Managing IT infrastructure has changed rapidly over the last few years, and with change comes challenges. Users today expect fluidity and ease of use in managing their environments. Supermicro is addressing these demands with the introduction of SuperCloud Composer (SCC), a new way to easily provision, compose, recompose, and manage data center resources on the fly.
Managing IT infrastructure has changed rapidly over the last few years, and with change comes challenges. Users today expect fluidity and ease of use in managing their environments. Supermicro is addressing these demands with the introduction of SuperCloud Composer (SCC), a new way to easily provision, compose, recompose, and manage data center resources on the fly.

The traditional IT paradigm resulted in a cumbersome hardware provisioning process, with a fixed ratio of computing, storage, accelerator resources, and a lack of a one-size-fits-all platform capable of monitoring, telemetry, analytics, and intelligent system management.
In many ways, converged infrastructure (CI) and hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) tried to solve some of these problems. By combining storage, compute, and networking resources into a common pool, provisioning certainly became easier. But this simplicity means that granular control isn’t always available, so organizations that need to be able to configure very specific resources are left looking for alternatives.
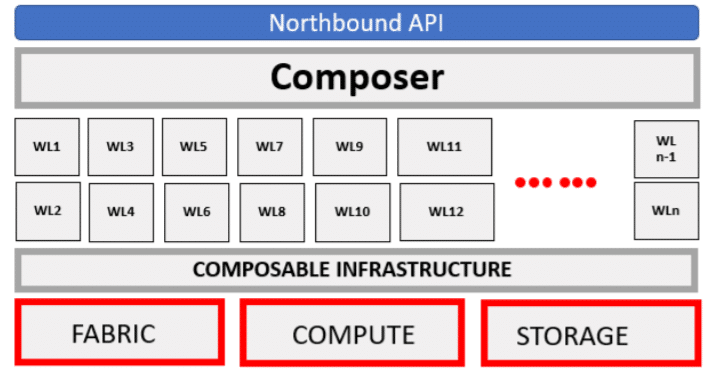
This demand for ultimate deployment flexibility has fed the trend of composable disaggregated infrastructure (CDI). In the composable infrastructure world, compute, storage, networking, and other IT resources are abstracted from their physical locations and are aggregated and deployed via software. Composable infrastructure is leading the way in modern data centers that need to deliver cloud-like resource consumption through an intuitive interface.
Overview of Supermicro SuperCloud Composer
SCC embodies Supermicro’s approach to software-defined and composable cloud solutions for future-forward data centers. Supermicro is aligning with the demands of its customers by focusing on an Infrastructure Management Solution aligned with industry trending consumption-based models. Presenting a single pane of glass (if you will) to IT administrators with SCC.
SCC also aggregates compute, storage, and fabric resources to create and manage a composable infrastructure in which workloads can be deployed upon.
To summarize some of the benefits and features of Supermicro SuperCloud Composer:
- A unified dashboard that encompasses compute, storage, networking, and rack management
- The ability to monitor and manage all elements of the resource pools in a Composable Disaggregated Infrastructure
- Rich analytics, telemetry, and intelligent system lifecycle management
- Parallel multi-system upgrade and configuration capability reducing hardware maintenance downtime
- A standardized Redfish Northbound API Message Bus for easy third-party software platform integration
- Role-based access control to support modern data center security policies
As IT organizations shift away from traditional siloed IT architectures and cumbersome multi-touch management solutions and move towards a Software-Defined Datacenter, IT management solutions need to be as flexible and fluid as the demands of the IT users.
SCC is built around an Open Distributed Infrastructure Management (ODIM) framework and is highly flexible in the range of systems that it supports. It can be used with everything from Supermicro’s blades (SuperBlade or MicroBlade) to their extensive range of standard rackmount servers. The systems can be on the Edge or in a data center. Regardless of the location and type of system, it will use the same workflow. Not only does it support Supermicro equipment it also supports systems that use iLO, iDRAC, and other out-of-band (OBM) management tools.
In addition, SCC can be deployed on a physical system or as a virtual machine that is running CentOS, RHEL, or VMware ESXi. Connectivity is simple via Chrome or Firefox web browser.
To ensure operational security SCC has role-based access controls (RBAC), which gives users only access to the systems and functions required to fulfill their tasks. Users can be local accounts to SCC or it can be integrated with OpenLDAP or Active Directory.
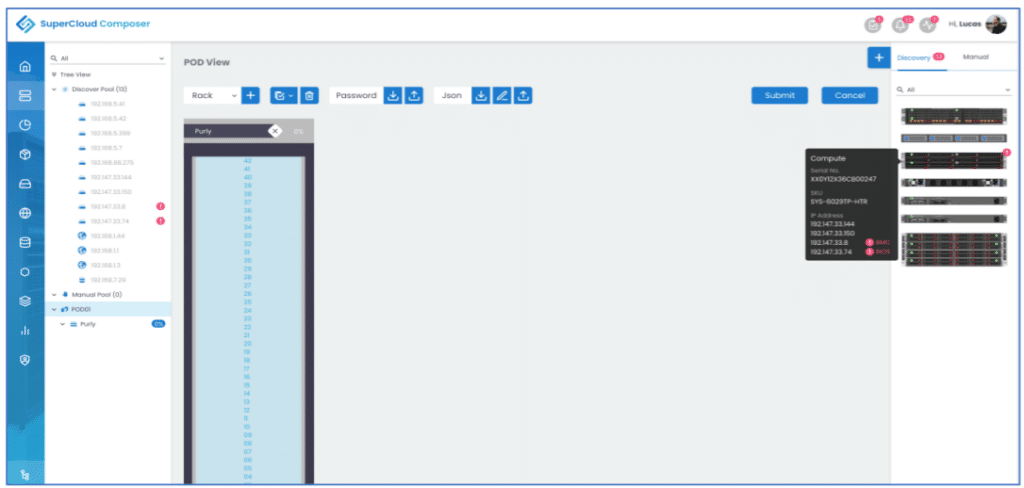
Knowing what you have and where it is located is crucial when administering a data center. SCC has different logical and physical views that makes the location of resources and assets quick to determine. For example, SCC’s pod view allows quick visibility into what assets are available and where inside the rack they are located. IT organizations can quickly see if they need more space or have enough space to run existing and new workloads. Having quick visibility and IT asset information at your fingertips saves time and aggravation when it comes to documenting corporate resources. Visibility and manageability of compute, storage, and other resources from a single interface remove the burden of having to log in to multiple systems and then learn the various tools to manage the discrete components in an environment.
Day 2 Operational Efficiency
Complexity kills productivity when deploying and maintaining IT infrastructure. As such, Supermicro is focused on trying to alleviate and simplify Day 2 challenges with SCC. SCC was designed by IT professionals to make life easier for IT administrators so they can meet the ever-increasing demands of IT end-users while keeping the environment running smooth and secure with the latest patches and updates.
SCC gives IT organizations flexibility in deployment at scale, whether organizations need to deploy a single node on the edge or dozens of servers in a data center, SCC provides not only the visibility but functionality IT organizations require for data center operational efficiency.
Fluidity in managing, deploying, and redeploying IT resources has been brought to the forefront by SCC. Alleviating the stress and cumbersome workload of updating multiple systems is minimized by SCC as it has the ability to quickly deploy or repurpose resources with just a few clicks.
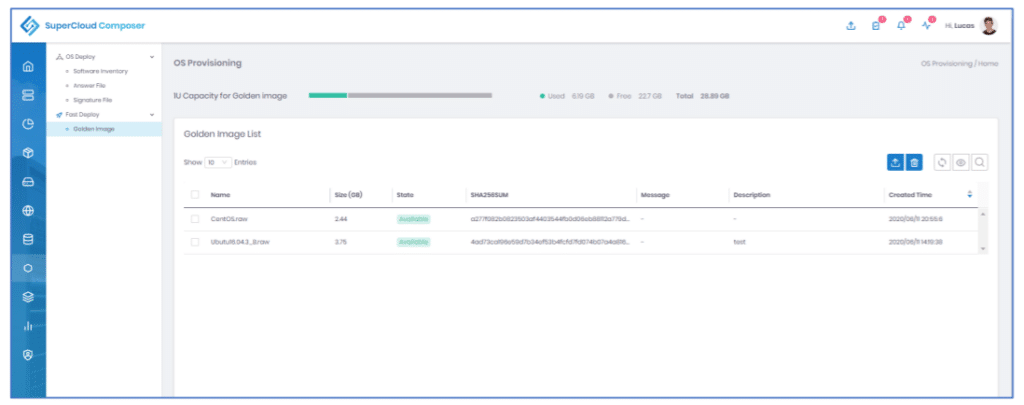
In order to standardize, streamline and have a consistent workflow SCC has a software inventory repository. This contains the ISOs that can be used by SCC’s built-in PXE boot server. To provision a system, a new golden operating system (OS) image is deployed in conjunction with the customer’s metadata using the fast-deploy wizard in SCC. For the metadata, SCC users can use prebuilt answer files or they can create their own. Using this methodology administrators are guaranteed a standardized, proven OS-deployment model.
Logging into multiple systems to perform updates is a critical task for IT administrators but it can quickly become tedious and take a considerable amount of their time to complete. Utilizing SCC IT administrators can quickly identify which systems need to be updated and then apply the required updates to them. This greatly reduces the time it takes to update systems and frees up IT administrators to perform other, more pressing, tasks.
Supermicro SuperCloud Composer Monitoring
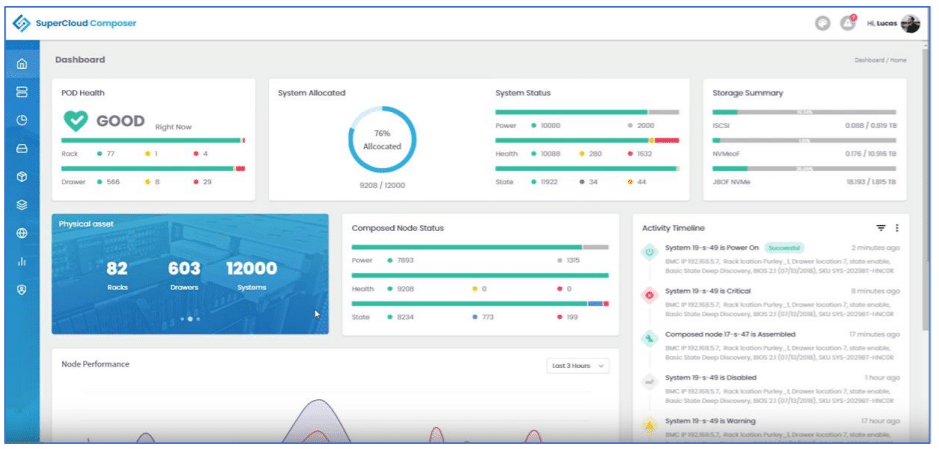
SCC comes with a built-in database and analytics engine that collects, analyzes, and displays the collected data via charts, graphs, and tables. This information is displayed in real-time with the ability to send out alerts if needed. This data is also used for predictive analytics and usage trending. Data is collected and displayed at the pod, rack, chassis, node, and component level.
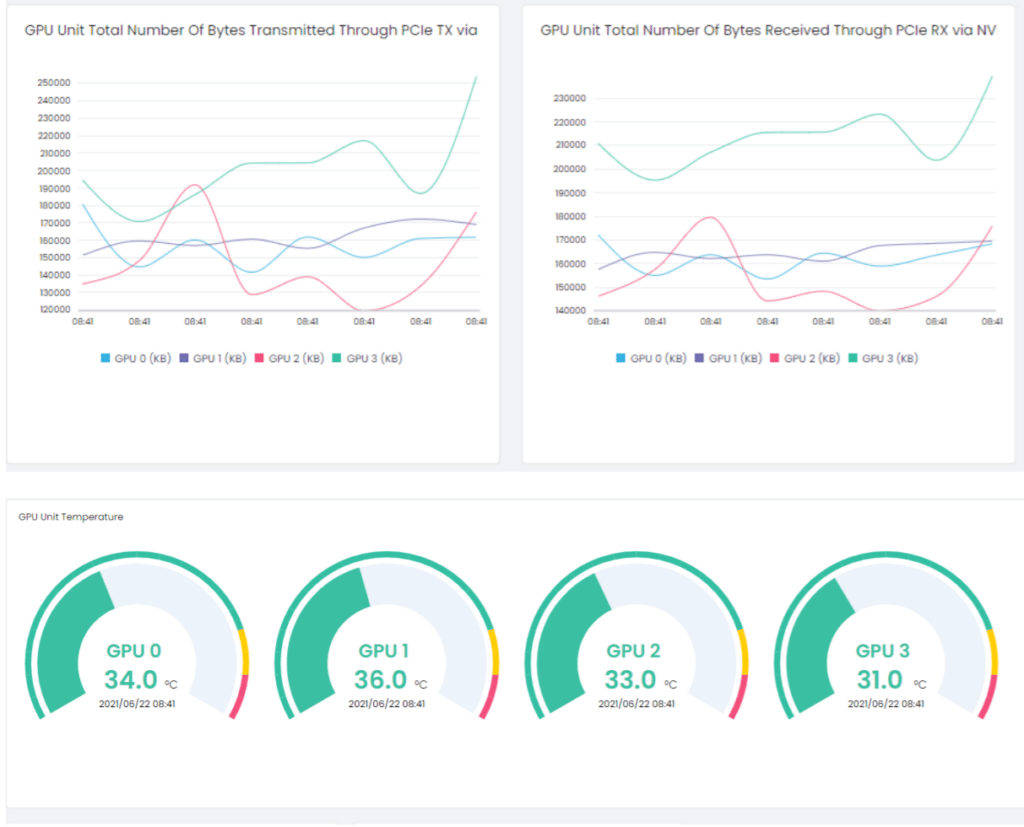
SCC collects and displays data for the traditional resources (CPU, memory, and network), but it can be customized and enhanced for other resources as well. A prime example of this flexibility and the depth of SCC’s monitoring capabilities is using a custom dashboard to monitor a data center’s GPU workload. The screen capture below shows a custom widget that was created to chart the transmittal rate and temperature of GPUs.
Supermicro knows that very few data centers are homogeneous with regards to hardware and software, so it uses Redfish to allow for the extension of SCC. Redfish is a RESTful interface standard for the management of servers, storage, networking, and converged infrastructure that has been widely adopted by the industry. This gives IT administrators the flexibility to extend SCC to fit their environment through the use of 3rd party integrations.
Using Supermicro SuperCloud Composer
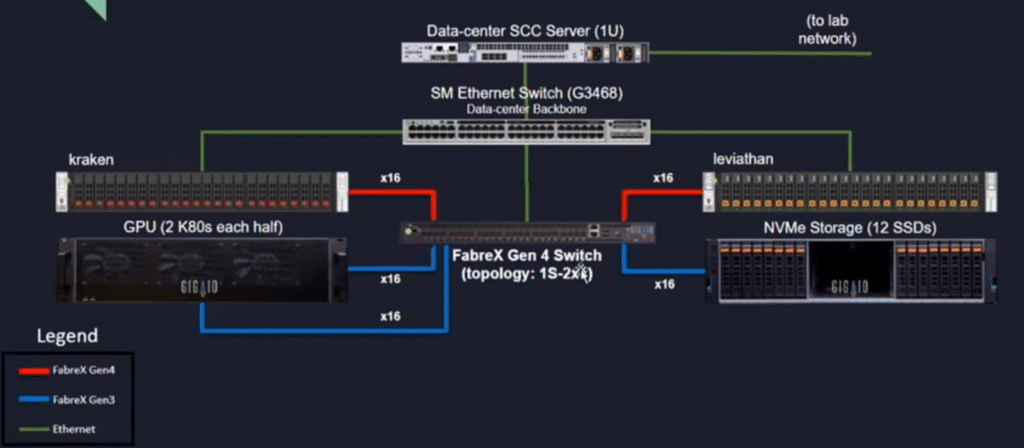
To get hands-on, we worked with Supermicro on how SCC is used to compose a server using disaggregated GPUs and NVMe storage with FabreX, a GigaIO technology that enables disaggregation and composition of compute resources. FabreX not only composes resources to servers, but it is also can compose servers using PCIe rather than Ethernet or InfiniBand.
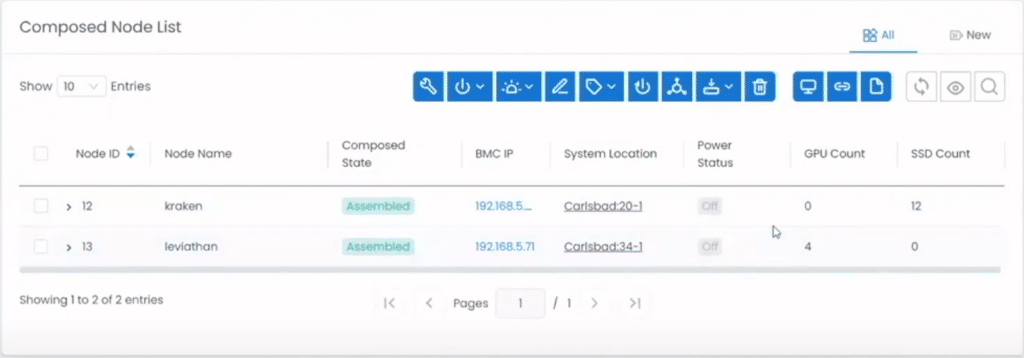
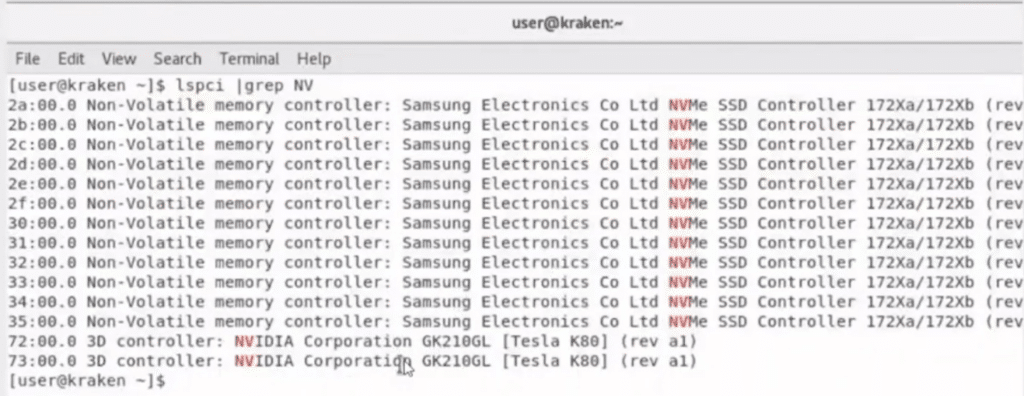
The hardware in this example was composed of two server nodes (kraken and leviathan), a drawer of 12 NVMe drives and two NVIDIA K80 GPUs. The nodes were connected to these resources via PCIe through a FabreX Gen4 switch.
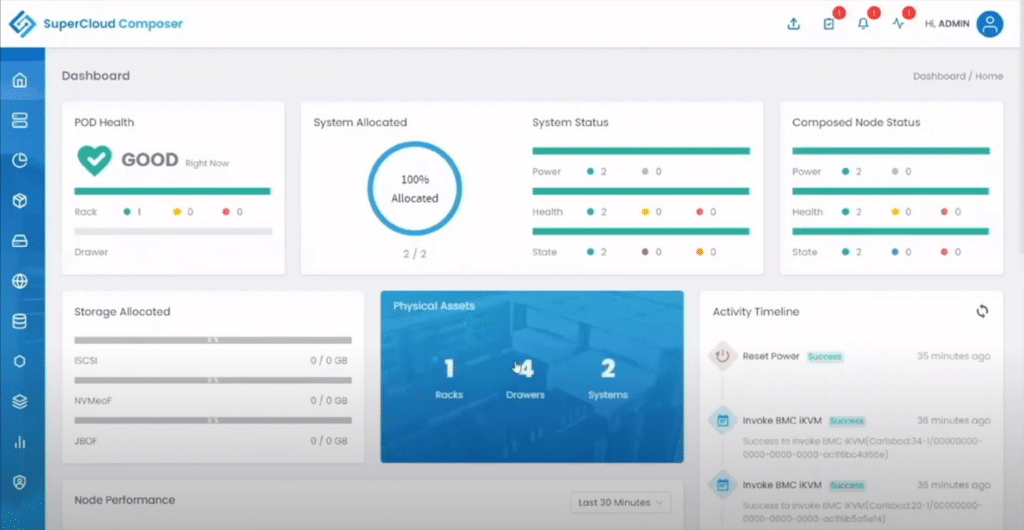
The SCC dashboard showed that it had two nodes and four drawers in the rack and that the two nodes were powered on and healthy.
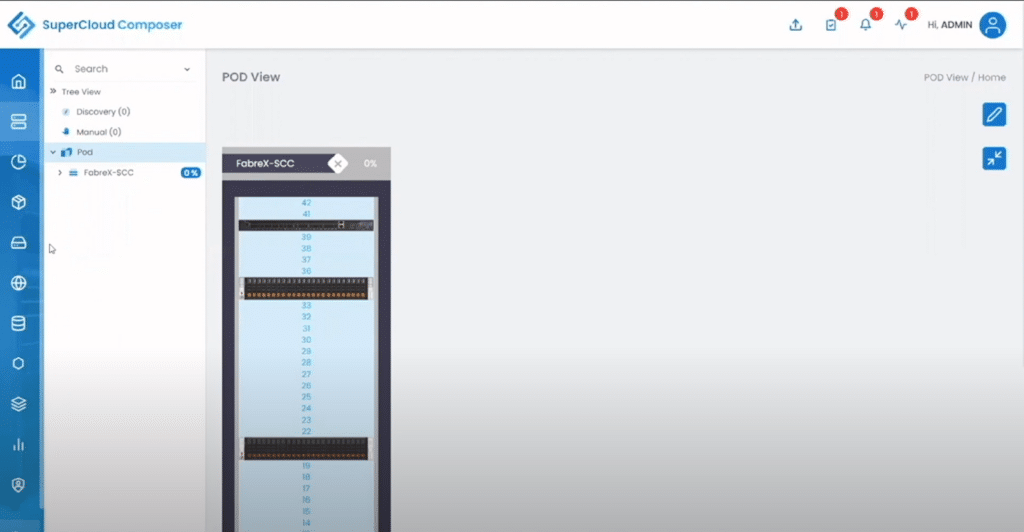
The Pod view showed a graphical view of the two servers and the Ethernet switch.
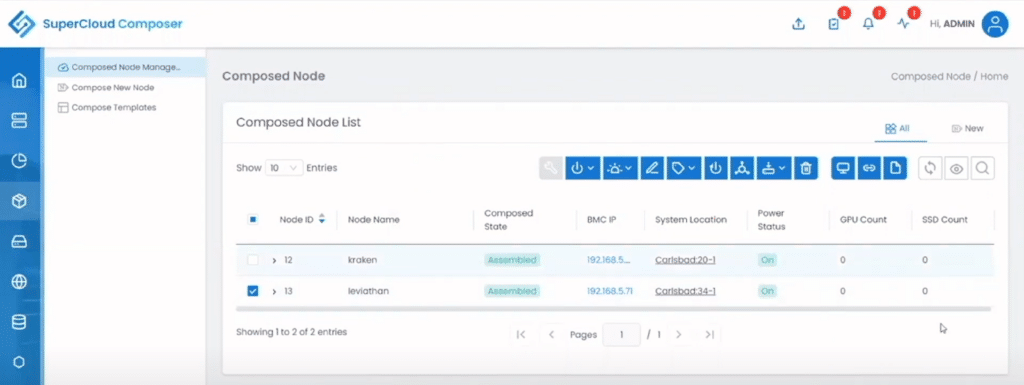
The Composer view verified that the server nodes didn’t have any resources associated with them.
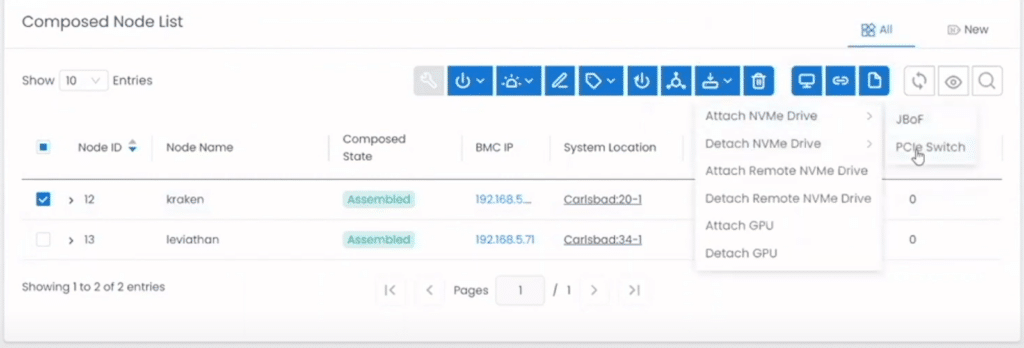
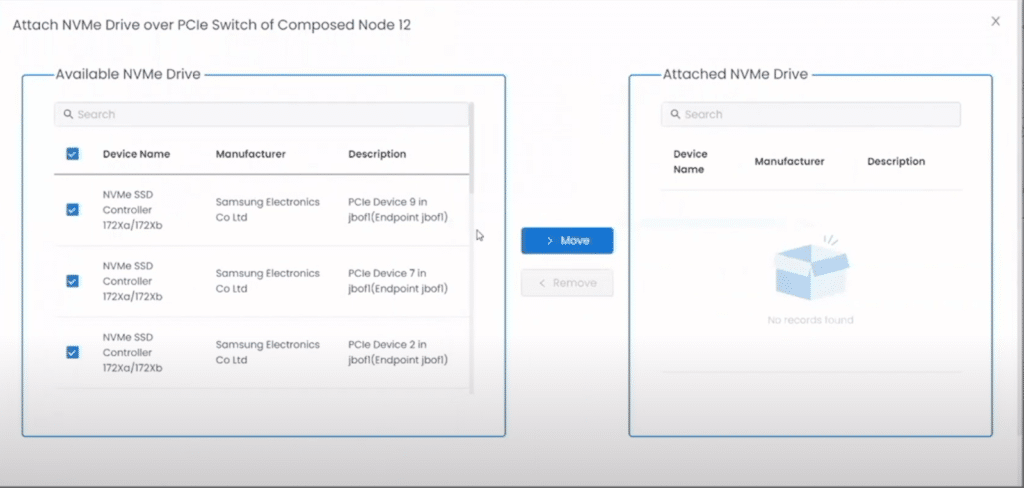
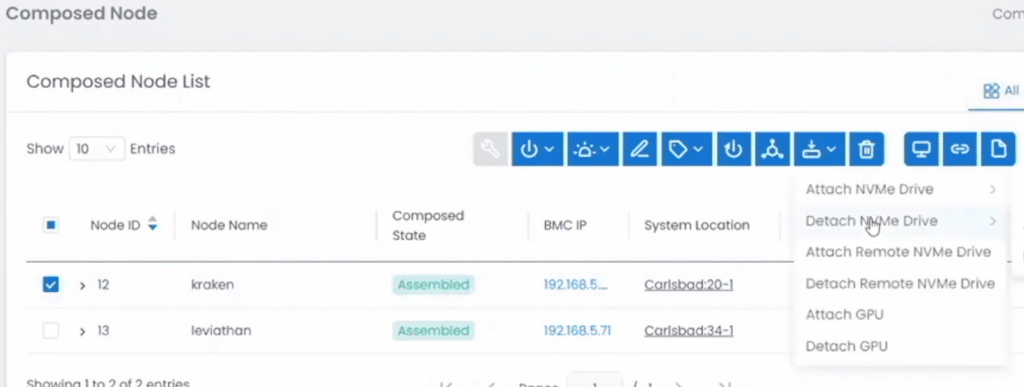
From the drop-down menu, they selected a server node (kraken) and a resource (NVMe Drive), and how it was to be attached (PCIe Switch) to the node.
This brought up a list of the NVMe drives and allowed them to select the ones that they wanted to associate with the nodes.
They then attached the GPU resources to the other server (leviathan) using the same workflow. When adding the resources, SCC was intelligent enough to realize that it needed to power off the nodes.
Once the nodes were powered back on, they logged on to the nodes and showed us that the resources were indeed associated with them.
They then went on to show us how the systems could be decomposed using SCC.
This example really demonstrated the power of SCC. Although systems could be composed and decomposed manually, it would have involved logging on to multiple servers, switches and using various tools to do so.
Moreover, using SCC an IT administrator can compose or recompose systems as needed to address the workloads that they currently have. For example, during the day when analysts are visualizing data GPU resources could be associated with some of the servers, and then, at a later time, when the data is being processed the resources could be associated with other servers.
Final Thoughts
Workloads are no longer static; they are constantly changing and evolving. IT organizations need to be just as fluid as these workloads. Supermicro SuperCloud Composer is designed not only with understanding the challenges of today’s software-defined datacenter but also to provide the flexibility to meet the challenges of tomorrow.
Supermicro definitely has an impressive offering in the CDI field with SCC. For organizations that want to have a better understanding of what the CDI movement could mean for their infrastructure, the best thing to do is get hands-on experience with it.
To help you evaluate SCC Supermicro has a free 90-day trial program.
More Info on SuperCloud Composer
Engage with StorageReview
Newsletter | YouTube | Podcast iTunes/Spotify | Instagram | Twitter | Facebook | RSS Feed