At the very tail end of last year, HGST released a slew of new drives for its investor day. One of the drives announced was the Ultrastar SS200. The SS200 is an 2.5” SAS SSD aimed at enterprise. The drives are all about capacity (with the upper capacity being 7.68TB) and performance. HGST states that the drives are able to hit up to 250K IOPS read and 86K IOPS write (for the read intensive drive) for a random 70/30 4KiB test. There are two types of drives in the family, though they all have the same moniker, an endurance or write optimized and a capacity or mixed workloads optimized.

Available in a 2.5” form factor, the SN200 is12Gb/s SAS SSD. By leveraging the common SAS interface, the SS200 can be deployed in most data centers aiding them as they struggle with exploding data not to mention the need for faster storage. The new SSDs leverage SanDisk 15nm NAND along with HGST’s Guardian Technology platform. This platform consists of flash management, data path protection, and protection against data loss in the event of a power failure.
As mentioned, there are two types of SS200 drives, a mixed-use (reviewed here) and a read-intensive (reviewed here). The mixed-use drive comes in capacities from 400B to 3.2TB but has more drive writes per day (DWPD) at 3. The mixed use drive is ideal for OLTP, financial transactions, E-commerce, email/messaging/collaboration, and virtual environments. The read-intensive drive runs in capacity from 480GB to 7.68TB with 1 DWPD. This drive is ideal for ERP, CRM, data warehousing, video streaming, VOD, file servers, and database analytics.
HGST Ultrastar SS200 specifications:
- Form factor: 2.5”
- Interface: SAS 12Gb/s
- Capacity: 7.68TB, 3.84TB, 1.92TB, 960GB, 480GB
- DWPD: 1
- Performance
- Sequential Read (max MB/s, 128KiB): 1,800
- Sequential Write (max MB/s, 128KiB): 1,000
- Random Read (max IOPS, 4KiB): 250K
- Random Write (max IOPS, 4KiB): 37K
- Mixed Random Read/Write (max IOPS 70%R/30%W, 4KiB): 90K
- Write Latency 512B (μs): 100
- Reliability
- Error Rate in bits read: < 1 in 10^17
- MTBF: 2.5M hours
- Annual failure rate (AFR): 0.35%
- Limited warranty: 5 years
- Data Retention: 3-month at 40°C
- Power
- Requirement (DC +/- 5%): 5V & 12V
- Operating (W, typical): 9 or 11
- Idle (W): 3.8 to 4.3
- Physical
- z-height (mm): 15
- Dimensions (width x depth, mm): 69.85 x 100.45
- Weight (g, max): 200
- Environmental
- Temperature: 0°C to 70°C (Case)
Testing Background and Comparables
The StorageReview Enterprise Test Lab provides a flexible architecture for conducting benchmarks of enterprise storage devices in an environment comparable to what administrators encounter in real deployments. The Enterprise Test Lab incorporates a variety of servers, networking, power conditioning, and other network infrastructure that allows our staff to establish real-world conditions to accurately gauge performance during our reviews.
We incorporate these details about the lab environment and protocols into reviews so that IT professionals and those responsible for storage acquisition can understand the conditions under which we have achieved the following results. None of our reviews are paid for or overseen by the manufacturer of equipment we are testing. Additional details about the StorageReview Enterprise Test Lab and an overview of its networking capabilities are available on those respective pages.
We tested all SSDs in this review inside the Supermicro SuperServer 2028U-TNR4T. It is configured with 2 x Intel E5-2699 v3 CPUs, 768GB RAM (24 x 32GB DDR4) and is running ESXi 6.0 for a hypervisor. The HBA leveraged for SATA and SAS testing is a SuperMicro HBA based on the LSI Logic Fusion-MPT 12GSAS SAS3008 chipset.
Comparables for this review:
- Toshiba SAS3 1.6TB PX04SMB
- Seagate SAS3 1.6TB 1200.2
- Seagate 1200.2 3.84TB
- HGST SS200 3.2TB (Mixed)
- HGST 1.6TB SAS3
Application Workload Analysis
In order to understand the performance characteristics of enterprise storage devices, it is essential to model the infrastructure and the application workloads found in live production environments. Our benchmarks for the HGST SS200 are therefore the MySQL OLTP performance via SysBench and Microsoft SQL Server OLTP performance with a simulated TCP-C workload. For our application workloads, each drive will be running 2-4 identically configured VMs.
SQL Server Performance
Each SQL Server VM is configured with two vDisks: 100GB volume for boot and a 500GB volume for the database and log files. From a system resource perspective, we configured each VM with 16 vCPUs, 64GB of DRAM and leveraged the LSI Logic SAS SCSI controller. While our Sysbench workloads tested previously saturated the platform in both storage I/O and capacity, the SQL test is looking for latency performance.
This test uses SQL Server 2014 running on Windows Server 2012 R2 guest VMs, being stressed by Quest's Benchmark Factory for Databases. StorageReview’s Microsoft SQL Server OLTP testing protocol employs the current draft of the Transaction Processing Performance Council’s Benchmark C (TPC-C), an online transaction-processing benchmark that simulates the activities found in complex application environments. The TPC-C benchmark comes closer than synthetic performance benchmarks to gauging the performance strengths and bottlenecks of storage infrastructure in database environments. Each instance of our SQL Server VM for this review uses a 333GB (1,500 scale) SQL Server database and measures the transactional performance and latency under a load of 15,000 virtual users.
SQL Server Testing Configuration (per VM)
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Storage Footprint: 600GB allocated, 500GB used
- SQL Server 2014
- Database Size: 1,500 scale
- Virtual Client Load: 15,000
- RAM Buffer: 48GB
- Test Length: 3 hours
- 2.5 hours preconditioning
- 30 minutes sample period
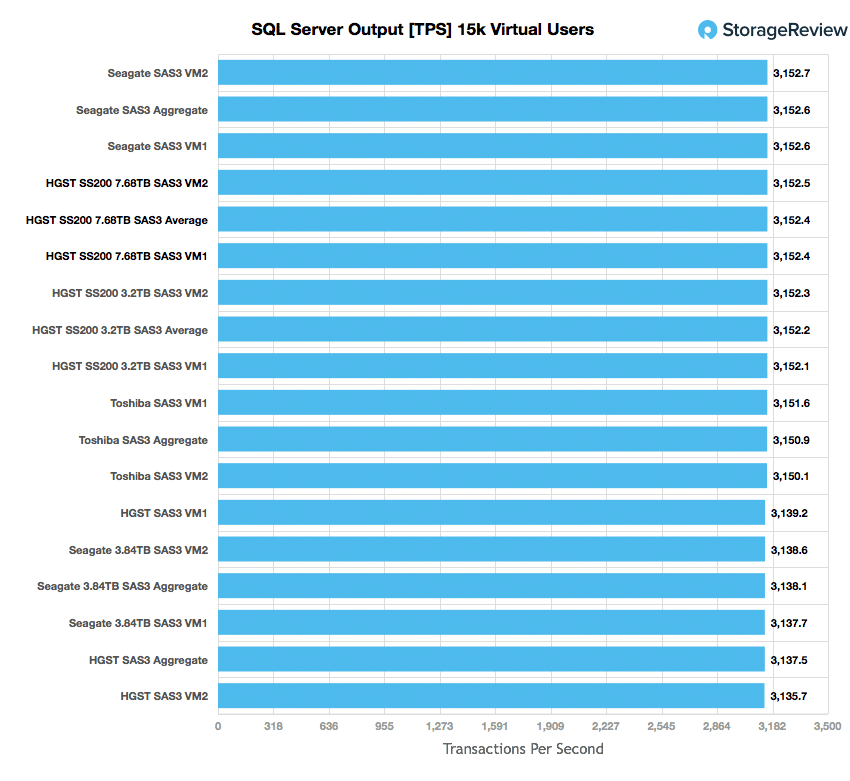
When looking at SQL Server Output, the SS200 read drive placed near the top with an aggregate score of 3,152.4 TPS and individual VMs running from 3,152.4 to 3,152.5 TPS.
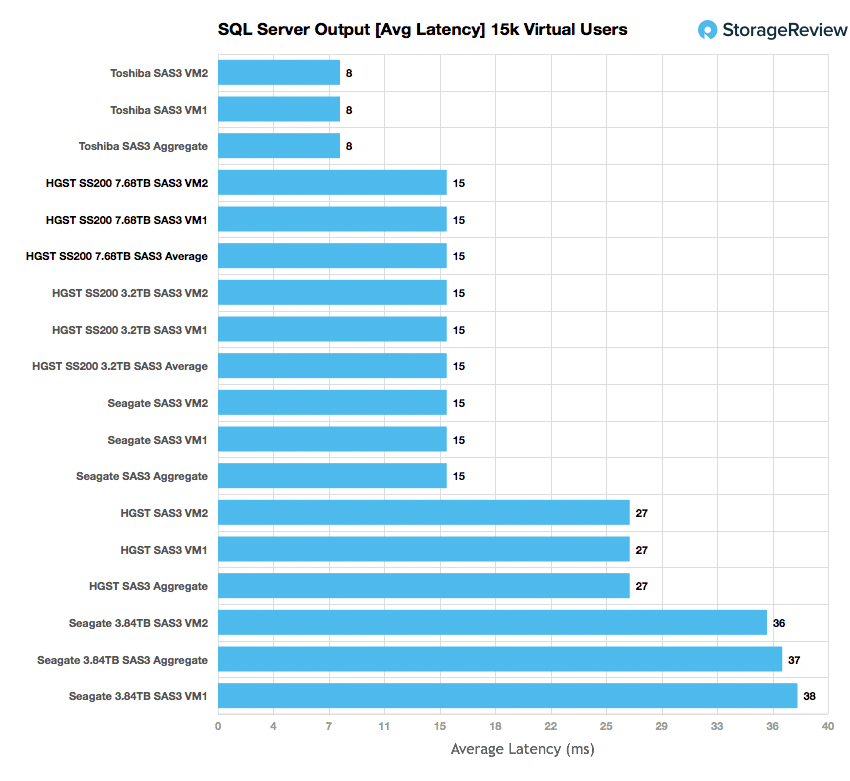
The average latency results during the 15k user SQL Server benchmark placed the SS200 read near the top with aggregate and individual VM latency of 15ms. This put it right inline with its mixed workload brother.
Sysbench Performance
The next application benchmark consists of a Percona MySQL OLTP database measured via SysBench. This test measures average TPS (Transactions Per Second), average latency, and average 99th percentile latency as well.
Each Sysbench VM is configured with three vDisks: one for boot (~92GB), one with the pre-built database (~447GB), and the third for the database under test (270GB). From a system resource perspective, we configured each VM with 16 vCPUs, 60GB of DRAM and leveraged the LSI Logic SAS SCSI controller.
Sysbench Testing Configuration (per VM)
- CentOS 6.3 64-bit
- Percona XtraDB 5.5.30-rel30.1
- Database Tables: 100
- Database Size: 10,000,000
- Database Threads: 32
- RAM Buffer: 24GB
- Test Length: 3 hours
- 2 hours preconditioning 32 threads
- 1 hour 32 threads
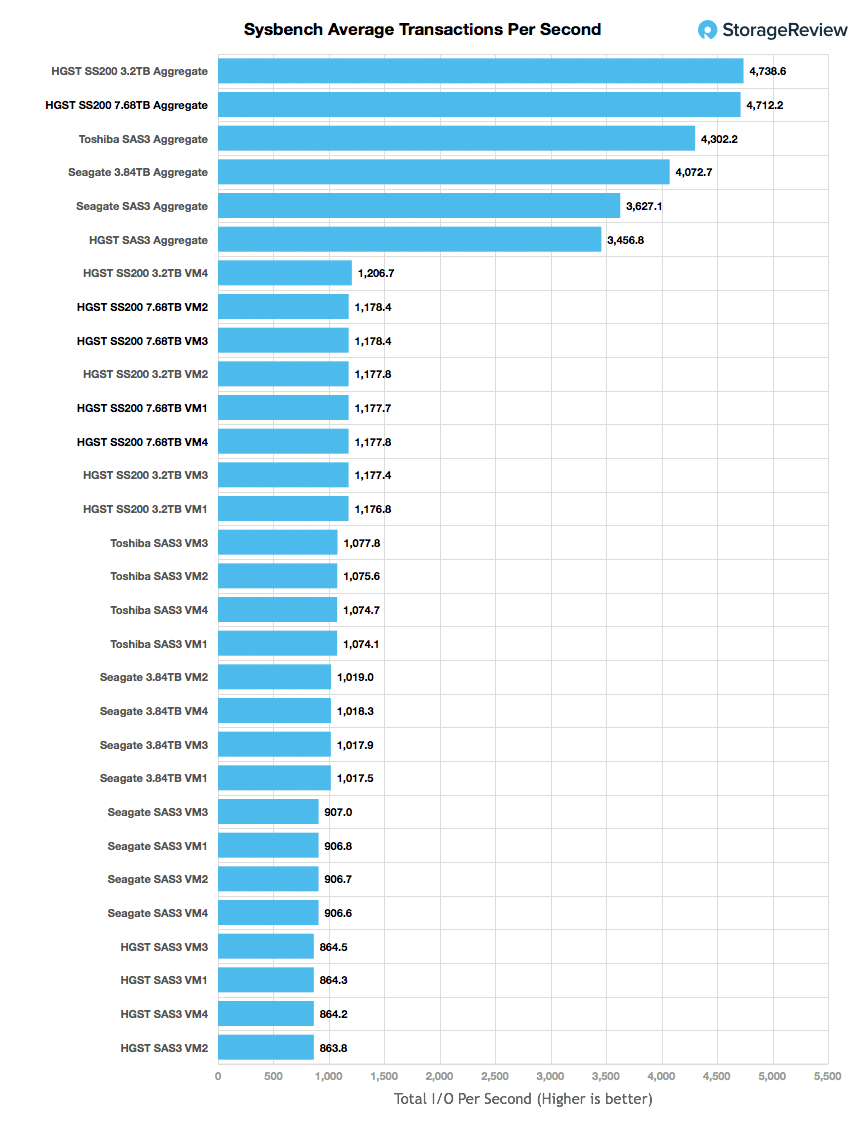
With the Sysbench transactional benchmark the SS200 read came in second behind its lower capacity brother with an aggregate score of 4,712.2 TPS and individual VMs running from 1,177.7 TPS to 1,178.4 TPS.
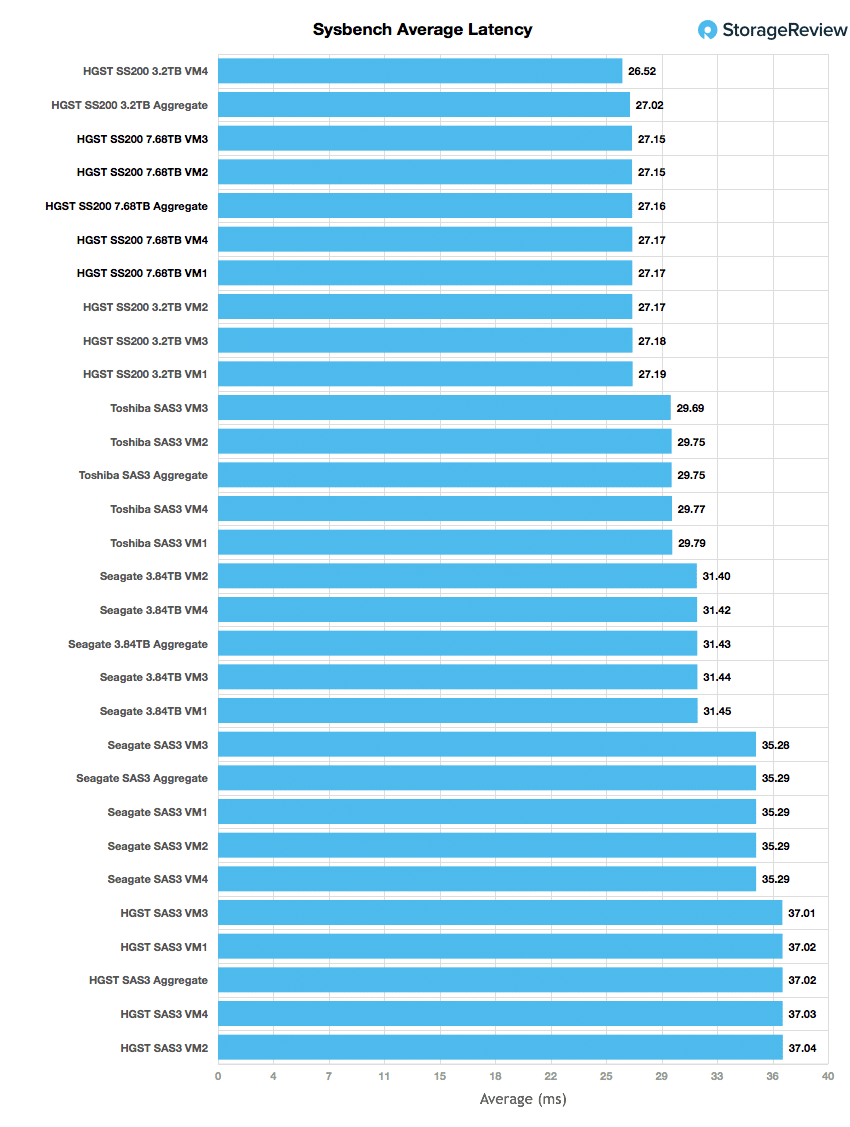
Switching gears to Sysbench average latency, the SS200 read found itself in second once again with an aggregate average latency of 27.16ms.
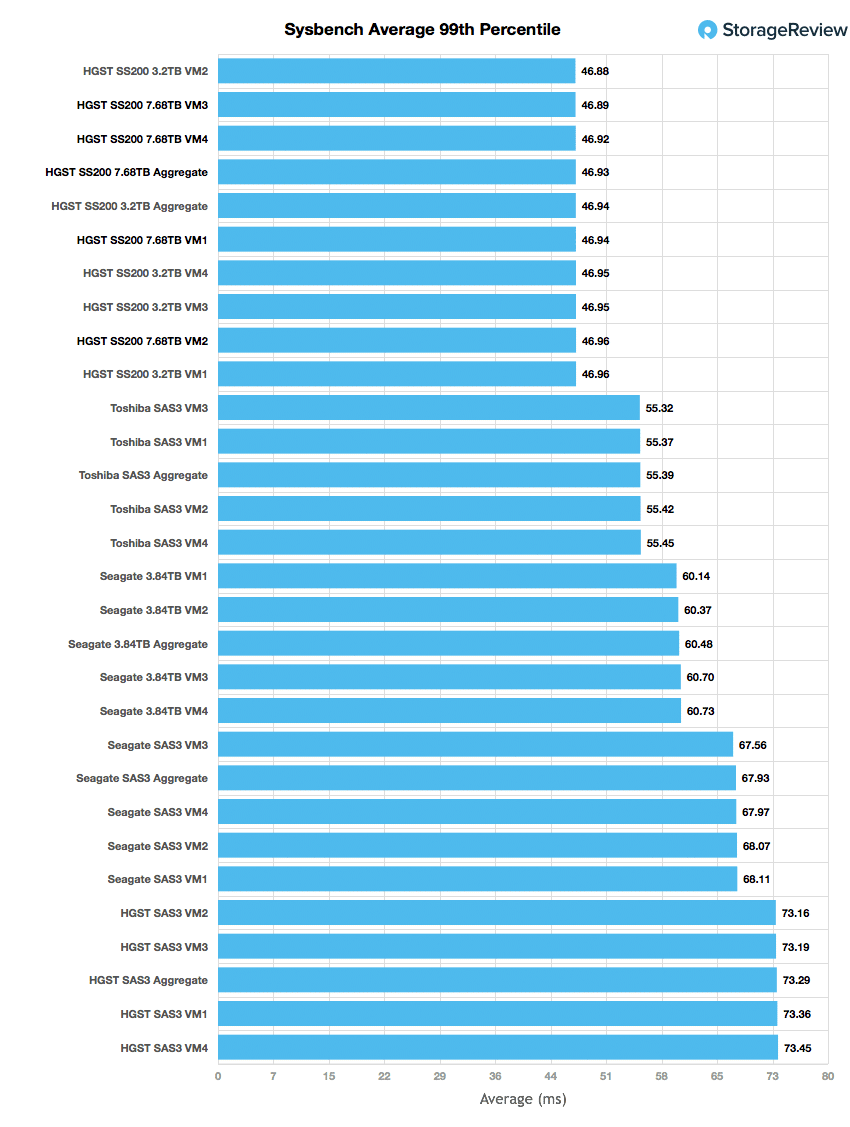
In terms of our worst-case MySQL latency scenario (99th percentile latency), the SS200 read knocked its smaller capacity brother off its perch to take first with an aggregate latency of 46.93ms.
Conclusion
The HGST Ultrastar SS200 is a 12Gb/s SAS SSD. The drive comes in two flavors, a read-intensive and mixed workload. The drive comes in a 2.5” form factors and runs in capacity up to 7.68TB. HGST states that the drive can hit 1.8GB/s in sequential read and 250K in random read/write with less than 100μs of latency. This level of performance and capacity makes the drive ideal for use cases such as the video streaming, VOD, file servers, and database analytics depending on the drive type selected, read-intensive or mixed use.
Looking at performance, the HGST Ultrastar SS200 Read-Intensive SAS SSD put up very good numbers across the board in our application workloads. It scored near the top in both of our SQL Server benchmarks with a transactional aggregate score of 3,152.4 TPS and an average latency of 15ms. Its main source of competition in the Sysbench tests were its mixed workload brother. The drive took second place in TPS with 4,712.2 and average latency with 27.16ms. However, the drive barely edged out the mixed workload drive in worst-case scenario latency with 46.93ms compared to the other drives 46.94ms.
The Bottom Line
The HGST Ultrastar SS200 Read-Intensive SAS SSD offers up to 7.68TB of capacity and plenty of performance for read-intensive workloads.
HGST Ultrastar SS200 product page
Sign up for the StorageReview newsletter