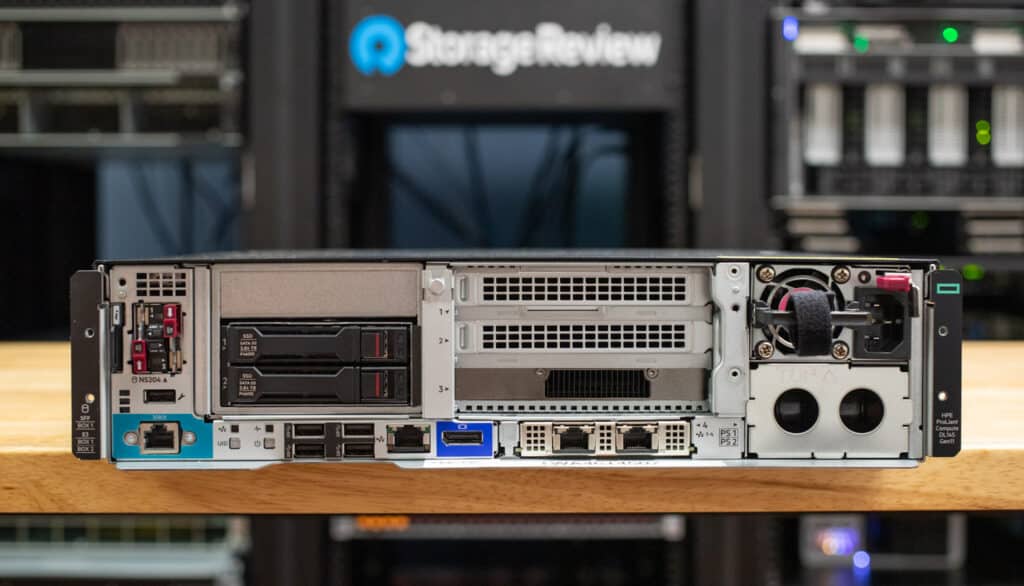
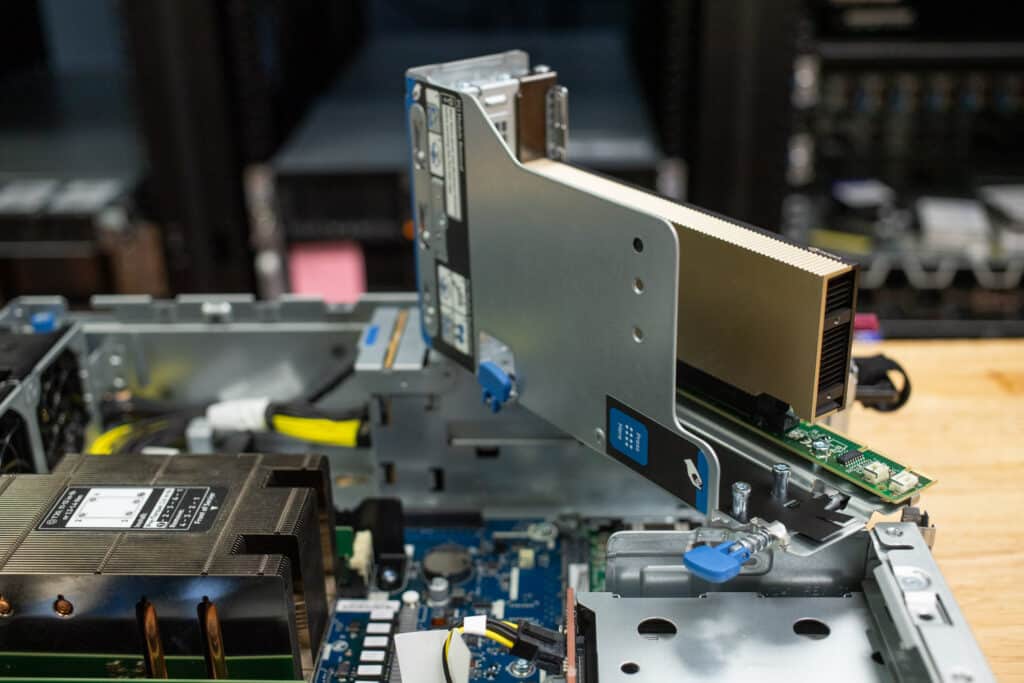
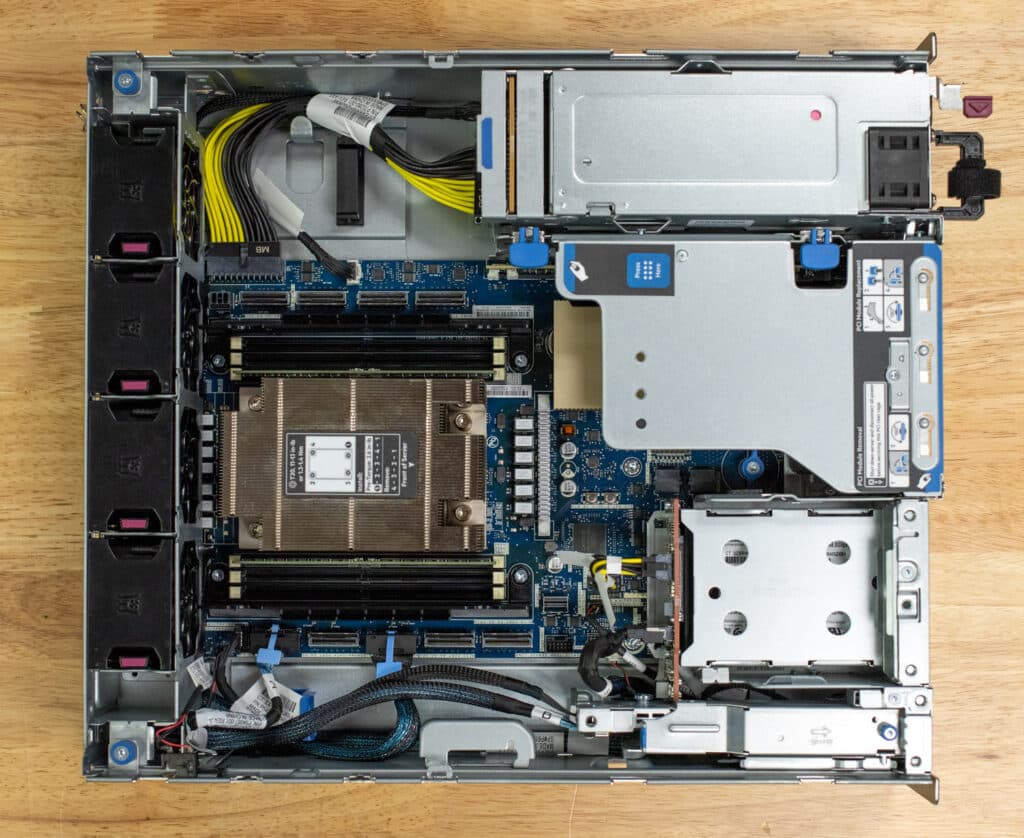
The HPE DL145 Gen11 is a compact edge platform that offers a balance of expandability, energy efficiency, and robust management.
The HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11 is a compact and comprehensive edge server built to deliver high performance and flexibility in environments where space, power, and cooling are constrained. Whether you’re in retail, manufacturing, or telecommunications, the DL145 hopes to bring flexibility and performance where traditional data center servers simply wouldn’t be practical.
HPE ProLiant DL145 G11 Processor Options
Powered by AMD’s latest EPYC 8004 (Siena) processors, these systems offer options ranging from 8 to 64 cores with a TDP of up to 200W. This allows for powerful, energy-efficient processing, letting you tailor the system to your specific workload needs. The EPYC 8534P is a strong choice for data-heavy applications, offering 64 cores and a base frequency of 2.3 GHz. Its high core count and processing power make it ideal for handling intensive workloads, providing the performance needed for demanding tasks.
If you’re more focused on balancing performance with energy efficiency, options like the 8124P, which has 16 cores and a TDP of 125W, might be more suitable. Each of these CPUs has 6 DDR5 memory channels, meaning they can handle memory at speeds up to 4800 MT/s, ensuring high throughput for tasks that need fast data access.
Here’s an overview of the available processor options you can configure with the DL145 Gen11:
| EPYC Model | Cores | Base Frequency (GHz) | Max Frequency (GHz) | DDR5 Channels | Default TDP (W) | L3 Cache (MB) | Memory Speed |
| 8534P | 64 | 2.3 | 3.1 | 6 | 200W | 128 | 4800 MT/s |
| 8434P | 48 | 2.5 | 3.1 | 6 | 200W | 128 | 4800 MT/s |
| 8324P | 32 | 2.65 | 3.0 | 6 | 180W | 128 | 4800 MT/s |
| 8224P | 24 | 2.55 | 3.0 | 6 | 160W | 64 | 4800 MT/s |
| 8124P | 16 | 2.45 | 3.0 | 6 | 125W | 64 | 4800 MT/s |
| 8024P | 8 | 2.4 | 3.0 | 6 | 90W | 32 | 4800 MT/s |
| 8534PN | 64 | 2.3 | 3.1 | 6 | 175W | 128 | 4800 MT/s |
| 8434PN | 48 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 6 | 155W | 128 | 4800 MT/s |
| 8324PN | 32 | 2.05 | 3.0 | 6 | 130W | 128 | 4800 MT/s |
| 8224PN | 24 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 6 | 120W | 64 | 4800 MT/s |
| 8124PN | 16 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 6 | 100W | 64 | 4800 MT/s |
| 8024PN | 8 | 2.05 | 3.0 | 6 | 80W | 32 | 4800 MT/s |
HPE ProLiant DL145 G11 Storage, Expansion, and Other Features
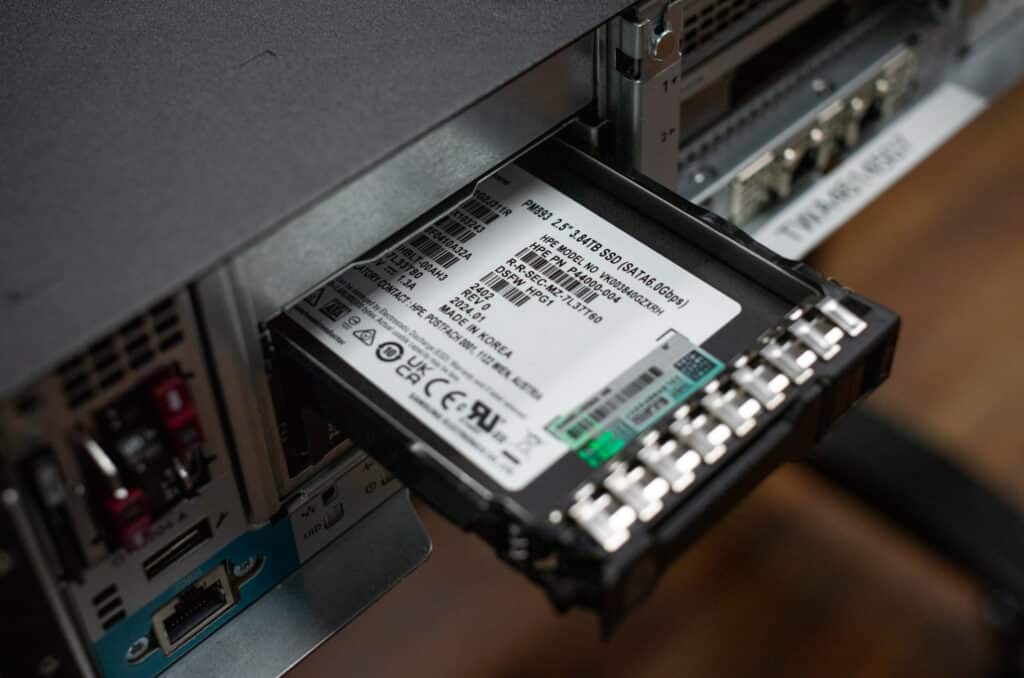
On the storage front, the DL145 Gen11 can handle up to performance-dense 92.16TB using EDSFF E3.S drives or up to two SFF drives if you’re looking for a more traditional edge deployment. It’s also worth noting that it supports Self-Encrypting Drives (SEDs), which is crucial if you’re dealing with sensitive data at the edge—these offer an extra layer of security that’s easy to overlook but very necessary.
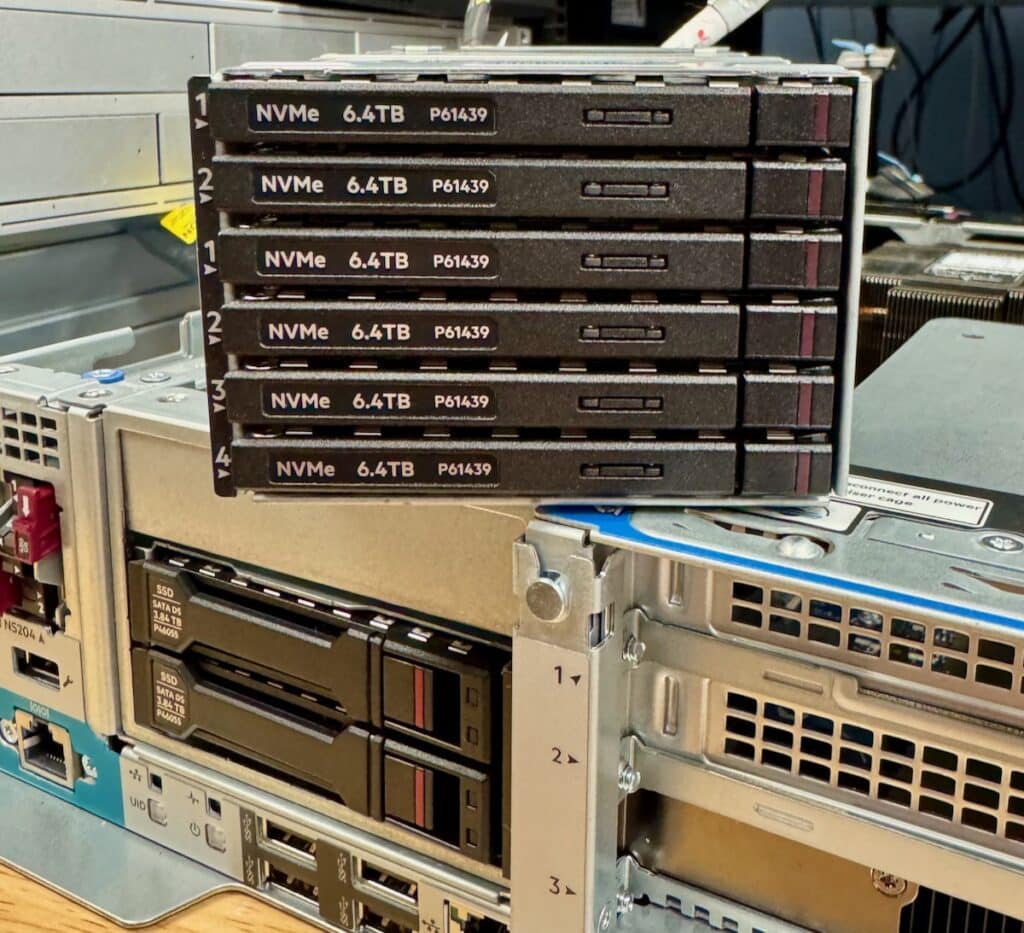

Optional E3.S Six Drive Chassis
For expansion, the DL145 Gen11 comes with 3 PCIe Gen5 slots, giving you room for full-size GPUs or accelerator cards. This is ideal if you need to scale your computing power for AI or machine learning tasks. The server also supports Nvidia L4 GPUs, which are great for those more specialized workloads requiring GPU acceleration. If you’re looking for network flexibility, the OCP 3.0 PCIe Gen5 slot allows you to slot in various network adapters, ensuring your current setup does not box you in.
The DL145 Gen11 is also built to withstand extreme operating conditions, supporting temperatures ranging from -5°C to 55°C. It also features a bezel with a large air filter, providing protection from dusty or industrial environments. This makes it a reliable choice for remote or harsh-edge deployments where maintaining consistent performance under challenging conditions is critical.
The HPE server offers comprehensive security features, including HPE’s Silicon Root of Trust, which ensures hardware integrity by verifying firmware at boot, iDevID for secure device identity, and TPM 2.0 (Trusted Platform Module) for secure encryption and hardware-based security. Additionally, it includes chassis intrusion detection and physical security mechanisms like a Kensington lock, ensuring protection against unauthorized access in environments where physical security is a concern.
In terms of power, you have options for up to two redundant AC or DC power supplies, which is essential for keeping things up and running even when power conditions are unstable. Moreover, if you’re working in telecommunications, it’s worth noting that the server is designed to qualify for NEBS Level 3 compliance, meaning it’s built to withstand the rigorous demands of telecom environments.
HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11 Specifications |
|
| Processor | AMD EPYC 8004 Series (Siena) Core options: 8 to 64 cores TDP: Up to 200W Max Frequency: Up to 3.1 GHz |
| Memory | 6 DDR5 DIMM Slots DDR5-4800 MT/s Maximum capacity: Up to 768 GB |
| Storage | Drive Bays: – Option 1: Up to 2 SFF SATA/NVMe – Option 2: Up to 6 EDSFF E3.S NVMe Maximum storage capacity: Up to 92.16TB Self-Encrypting Drive (SED) support |
| Expansion Slots | 3 PCIe 5.0 x16 slots (2 full-height, full-length; 1 half-length) 1 OCP 3.0 PCIe 5.0 x16 slot for additional network adapters |
| Cooling | 4 Hot-Pluggable 2U Standard Fans (optional upgrade to 2U Performance Fans) |
| Power Supply | Dual Flex-Slot Power Supply support for redundancy (1 standard, 1 optional) |
| Networking | iLO Management Port for remote management NIC Status LED Optional OCP 3.0 PCIe 5.0 x16 slot for customizable network adapters |
| I/O Ports | 1 DisplayPort 2 USB 3.2 Gen1 Ports |
| Security | – Kensington Lock – Access Panel Keys – Chassis Intrusion Detection Switch – HPE Silicon Root of Trust – iDevID, Platform Certificates, TPM 2.0 |
| Management | HPE iLO 6 with Intelligent Provisioning Optional: iLO Advanced, iLO Advanced Premium Security Edition HPE GreenLake for Compute Ops Management compatible |
| Environmental Support | Operating Temperature: -5°C to 55°C Bezel with air filter for dust protection |
| Dimensions | 15 inches wide x 16 inches deep (without bezel), 20 inches deep (with bezel) |
| Mounting Options | Wall, Desk, and Rack mountable |
| Additional Features | NS204i-u Boot Device (optional) |
HPE ProLiant DL145 G11 Design and build
Measuring 15 inches wide and 16 inches deep without the bezel (or 20 inches with it), the DL145 is designed to be tucked into cramped spaces. So, if space is tight in your use case, its compact form factor will be a huge benefit.
The front panel of the HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11 offers plenty of flexibility and expandability. With three PCIe 5.0 x16 slots, two full-height and full-length, you can add high-performance components like GPUs or additional networking cards. The third slot provides a half-length option for smaller expansion cards.
The Flex-Slot Power Supplies are another great feature, offering hot-swappable, redundant power options. You get one standard unit with the option to add a second for redundancy, which is vital for environments where uptime is critical. These supplies can be swapped out easily without powering down the system, which keeps things running smoothly during maintenance.
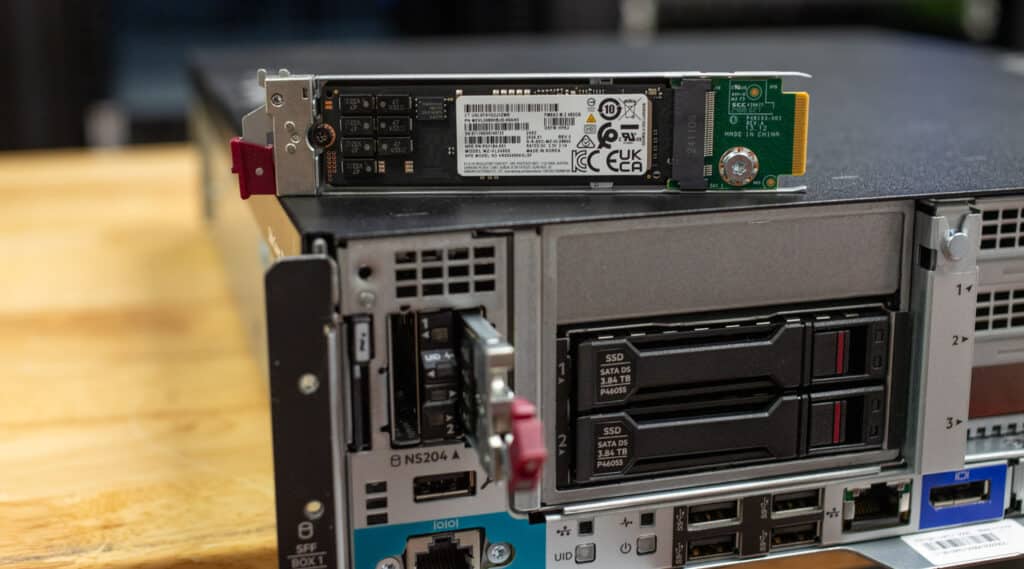
The HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11 also features a handy NS204 port on the front panel, designed specifically for HPE’s NS204i-u boot device. This module holds dual M.2 SSDs in a RAID 1 setup, creating a secure, dedicated space just for the server’s operating system. By keeping the OS on this separate boot device, you free up the main storage drives entirely for application data, ensuring that the system boots reliably and independently from the primary storage.
The iLO Management Port allows remote access, while the OCP 3.0 PCIe 5.0 x16 slot offers customizable high-speed network connectivity for networking and management. You’ve also got USB 3.2 Gen1 ports for peripherals and a DisplayPort for direct video output. LEDs for system health, power, and NIC status provide quick visual cues to help with troubleshooting, and the Unit ID button makes identifying the server in a busy rack setup easy. On the storage side, you will see that it can handle either 2 SFF SATA/NVMe drives or 6 EDSFF E3.S NVMe drives, giving you options for both high-capacity and high-speed storage setups.
The rear panel includes Access Panel Keys, which allow quick access to the internal components. This provides a secure method for technicians to perform upgrades or maintenance without unnecessary downtime. There’s also a Kensington Lock option for environments requiring a higher level of physical security.
Opening the system up via the Quick Removal Access Panel made things easy. The panel provides tool-free access to the server’s internals, streamlining upgrades and maintenance tasks.
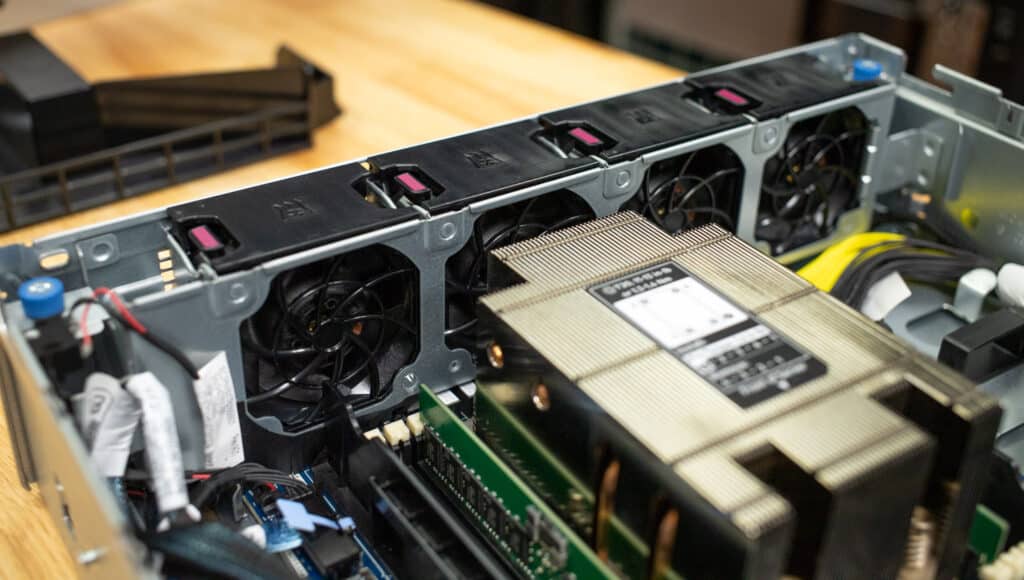
The AMD EPYC processor is at the server’s core, with a 2U heat sink to manage heat dissipation. Depending on the configuration, six DDR5 DIMM slots surround the processor, allowing for up to 768GB of memory.
The system includes four hot-pluggable 2U fans strategically placed around the chassis for cooling. These fans can be swapped out easily without shutting down the system, ensuring consistent cooling and minimizing downtime. If the system is operating in particularly challenging or high-temperature environments, there is also an option to upgrade to 2U performance fans.
Another important feature is the Chassis Intrusion Detection Switch, which adds a layer of security by notifying administrators if the chassis has been opened, protecting against unauthorized physical access. Overall, the internal design focuses on providing a balance between performance, security, and ease of service.
HPE ProLiant DL145 G11 HPE iLO Management
HPE’s Integrated Lights-Out (iLO) management suite is a comprehensive tool designed for managing servers remotely. It is especially useful for administrators who need to maintain and monitor multiple systems without constant physical access. The iLO platform offers a range of features for monitoring system health, power consumption, thermal performance, and security, allowing administrators to optimize the server’s performance and troubleshoot issues efficiently. Below is a rundown of its main features and how they will help administrators.
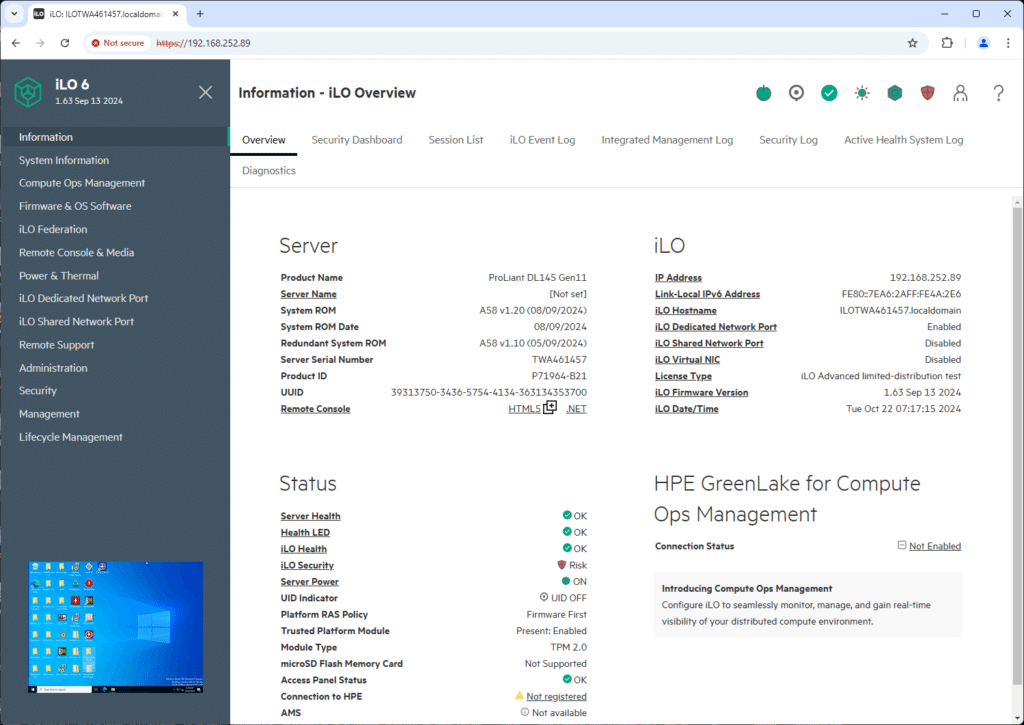
The main Overview dashboard provides vital system information, such as the server model (in this case, the ProLiant DL145 Gen11), system health, and basic details about the iLO configuration, including the firmware version.
This overview is the starting point for any administrator. It offers a concise look at the server’s current operational status and highlights important metrics such as server health, iLO security, and power status. The HPE GreenLake for Compute Ops Management integration is shown here, indicating that the system can be integrated into a broader cloud management framework. This is a major plus for administrators managing hybrid cloud environments, providing real-time visibility into distributed computing resources.
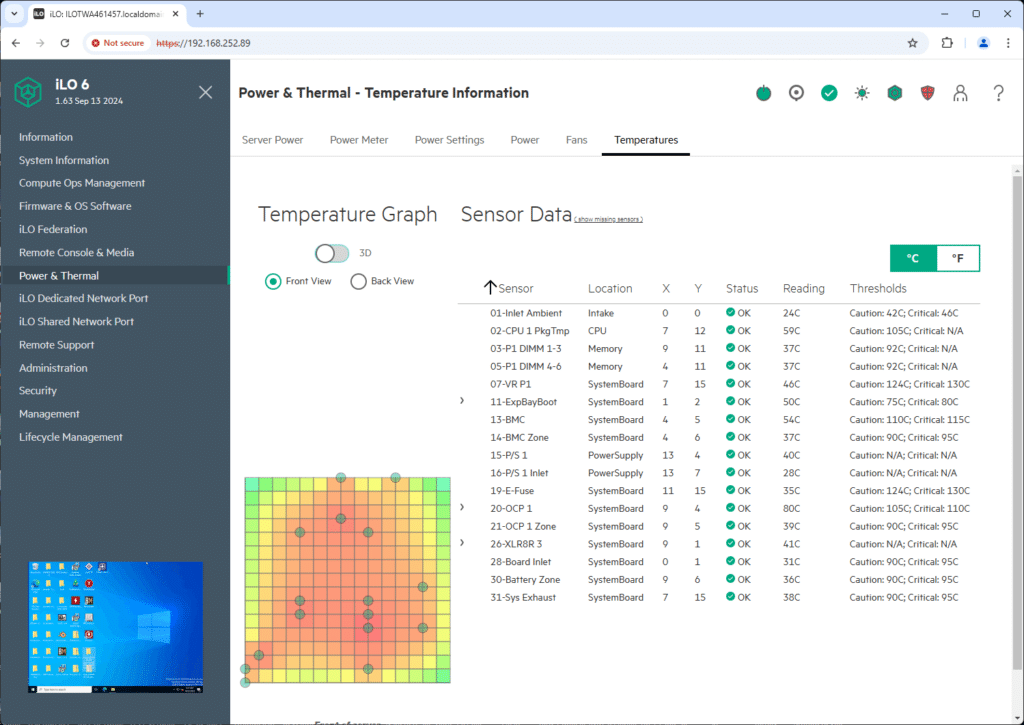
The Power & Thermal – Temperature Information area is important for monitoring the server’s thermal performance. The temperature graph shows a color-coded map of the server’s internal temperatures, making it easy to identify hotspots and areas where the system might be under thermal stress. The Sensor Data table on the right provides detailed readings for components like the CPU, memory, and system board, with specific thresholds for caution and critical temperatures.
This allows administrators to monitor specific areas prone to overheating and take preemptive measures, such as adjusting fan speeds or redistributing workloads, to prevent hardware failures. This makes it easier to maintain server health in real-time.
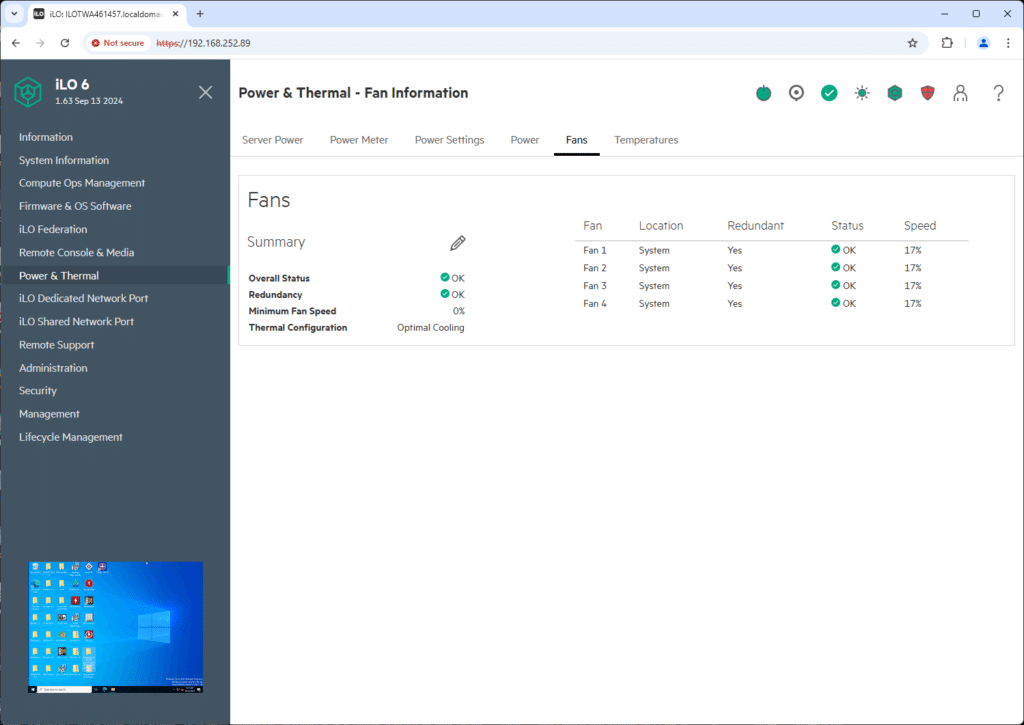
Next, we have the Power & Thermal—Fan Information section. Here, iLO summarizes the system’s cooling status, showing the overall condition of the fans, redundancy, and fan speeds. In this case, all fans function correctly, with redundancy enabled, safeguarding the system against a potential fan failure.
Seeing the minimum fan speed and current configuration (e.g., “Optimal Cooling”) allows users to make decisions based on cooling performance versus energy consumption. While the interface is not overloaded with unnecessary information, it provides enough detail to confirm that cooling is functioning as expected.
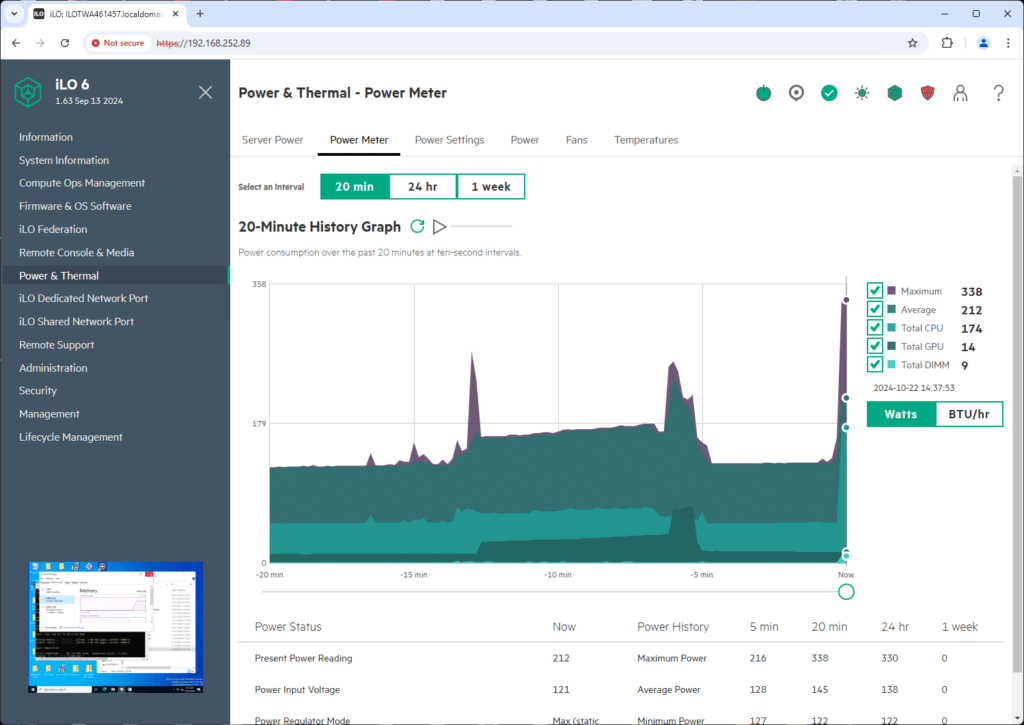
The Power & Thermal – Power Meter section showcases a power consumption graph over time. Selecting intervals like 20 minutes, 24 hours, or a week offers flexibility in analyzing power trends, particularly useful for identifying consumption spikes or inefficiencies.
The graph also breaks down power consumption across various components, including CPU, GPU, and DIMMs, giving administrators visibility into how power is being used by specific hardware. The summary table below shows key metrics like the present power reading and historical maximums, offering an at-a-glance view of power performance.
This tool is very useful for organizations aiming to manage power consumption closely—either for environmental concerns or cost reduction. It lets administrators identify periods of peak consumption and adjust accordingly, whether through power capping, workload balancing, or hardware upgrades.
Overall, we found HPE’s iLO suite very intuitive. It offers a comprehensive set of tools that allow administrators to manage and monitor their servers remotely with confidence. It strikes a nice balance between providing detailed data for power users and keeping the interface clear enough for less-experienced administrators to navigate efficiently.
HPE ProLiant DL145 G11 Performance
We tested the HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11 configured as follows :
- Windows Server 2022 Standard
- AMD EPYC 8434p 48-Core Processor, 2500 Mhz, 48 Core(s), 96 Logical Processor
- NVIDIA L4
- 64 GB, DDR5
- Samsung PM893 3.8TB SSD
For comparison, we also added results from the PowerEdge XR7920, which has the following configuration:
- Windows Server 2022 Standard
- 2 x Xeon Gold 6426Y – 16-core 2.5GHz
- NVIDIA L4
- 128GB DDR5
- 480GB BOSS RAID1
Our performance tests will compare the HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11 with the Dell PowerEdge XR7920. As we indicated above, the DL145 Gen11 is powered by a 48-core AMD EPYC 8434P processor, 64 GB of DDR5 memory, and an NVIDIA L4, making it built for handling demanding, data-intensive tasks. The PowerEdge XR7920 features two 16-core Intel Xeon Gold 6426Y processors, 128GB of DDR5 memory, and an NVIDIA L4.
Luxmark
In the LuxMark benchmarking test, which evaluates OpenCL performance by rendering complex 3D scenes, the HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11 demonstrates respectable results. With the AMD EPYC 8434 processor and 64GB of RAM, the system scored 11,828 in the Hallbench test and 4,716 in the Food scene test. These results reflect solid OpenCL compute performance, particularly in rendering tasks that rely heavily on parallel processing.
| Luxmark (Higher is better) | HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11 (NVIDIA L4) |
| Hallbench | 11,828 |
| food | 4,716 |
OctaneBench
In the OctaneBench benchmark, which evaluates performance on OctaneRender, the HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11 powered by the AMD EPYC 8434 with 64 GB of RAM provides competitive results across a variety of test kernels.
Scores varied depending on the rendering scenario, with the system performing strongest in Path Tracing tests, scoring up to 52.35 in the ATV kernel, and Direct Lighting, reaching 41.43 in the same kernel. For scenarios requiring detailed visibility, like Info Channels, the server showed respectable scores across all models, peaking at 20.43. ButOverall, the DL145 Gen11 demonstrates reliable performance in both lighting and rendering-focused workloads.
| OctaneBench (Score, higher is better) | Kernel | HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11 (NVIDIA L4) |
| Interior | Info channels | 14.95 |
| Interior | Direct lighting | 41.02 |
| Interior | Path tracing | 48.41 |
| Idea | Info channels | 8.30 |
| Idea | Direct lighting | 32.07 |
| Idea | Path tracing | 38.46 |
| ATV | Info channels | 20.43 |
| ATV | Direct lighting | 41.43 |
| ATV | Path tracing | 52.35 |
| Box | Info channels | 11.56 |
| Box | Direct lighting | 38.57 |
| Box | Path tracing | 42.41 |
7-Zip Compression
The 7-Zip Compression Benchmark is a performance test that evaluates a computer’s ability to compress and decompress files using the 7-Zip utility. It provides a measure of the CPU’s speed and efficiency during these tasks, with higher scores indicating better performance.
During the compression phase, the ProLiant DL145 Gen11 reported a current rating of 122.462 GIPS, with a resulting rating of 122.364 GIPS. Despite the higher CPU usage at over 2800% for the ProLiant, these ratings reflect the server’s ability to handle intense compression tasks with greater speed and efficiency.
In the decompression phase, the ProLiant was measured with a current rating of 146.193 GIPS and a resulting rating of 146.453 GIPS. The ProLiant’s AMD EPYC 8434 processor excels in these tasks, indicating its superior ability to manage large datasets and compress/decompress them efficiently.
The total rating for the HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11 was 134.408 GIPS. This shows that, in terms of compression and decompression workloads, the ProLiant DL145 Gen11 can handle intensive tasks, making it ideal for scenarios where large file sets need to be processed frequently, such as in backup, archiving, or data migration workloads. The high GIPS ratings indicate robust multithreaded performance, especially useful for enterprise environments requiring quick and reliable compression.
| 7-Zip Compression Benchmark (Higher is better) | HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11(AMD EPYC 8434, 64 GB) | |
| Compressing | ||
| Current CPU Usage | 2872% | |
| Current Rating/Usage | 4.264 GIPS | |
| Current Rating | 122.462 GIPS | |
| Resulting CPU Usage | 2846% | |
| Resulting Rating/Usage | 4.300 GIPS | |
| Resulting Rating | 122.364 GIPS | |
| Decompressing | ||
| Current CPU Usage | 3083% | |
| Current Rating/Usage | 4.742 GIPS | |
| Current Rating | 146.193 GIPS | |
| Resulting CPU Usage | 3061% | |
| Resulting Rating/Usage | 4.785 GIPS | |
| Resulting Rating | 146.453 GIPS | |
| Total Rating | ||
| Total CPU Usage | 2953% | |
| Total Rating/Usage | 4.543 GIPS | |
| Total Rating | 134.408 GIPS | |
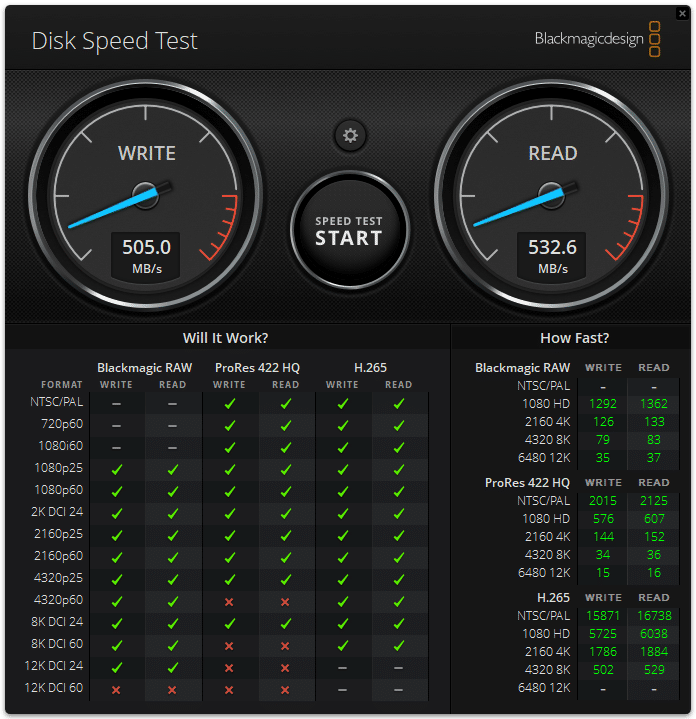
Blackmagic Disk Speed Test
In the Blackmagic Disk Speed Test, the HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11 with its primary storage drive outperformed the Dell PowerEdge T360 in both read and write speeds. The ProLiant DL145 Gen11 achieved 532.6 MB/s read and 505.0 MB/s write.
Blackmagic CPU Speed Test
The Blackmagic RAW Speed Test evaluates a system’s CPU performance by measuring how many frames per second it can process different resolutions and compression settings of Blackmagic RAW footage.
As expected, the HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11 can handles high-resolution video processing tasks very well, as shown by the Blackmagic RAW Speed Test results of 106 FPS (CPU) and 155 FPS (CUDA) at 8K resolution.
UL Procyon AI Inference
UL’s Procyon estimates a workstation’s performance for professional apps. Specifically, it measures the performance of various AI inference engines using standard machine vision tasks such as image classification, segmentation, object detection, and super-resolution. This benchmark helps determine the efficiency of hardware in executing AI workloads, with lower inference times indicating better performance.
The ProLiant DL145 Gen11 showed solid efficiency in more demanding models, achieving significantly lower inference times in ResNet 50, , DeepLab V3, and YOLO V3 . Additionally, the Real-ESRGAN super-resolution task showed a strong response time of 2727.03 ms, which is crucial for tasks requiring high-quality upscaling.
The HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11 achieved an overall score of 115, making it a better choice for AI-driven applications.
| UL Procyon Average Inference Times (ms, Lower is better) | HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11(AMD EPYC 8434, 64 GB) |
| MobileNet V3 | 3.20 |
| ResNet 50 | 11.49 |
| Inception V4 | 35.07 |
| DeepLab V3 | 34.01 |
| YOLO V3 | 53.44 |
| Real-ESRGAN | 2727.03 |
| Overall Score | 115 |
y-cruncher
y-cruncher is a multi-threaded and scalable program that can compute Pi and other mathematical constants to trillions of digits. Since its launch in 2009, it has become a popular benchmarking and stress-testing application for overclockers and hardware enthusiasts.
The DL145 Gen11 handles this test exceptionally well. For instance, it completes 1 billion digits in just 19.5 seconds, while the Dell PowerEdge XR7920 measured 9.805 seconds with its twin-processor configuration. As the workload scales, the DL145 Gen11 calculates 10 billion digits in 228.5 seconds. The single processor setup while more compact than the Dell PowerEdge XR7920, trailed some in this CPU-heavy workload.
| y-cruncher (Total Computation time; lower is better) | Dell PowerEdge XR7920 (2 x Xeon Gold 6426Y 16c, 128GB DDR5) | HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11(AMD EPYC 8434, 64 GB) |
| 1 billion digits | 9.805s | 19.506s |
| 2.5 billion | 27.344s | 50.262s |
| 5 billion | 60.564s | 106.319s |
| 10 billion | 133.100s | 228.507s |
Geekbench 6
Geekbench 6 is a cross-platform benchmark that measures overall system performance. You can find comparisons to any system you want in the Geekbench Browser. The benchmark scores are calibrated against a baseline score of 2500, typically represented by an Intel Core i7-12700 processor, with higher scores indicating better performance.
In the Geekbench 6 benchmark, the HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11’s AMD EPYC 8434 CPU trailed the twin Intel CPUs inside the Dell PowerEdge XR7920 slightly. The Dell PowerEdge XR7920 showed solid single-core results at 1,864 (compared to the ProLiant’s 1,705), and higher multi-core performance as well. The DL145 Gen11 scored 15,915 in multi-core performance, up against the 16,507 from the PowerEdge XR7920 with the dual Intel Xeon configuration.
| Geekbench 6 (Higher is better) | Dell PowerEdge XR7920 (2 x Xeon Gold 6426Y 16c, 128GB DDR5) | HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11(AMD EPYC 8434, 64 GB) |
| CPU Single-Core | 1,864 | 1,705 |
| CPU Multi-Core | 16,507 | 15,915 |
| GPU | N/A | 145,673 |
Cinebench R23
Cinebench R23 is a benchmark tool that evaluates a system’s CPU performance by rendering a complex 3D scene using the Cinema 4D engine.
The HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11 showcases superior multi-core performance, achieving an impressive score of 58,546 points, significantly outpacing the XR7920. Its single-core score of 1,095 points, while lower than the Xr7920, is still solid performance.
| Cinebench R23 (Higher is better) | Dell PowerEdge XR7920 (2 x Xeon Gold 6426Y 16c, 128GB DDR5) | HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11(AMD EPYC 8434, 64 GB) |
| Multi-Core | 46,544 pts | 58,546 pts |
| Single-Core | 1,292 pts | 1,095 pts |
Cinebench 2024
Here, the HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11 continues to dominate in multi-core performance with a score of 3,246 points and a notable GPU score of 13,075 points, showcasing its capabilities in more graphics-intensive applications. At the time we tested the Dell PowerEdge XR7920 we didn’t measure the performance of the NVIDIA L4 inside of it, which being the same GPU should offer similar if not identical performance.
| Cinebench R24 (Higher is better) | Dell PowerEdge XR7920 (2 x Xeon Gold 6426Y 16c, 128GB DDR5) | HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11(AMD EPYC 8434, 64 GB) |
| Multi-Core | 2,383 pts | 3,246 pts |
| Single-Core | 73 pts | 68 pts |
| GPU | N/A | 13,075 pts |
Conclusion
The HPE ProLiant DL145 Gen11 makes a strong case for itself in the edge computing arena. Its compact size doesn’t hold it back from delivering impressive performance, thanks to the AMD EPYC 8004 processors ranging from 8 to 64 cores. The flexibility in storage options, including support for up to six EDSFF E3.S drives, means it can handle various data-intensive tasks without breaking a sweat.
The DL145 Gen11 is also designed to thrive in challenging environments with temperatures ranging from -5°C to 55°C. Its air-filtered bezel provides added dust protection, making it particularly well-suited for industrial or remote deployments where environmental conditions are less controlled. Moreover, security features like HPE’s Silicon Root of Trust and TPM 2.0 add an extra layer of confidence, especially when deploying at the edge where physical security can be a concern. Moreover, the iLO management suite simplifies remote monitoring and maintenance, which is very important for administrators.
Regarding performance, the DL145 Gen11 holds its own for a compact edge platform. It’s not just about raw power; the server offers a good balance of expandability, energy efficiency, and robust management features. If you’re in sectors like retail, manufacturing, or telecommunications and need a reliable edge server that doesn’t compromise on performance or flexibility, the DL145 Gen11 is one of our new favorite edge platforms.
Engage with StorageReview
Newsletter | YouTube | Podcast iTunes/Spotify | Instagram | Twitter | TikTok | RSS Feed