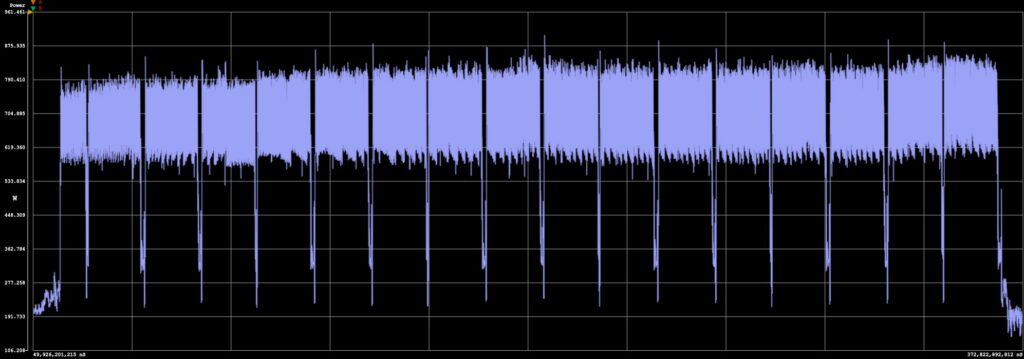
| Power Testing Summary |
AMD 9070 XT | NVIDIA RTX 5070 | ASUS Prime NVIDIA RTX 5070 Ti | NVIDIA RTX 5080 | NVIDIA RTX 5090 |
| Power Consumed | 3.41Wh | 2.46Wh | 1.66Wh | 1.39Wh | 1.16Wh |
| Test Duration | 17.4 s | 19.2 s | 11.1 s | 8.7 s | 5.1 s |
Conclusion
The ASUS Prime Radeon RX 9070 series from AMD combines high performance, efficiency, and affordability, making it an excellent choice for gamers and content creators. These GPUs built on RDNA 4 architecture excel at 1440p and 4K gaming while handling entry-level AI workloads. With 16GB of GDDR6 memory, the RX 9070 ensures ample bandwidth for demanding tasks.
The 3rd generation Ray tracing (RT) Accelerators provide significant improvements, including a second ray intersection engine and optimizations that double ray traversal capabilities over previous RDNA 3, enhancing ray tracing performance. Additionally, the RX 9070 series supports 2nd generation AI Accelerators, boosting AI performance for faster processing in gaming and content creation with support for new data types and optimizations.
The ASUS Prime Radeon RX 9070 series performed well in gaming workloads but trailed in AI tasks. In areas such as image generation, the 9070 XT consumes more power than its NVIDIA counterparts to complete the same work. This higher power consumption impacts efficiency during extended workloads, with NVIDIA holding an edge in efficiency and AI tasks. However, the RX 9070 series offers strong results at a more affordable price, making it an attractive option for users seeking AI acceleration and general-purpose performance. While drivers limited some AI workloads, we expect to see growth here as the cards mature, and we remain optimistic that AMD’s continued investment in this category will pay off and give consumers more choice.
Engage with StorageReview
Newsletter | YouTube | Podcast iTunes/Spotify | Instagram | Twitter | TikTok | RSS Feed