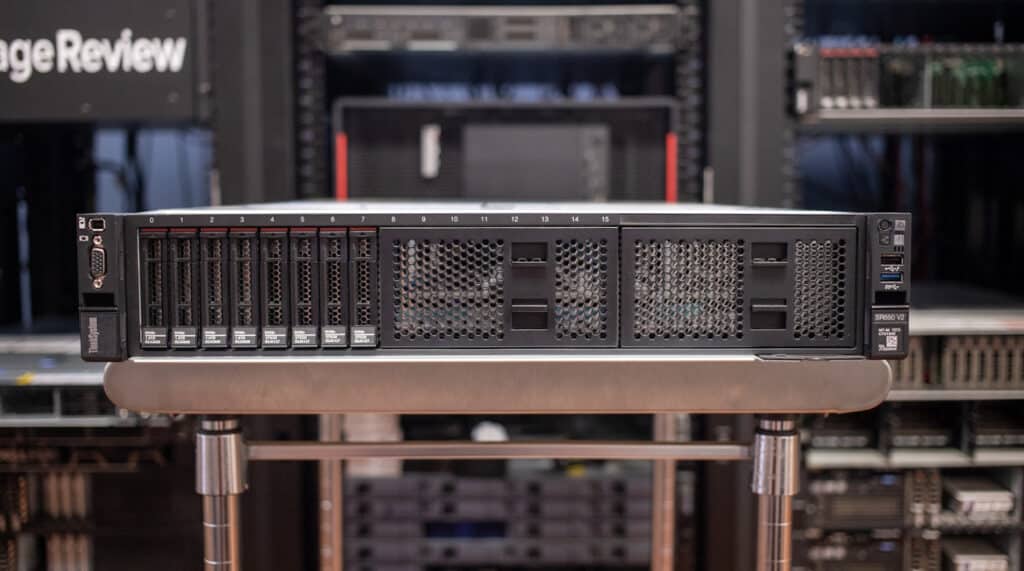
Even more versatile in its second generation, the Lenovo ThinkSystem SR650 V2 is a mainstream server ideally suited for cloud storage, VDI, HPC, compute, and enterprise applications. This 2U, two-socket server is configurable with 40 storage drives or eight GPUs and 8TB of RAM.
Even more versatile in its second generation, the Lenovo ThinkSystem SR650 V2 is a mainstream server ideally suited for cloud storage, VDI, HPC, compute, and enterprise applications. This 2U, two-socket server is configurable with 40 storage drives or eight GPUs and 8TB of RAM.

Lenovo ThinkSystem SR650 V2 Specifications
The SR650 V2 significantly improves on the SR650 by offering newer technology and superior expansion (for instance, 40 cores per CPU versus 28, 32 total DIMMs versus 24, and 40 2.5-inch bays versus 26). Lenovo’s goal was to better leverage every square inch of space.
The SR650 V2’s impressive flexibility allows this server to be tailored for any workflow. For GPU power, it houses three double-wide or eight single-wide cards. For pure storage, it scales to 40 2.5-inch drives (24 hot-swap along the front, eight in the middle bays, and eight in the rear bays) or 20 3.5-inch (12 hot-swap front, four middle, and four rear). Meanwhile, the server’s OS can go on two M.2 drives (onboard RAID 1) or a hot-swap, RAID-supporting 2.5-inch rear drive bay.
The Lenovo ThinkSystem SR650 V2 CPU choices also impress, with one or two third-generation Intel Xeon Scalable “Ice Lake” processors, up to 40 cores and 270W TDP per socket. Each socket has 16 DIMM slots supporting eight channels; the maximum supported memory is 8TB using 256GB 3DS RDIMMs. The SR650 V2 also supports Intel Persistent Memory 200 series in 16 of the DIMM slots, making it an ideal database platform.
If you don’t need the SR650 V2’s expansion, Lenovo’s two-socket ThinkSystem SR630 V2 offers the same processor and memory options as the SR650 V2 in only 1U of space. It just depends on how much density vs. expansion your applications require.
For remote management, the SR650 V2 has a built-in XClarity Controller (XCC) for remote management. We did a rundown on XCC’s capabilities in SR630 V2 review linked above and our ThinkEdge SE450 review. In short, we found it intuitive and feature-rich. The XClarity app is available for Android and iOS. The SR650 V2 also has a dedicated USB port for a diagnostic handset, useful in datacenters where mobile devices aren’t allowed. The server can be ordered with a front diagnostics display if you’re willing to sacrifice drive bays.
The SR650 V2’s full specifications are as follows.
| Components | Specification |
| Machine types |
|
| Form factor | 2U rack |
| Processor | One or two third-generation Intel Xeon Scalable processor (formerly codenamed “Ice Lake”). Supports processors up to 40 cores, core speeds of up to 3.6 GHz, and TDP ratings of up to 270W. |
| Chipset | Intel C621A “Lewisburg” chipset, part of the platform codenamed “Whitley” |
| Memory | 32 DIMM slots with two processors (16 DIMM slots per processor). Each processor has 8 memory channels, with 2 DIMMs per channel (DPC). Lenovo TruDDR4 RDIMMs and 3DS RDIMMs are supported. DIMM slots are shared between standard system memory and persistent memory. DIMMs operate at up to 3200 MHz at 2 DPC. |
| Persistent memory | Supports up to 16x Intel Optane Persistent Memory 200 Series modules (8 per processor) installed in the DIMM slots. Persistent memory (Pmem) is installed in combination with system memory DIMMs. |
| Memory maximum | With RDIMMs: Up to 8TB by using 32x 256GB 3DS RDIMMs With Persistent Memory: Up to 12TB by using 16x 256GB 3DS RDIMMs and 16x 512GB Pmem modules |
| Memory protection | ECC, SDDC (for x4-based memory DIMMs), ADDDC (for x4-based memory DIMMs, requires Platinum or Gold processors), and memory mirroring. |
| Disk drive bays | Up to 20x 3.5-inch or 40x 2.5-inch hot-swap drive bays:
The server also supports these drives for OS boot or drive storage:
See Supported drive bay combinations for details. |
| Maximum internal storage |
|
| Storage controller |
|
| Optical drive bays | No internal optical drive |
| Tape drive bays | No internal backup drive |
| Network interfaces | Dedicated OCP 3.0 SFF slot with PCIe 4.0 x16 host interface. Supports a variety of 2-port and 4-port adapters with 1GbE, 10GbE and 25GbE network connectivity. One port can optionally be shared with the XClarity Controller (XCC) management processor for Wake-on-LAN and NC-SI support. |
| PCIe slots |
|
| GPU support | Supports up to 8x single-wide GPUs or up to 3x double-wide GPUs |
| Ports |
|
| Cooling | 6x (with two processors installed) or 5x (with one processor installed) single-rotor or dual-rotor hot swap 60 mm fans, configuration dependent. Fans are N+1 redundant, tolerating a single-rotor failure. One fan integrated in each power supply. |
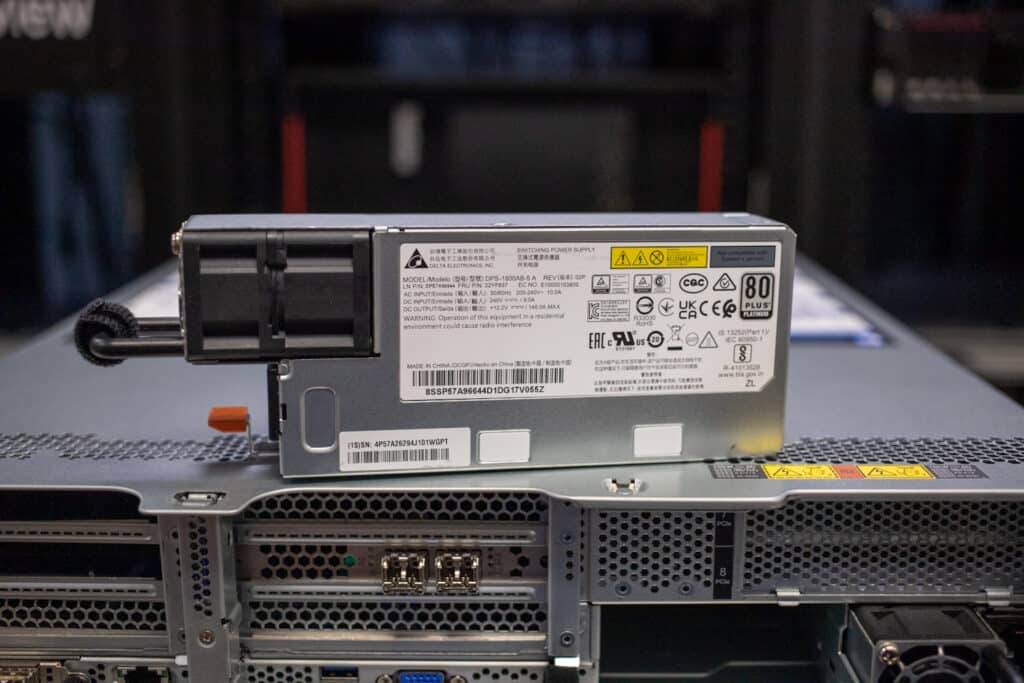
| Power supply | Up to two hot-swap redundant AC power supplies, 80 PLUS Platinum or 80 PLUS Titanium certification. 500 W, 750 W, 1100 W and 1800 W AC options, supporting 220 V AC. 500 W, 750 W and 1100 W options also support 110V input supply. In China only, all power supply options support 240 V DC. Also available is a 1100W power supply with a -48V DC input. |
| Video | G200 graphics with 16 MB memory with 2D hardware accelerator, integrated into the XClarity Controller. Maximum resolution is 1920×1200 32bpp at 60Hz. |
| Hot-swap parts | Drives, power supplies, and fans. |
| Systems management | Operator panel with status LEDs. Optional External Diagnostics Handset with LCD display. Models with 8x or 16x 2.5-inch front drive bays can optionally support an Integrated Diagnostics Panel. XClarity Controller (XCC) embedded management, XClarity Administrator centralized infrastructure delivery, XClarity Integrator plugins, and XClarity Energy Manager centralized server power management. Optional XClarity Controller Advanced and Enterprise to enable remote control functions. |
| Security features | Chassis intrusion switch, Power-on password, administrator’s password, Trusted Platform Module (TPM), supporting TPM 2.0. In China only, optional Nationz TPM 2.0. Optional lockable front security bezel. |
| Operating systems supported | Microsoft Windows Server, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, VMware ESXi. See the Operating system support section for specifics. |
| Limited warranty | Three-year or one-year (model dependent) customer-replaceable unit and onsite limited warranty with 9×5 next business day (NBD). |
| Service and support | Optional service upgrades are available through Lenovo Services: 4-hour or 2-hour response time, 6-hour fix time, 1-year or 2-year warranty extension, software support for Lenovo hardware and some third-party applications. |
| Dimensions | Width: 445 mm (17.5 in.), height: 87 mm (3.4 in.), depth: 764 mm (30.1 in.). See Physical and electrical specifications for details. |
| Weight | Maximum: 38.8 kg (85.5 lb) |
Lenovo ThinkSystem SR650 V2 Build and Design
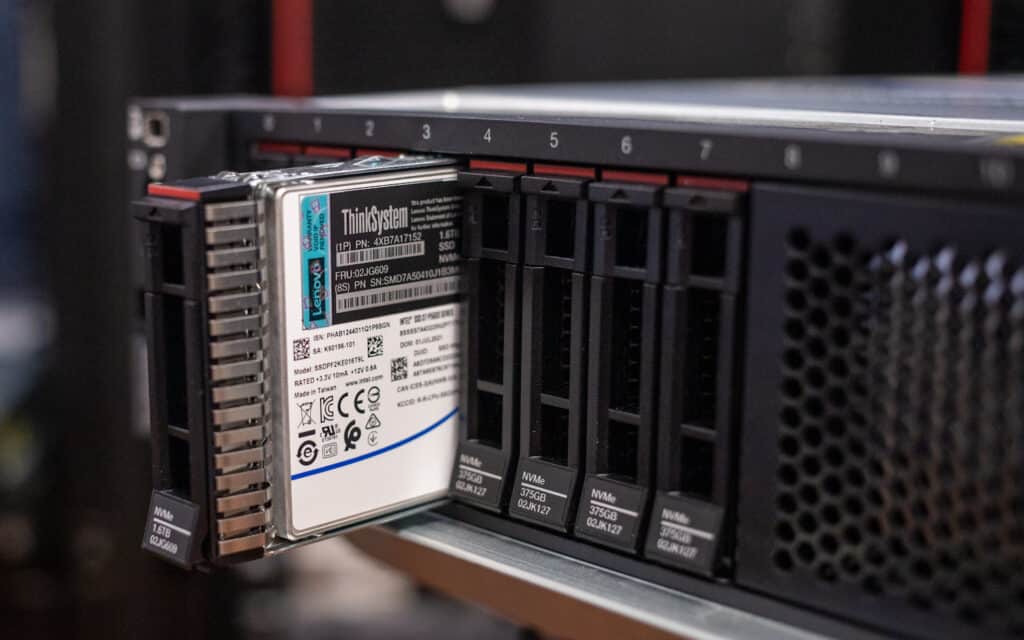
The ThinkSystem SR650 V2’s front panel is configurable for either 2.5-inch drives (8, 16, or 24 bays) or 3.5-inch drives (8 or 12 bays). The backplane can be switched after purchase should you wish to switch from 2.5-inch to 3.5-inch drives or vice versa. U.3 drives are supported with a RAID adapter. The server can also be ordered without drive bays. Our review model has eight 2.5-inch bays. Removing drives is a toolless affair; here’s one of the Solidigm 2.5-inch drives in its caddy.
Configurations with 2.5-inch drives can use the SR650 V2’s built-in RAID controller, which handles up to 12 drives, eliminating the need to use an expansion slot.
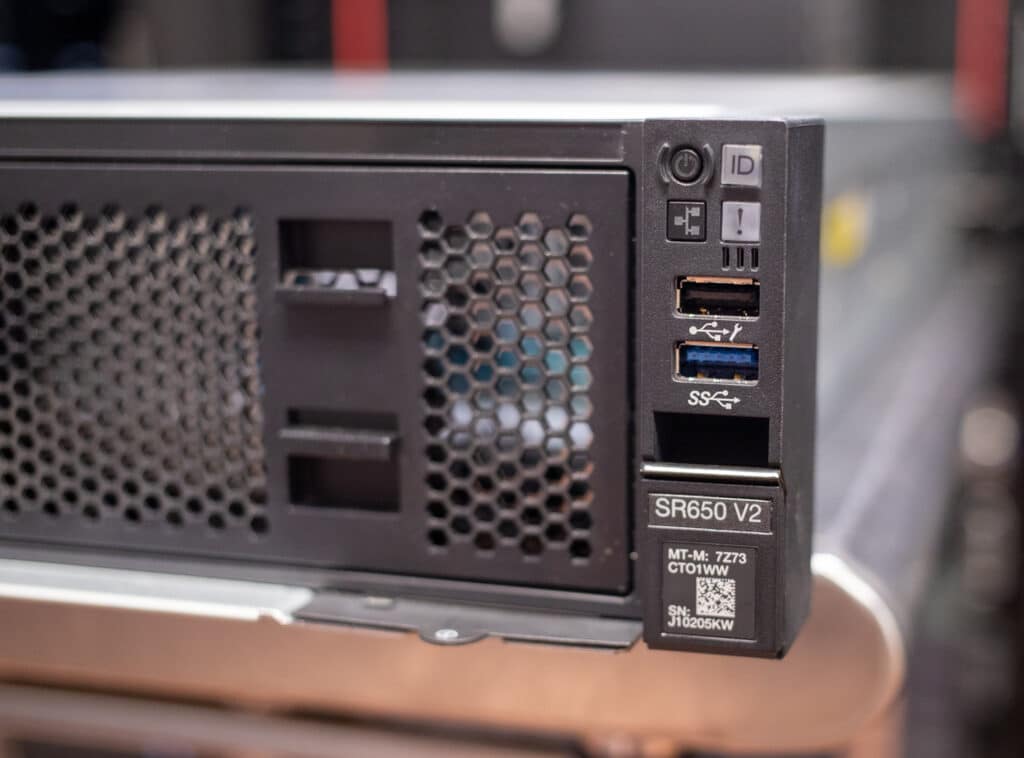
Front-panel connectivity starts with VGA output and a remote diagnostics connector for Lenovo’s XClarity handset, which reads data from the server’s XClarity Controller (XCC). The handset is cost-effective if you’re buying more than one server.
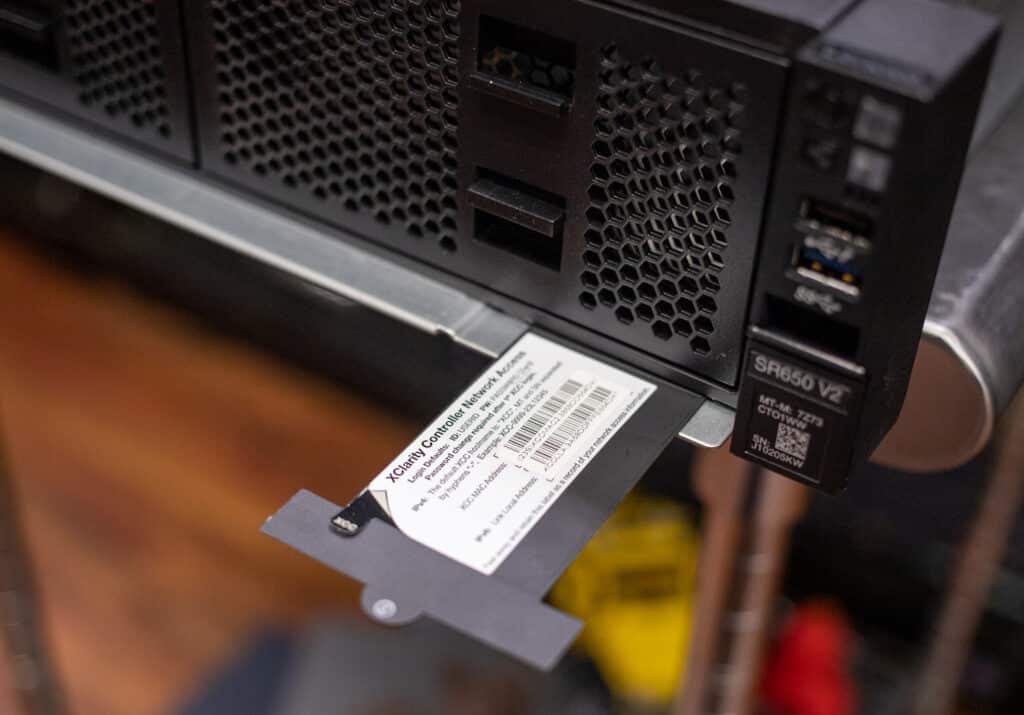
Lenovo also offers a built-in diagnostics display, though it requires sacrificing eight 2.5-inch bays. The XCC’s MAC and network address are on a pull tab on the front panel’s right edge.
Features on the front side include status indicators, a USB 2.0 diagnostics port (for connecting a mobile device via the XClarity app), a USB 3.2 Gen 1 (5Gbps) port, and the power button. For security, Lenovo offers a lockable front security bezel.
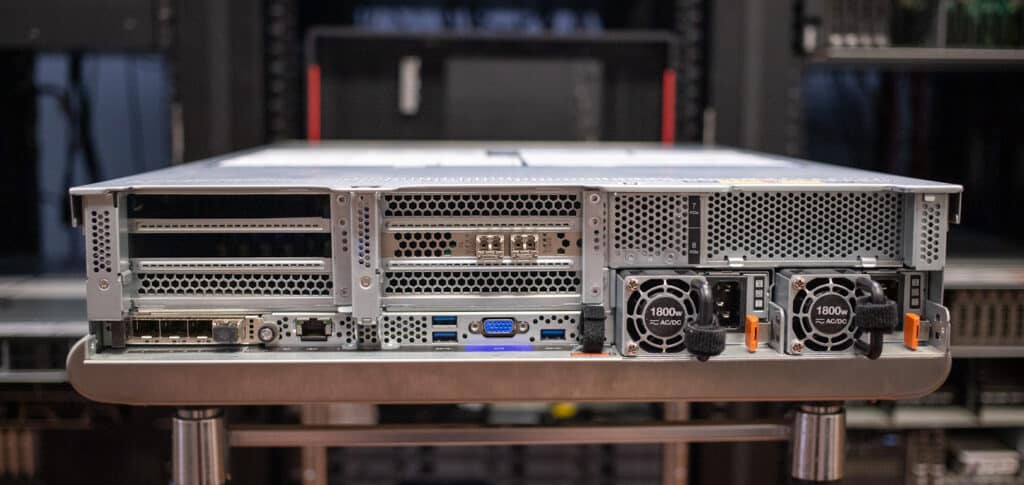
Rear connectivity includes 1Gbps Ethernet for IPMI, three USB 3.2 Gen 1 ports, and another VGA. The OCP 3.0 card in our unit, secured with a thumbscrew, has four Ethernet ports.
The 1,800-watt redundant hot-swappable power supplies are the most powerful that can be ordered in this server. The SR650 V2 can also be ordered with 500-, 750-, and 1,100-watt units.
Servicing the SR650 V2 is like most servers, though Lenovo goes the extra mile by including service diagrams on the top cover.
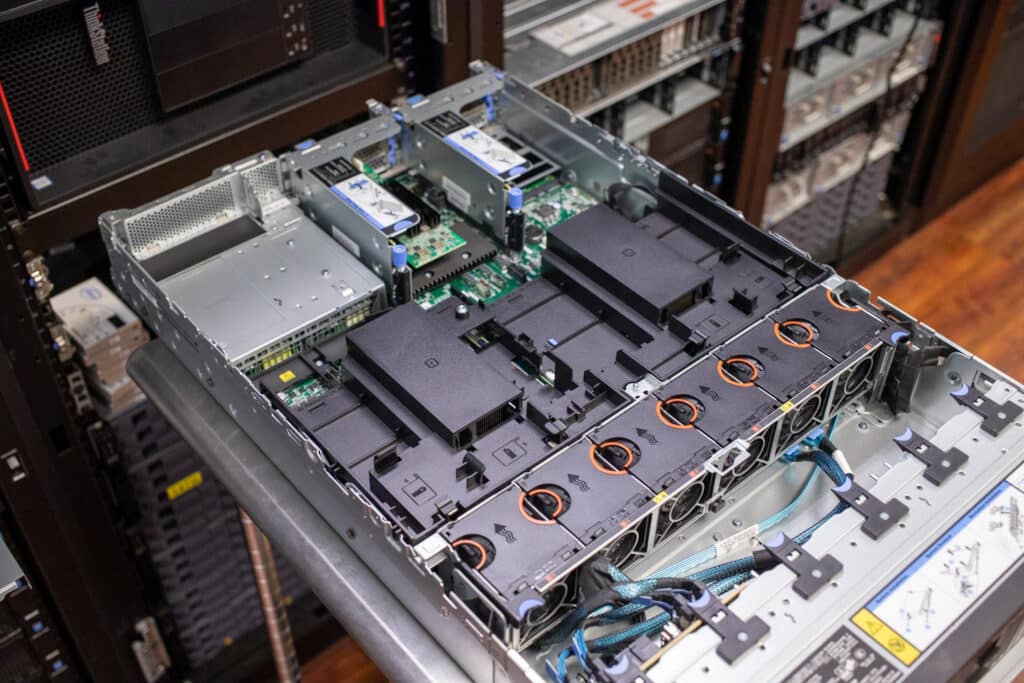
Removing the top cover reveals a tidy, well-laid-out interior. For security, the SR650 V2 has an intrusion prevention switch.
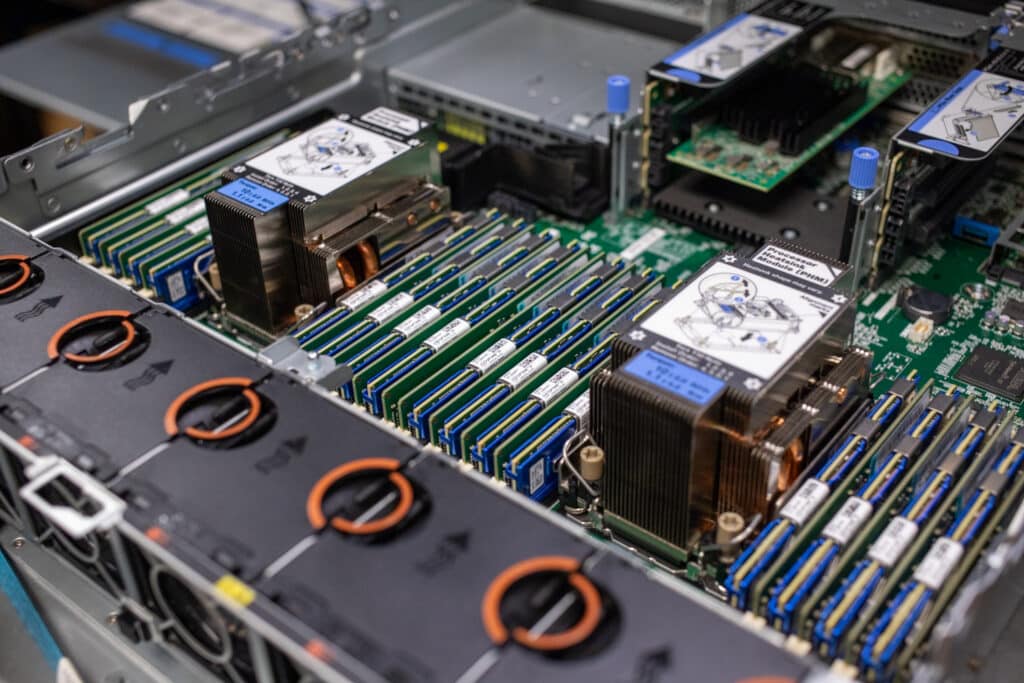
Our review model doesn’t have the mid-drive bays; they would go along the centerline and support eight 2.5-inch, four 3.5-inch drives, or M.2 adapters. Drives installed in those bays would lift out with a handle. Middle drive bays would be ordered for storage-focused deployments like SDS use cases. Servers so equipped would be limited to 205-watt TDP CPUs because of reduced airflow and would not support full-length adapter cards or GPUs.
The dual third-generation Xeon Silver 4314 processors in this unit have a 135-watt TDP and are topped by the standard heatsinks. Higher TDP chips may come with larger heatsinks; for this generation, Lenovo is offering heatsinks with auxiliary radiators that extend towards the centerline fans. Each CPU supports eight memory channels via 16 DIMM slots. Intel Persistent Memory Series 200 modules are supported.
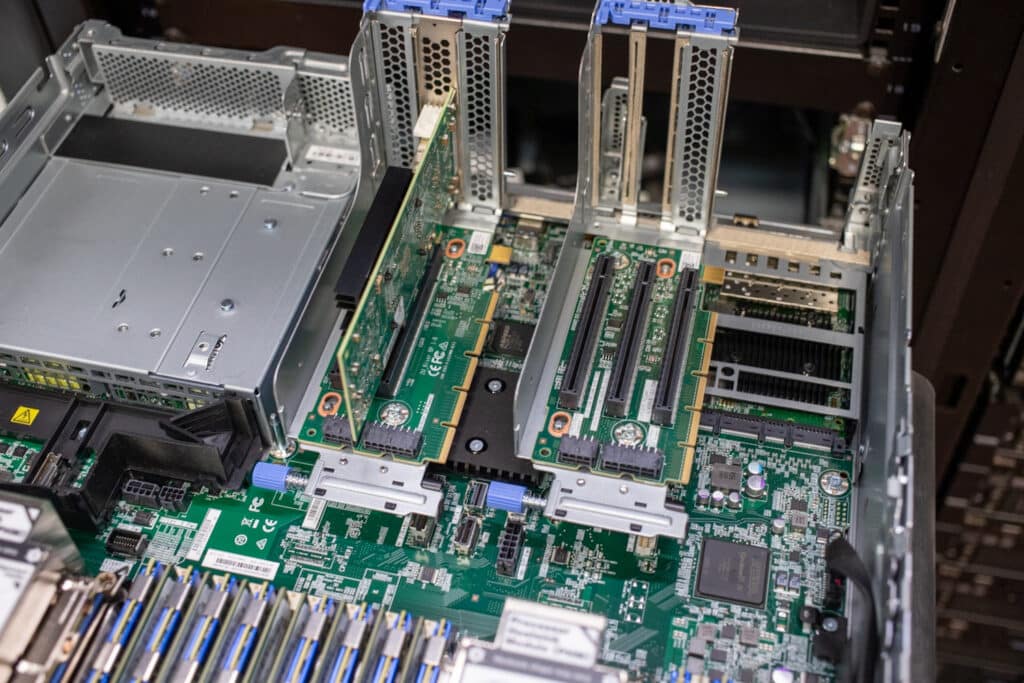
Our final stop is the expansion slots. The SR650 V2 has eight PCIe slots plus one OCP 3.0 SFF, all of which are PCIe 4.0. Three double-wide GPUs, such as the Nvidia A100, or eight single-wide GPUs, such as the Nvidia T4, are supported.
The expansion slots can be traded for storage; eight 2.5-inch or four 3.5-inch can fit in rear-facing bays. You can also opt for a pair of 2.5-inch/7mm hot-swap boot drives, which support RAID 1. The SR650 V2 also has two internal M.2 boot drive slots.
Lenovo ThinkSystem SR650 V2 Performance
We are testing the ThinkSystem SR650 V2 with the following hardware:
- 2x Intel Xeon Silver 4314 CPUs (Each 16-core/32-thread, 2.4GHz base, 3.2GHz Turbo, 24MB cache, 135W TDP)
- 256GB RAM (16x 16GB)
- 750W power supplies
- 6x Solidigm P5520 7.68TB Gen4 drives in JBOD
VDBench Workload Analysis
When it comes to benchmarking storage devices, application testing is best, and synthetic testing comes in second place. While not a perfect representation of actual workloads, synthetic tests do help to baseline storage devices with a repeatability factor that makes it easy to do apples-to-apples comparison between competing solutions.
These workloads offer a range of different testing profiles ranging from “four corners” tests, common database transfer size tests, as well as trace captures from different VDI environments. All of these tests leverage the common vdBench workload generator, with a scripting engine to automate and capture results over a large compute testing cluster. This allows us to repeat the same workloads across a wide range of storage devices, including flash arrays and individual storage devices.
Profiles:
- 4K Random Read: 100% Read, 128 threads, 0-120% iorate
- 4K Random Write: 100% Write, 128 threads, 0-120% iorate
- 64K Sequential Read: 100% Read, 32 threads, 0-120% iorate
- 64K Sequential Write: 100% Write, 16 threads, 0-120% iorate
- Synthetic Database: SQL and Oracle
- VDI Full Clone and Linked Clone Traces
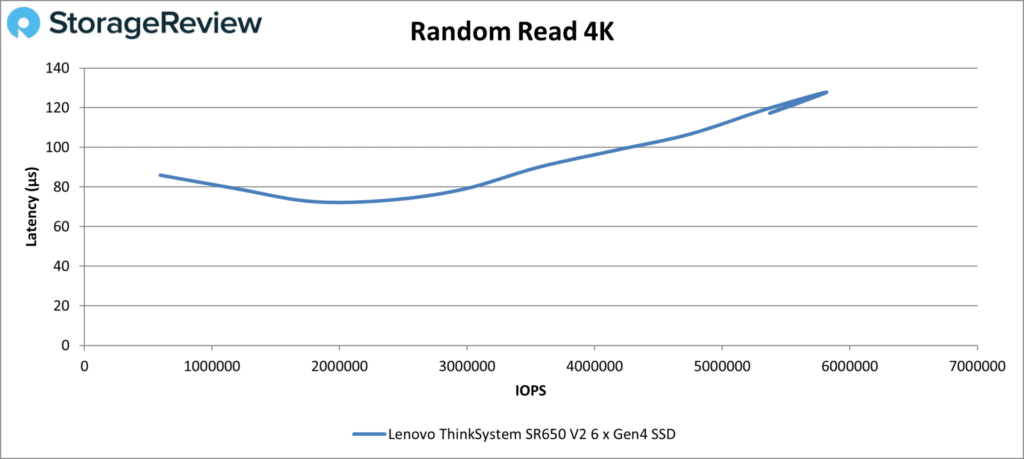
Our first test, Random Read 4K, saw the SR650 V2 putting up good numbers for testing with just six Gen4 drives. Latencies were below 100µs for most of the test; the final number was just over 5.7 million IOPS at 126µs.
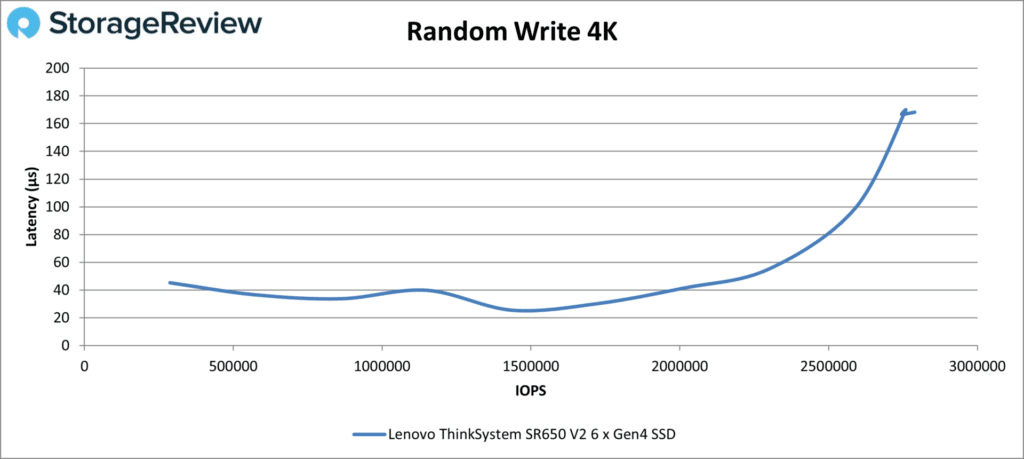
The Random Write 4K numbers were less impressive, with a large spike past about two million IOPS. The peak number was 2.79 million IOPS at 168µs, though before the spike it had achieved 2.59 million IOPS at sub-100µs.
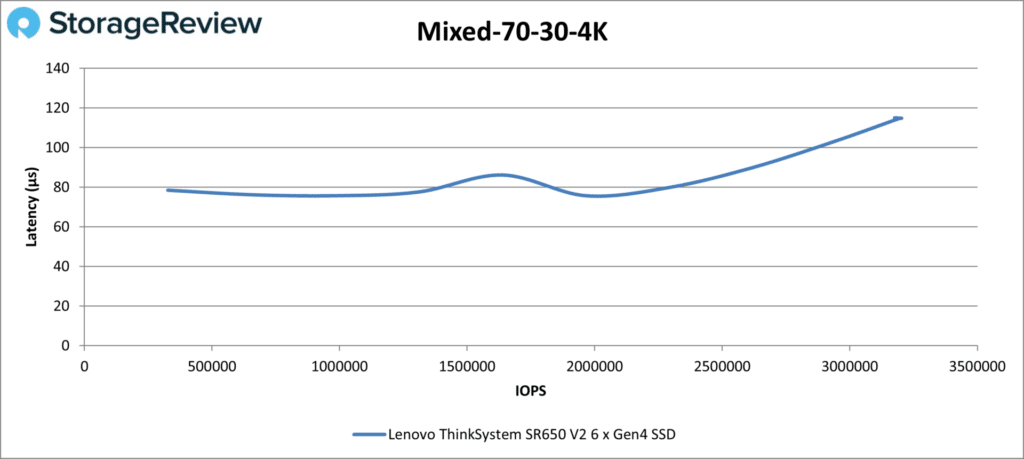
The Mixed 70-30 4K results show a curve similar to Random Read 4K. Latency was low; the SR650 V2 achieved 3.18 million IOPS at 115µs.
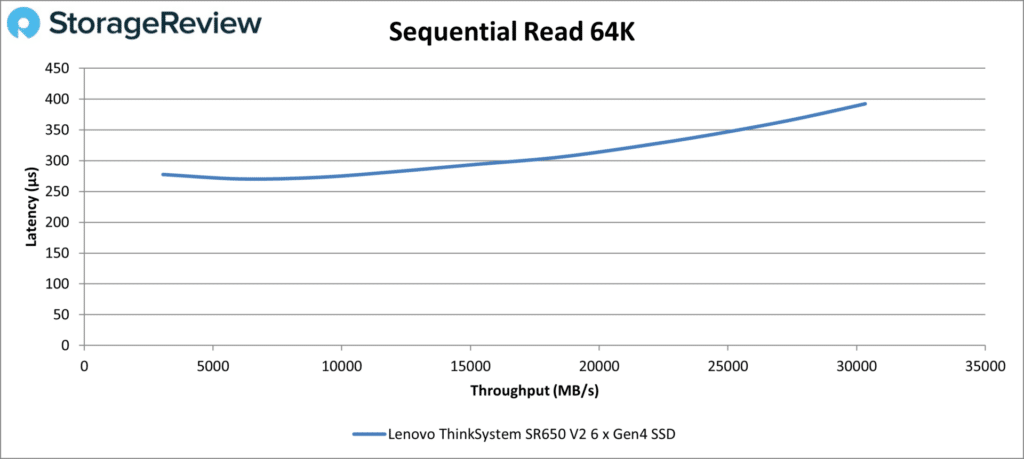
Our 64K sequential tests are next. Starting with Read, the SR650 V2 maintained a steady, stable line and did about as well as could be expected given our configuration. The top number was 30,320MB/s at 392µs.
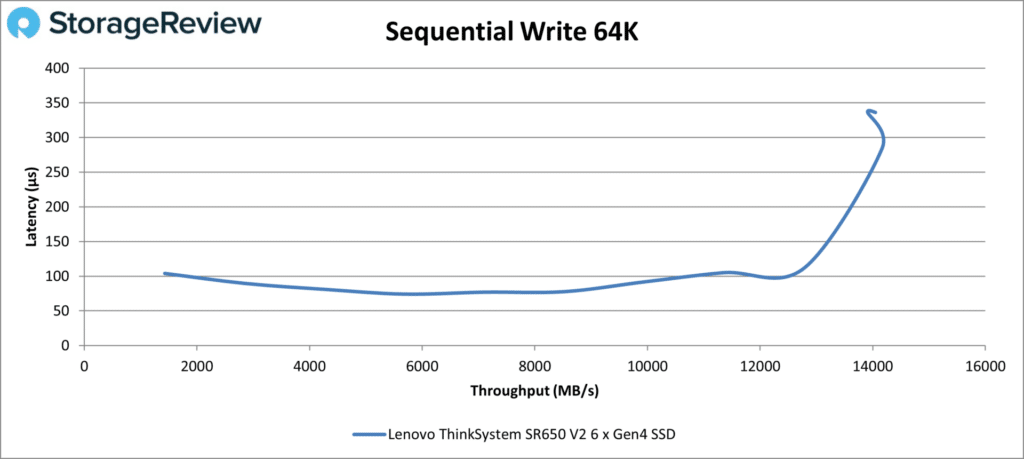
The SR650 V2 spiked in the write test towards the end, not unusual behavior. It otherwise maintained low latency, topping 12,779MB/s at 112µs before the spike.
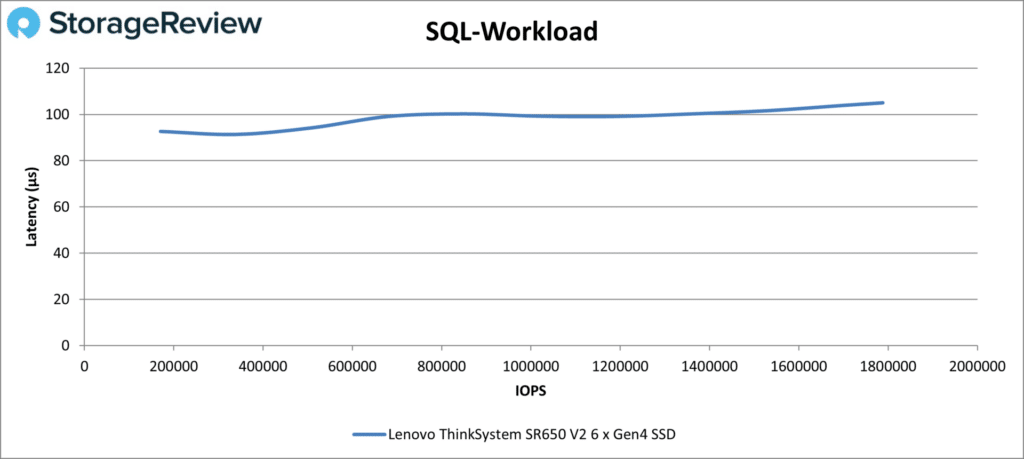
Next up are our SQL tests. The SR650 V2 looked very good in SQL Workload; latencies were at or just above 100µs throughout. Its final number was 1.79 million IOPS at just 105µs.
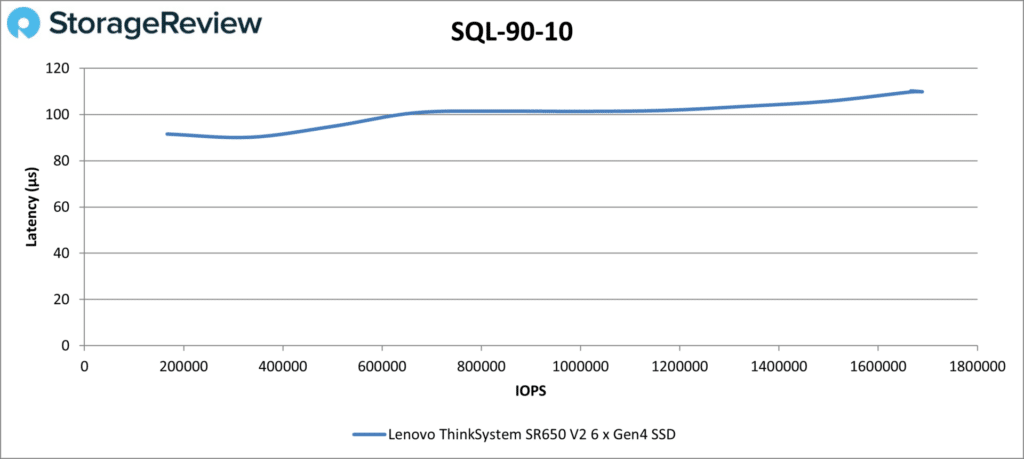
The SR650 V2 continued its stable performance in SQL 90-10, achieving 1.67 million IOPS at 110µs.
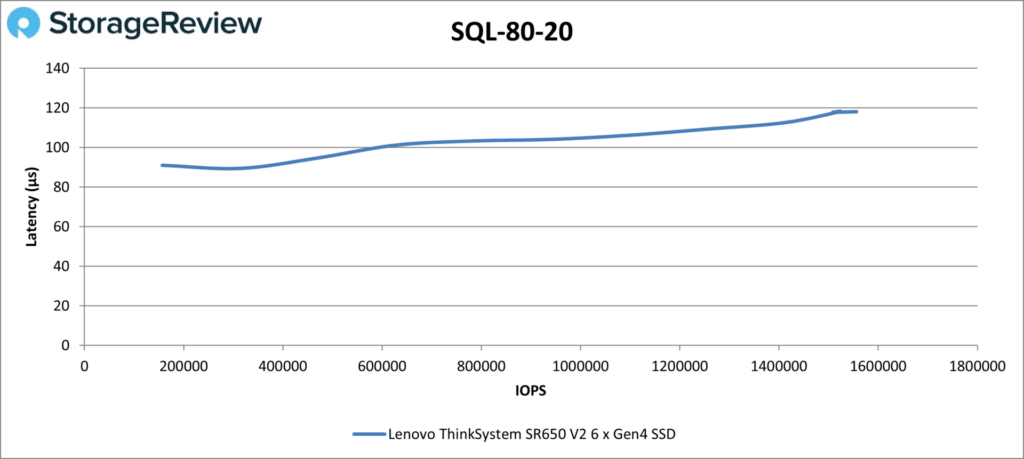
The story was similar in SQL 80-20; the SR650 V2’s top number was 1.56 million IOPS at 118µs.
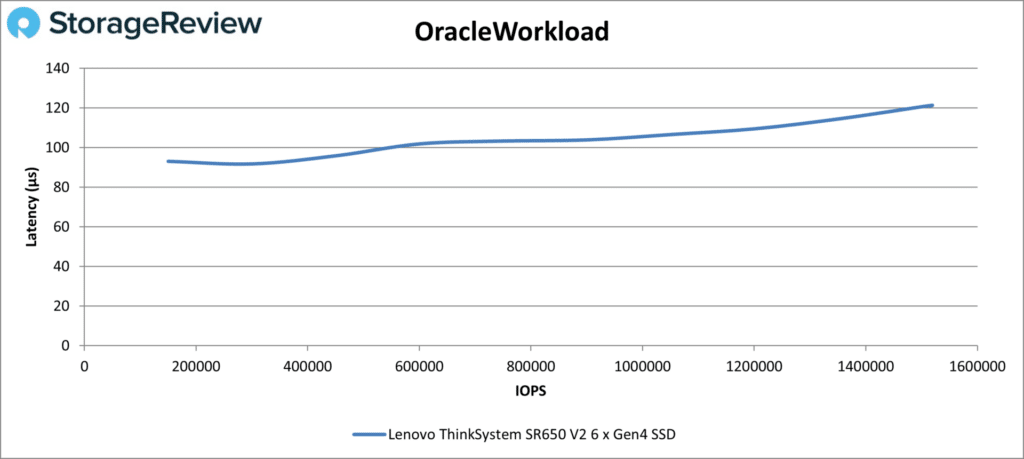
The Oracle testing is next. Starting with Oracle Workload, the SR650 V2 continued maximizing its six NVMe drives, staying under 100µs until about 600,000 IOPS, then peaking at 1.51 million IOPS at 121µs.
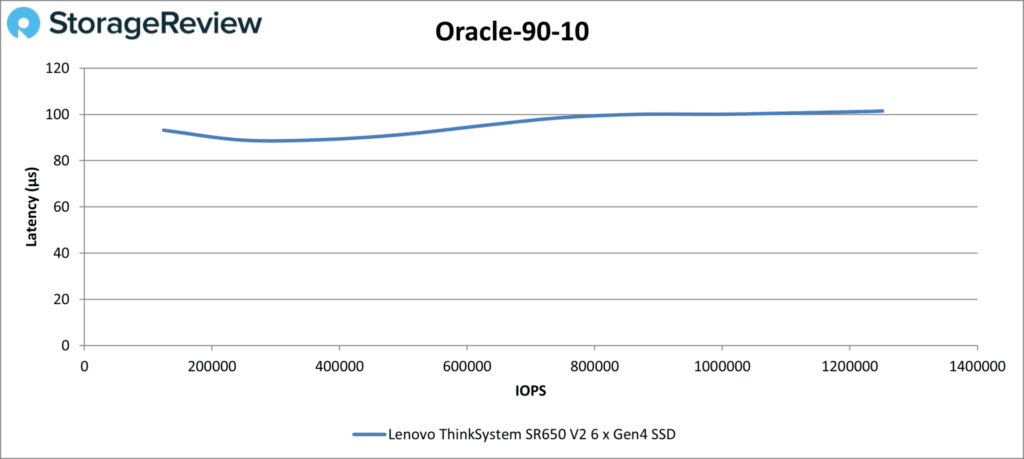
The SR650 V2 did even better in Oracle 90-10, staying below or near 100µs the entire time. It finished with 1.25 million IOPS at 102µs.
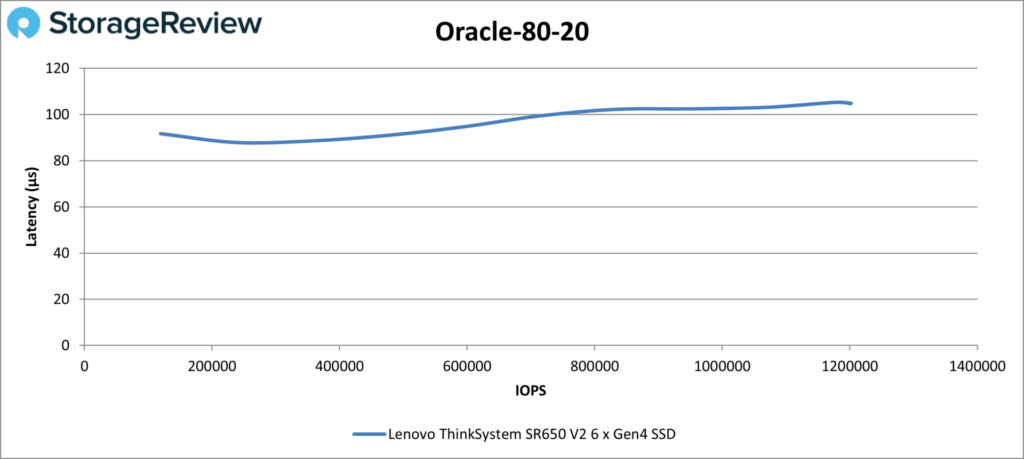
Last in the database tests is Oracle 80-20. The curve mirrored those of the other Oracle tests. The SR650 V2’s top number was 1.2 million IOPS at 105µs.
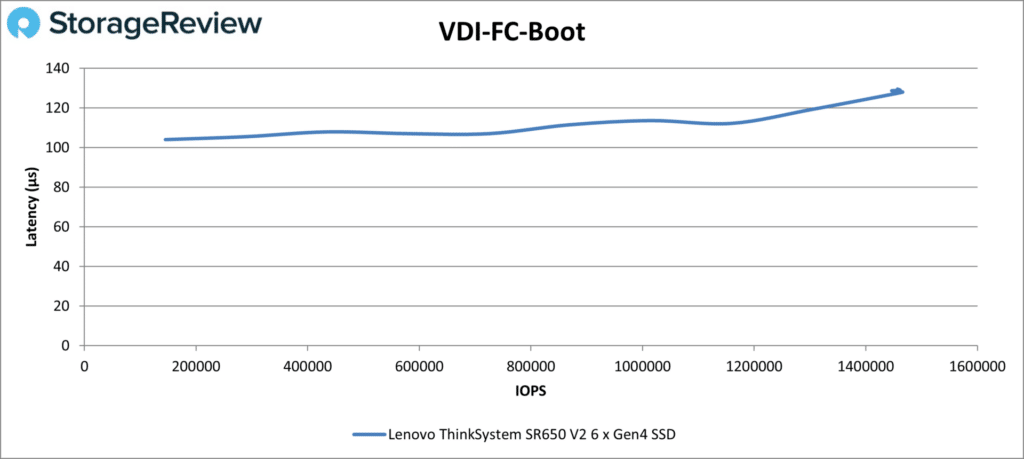
Our final series of tests are VDI Full Clone (FC) and Linked Clone (LC). In VDI FC Boot, the SR650 V2 did well minus a touch of instability at the end. Latency was usually under 120µs; the peak number was 1.46 million IOPS at 130µs.
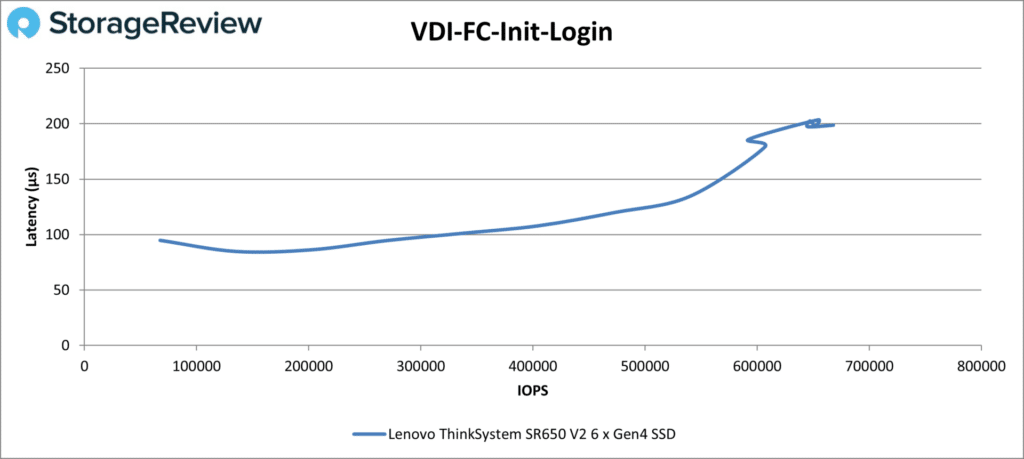
The SR650 V2 showed some tail instability in the VDI FC Initial Login test as well, though nothing unheard of for this test. It achieved 540,226 IOPS at 135µs before the instability, ending at 667,928 IOPS at 199µs.
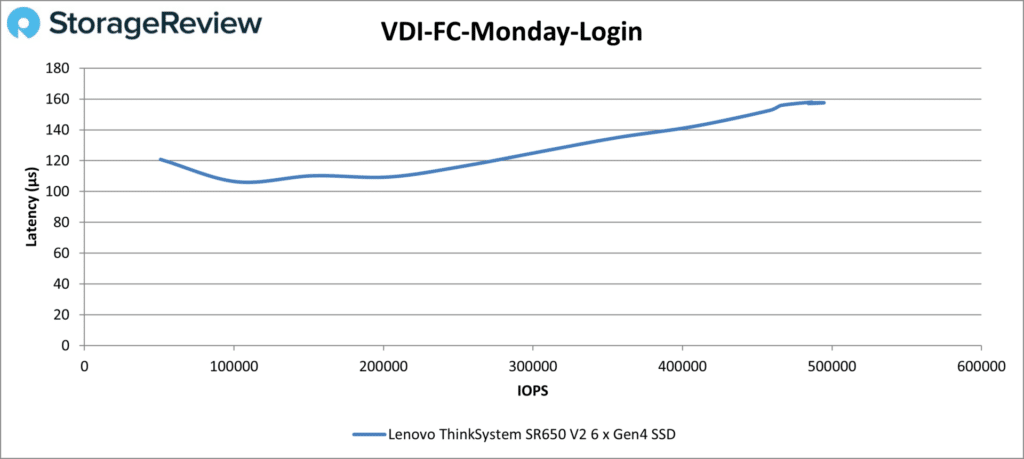
The SR650 V2 looked better in the last VDI FC test, Monday Login. It peaked at 484,279 IOPS at 157µs. You’d need more drives for higher IOPS.
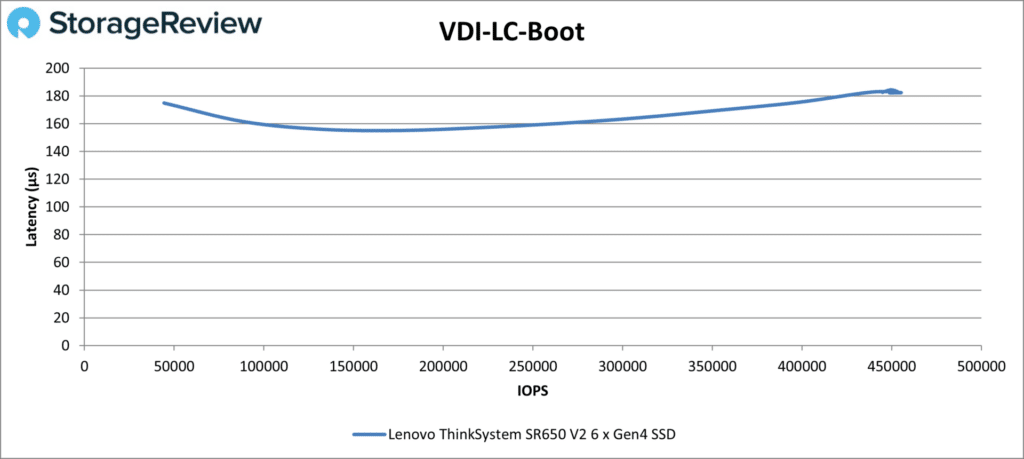
Moving onto the LC tests, the SR650 V2 showed a nice predictable curve in VDI LC Boot, ending at 444,657 IOPS at 183µs.
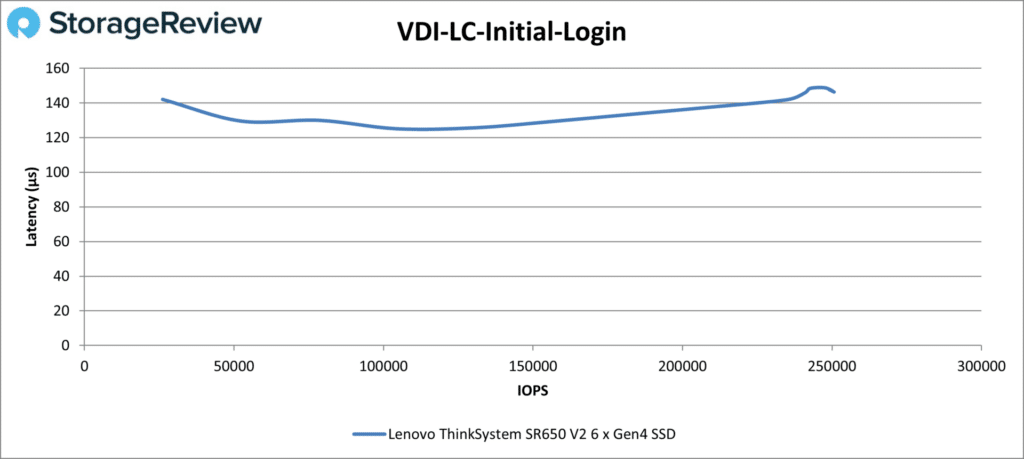
The SR650 V2 didn’t have quite as smooth of a curve in Initial Login. It ended the test at 250,744 IOPS at 146µs.
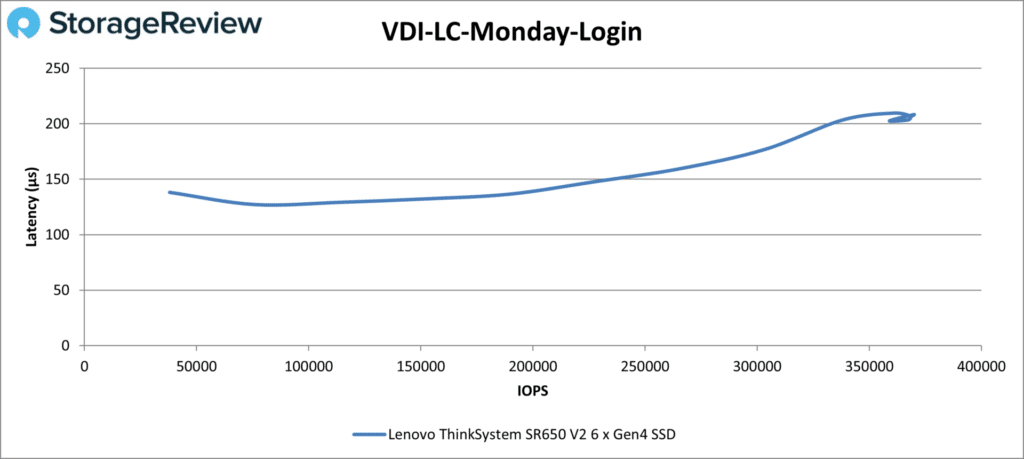
Last up is Monday Login; the SR650 V2 did fine here, too, ending at 368,856 IOPS at 207µs. The minor instability at the end isn’t unusual. Again, more drives would have yielded better results.
Conclusion
Lenovo’s ThinkSystem SR650 V2 is as versatile as a 2U, two-socket server can be. It’s highly configurable from the factory and can be reconfigured after purchase should your needs change.
Server highlights include two third-generation Intel Xeon Scalable CPUs, with up to 270W TDP and eight memory channels across 16 DIMMs per socket; Intel Persistent Memory 200 Series support; and support for three double-wide or eight single-wide GPUs. Storage-heavy configurations can fit up to 40 2.5-inch or 20 3.5-inch drives. It can also be a hybrid storage and compute server. Remote management support comes from a robust XClarity Controller, which offers many ways to manage it, including a mobile app.
Our review server performed as well as we could have expected. Numbers from our test server, equipped with two Xeon Silver 4314 CPUs and six Solidigm P5520 7.68TB SSDs, include 5.7 million IOPS in random read 4K; 30,312MB/s in sequential read 64K; 12,779MB/s in sequential write 64K; 1.79 million IOPS in SQL Workload; and 1.51 million IOPS in Oracle Workload. It showed stable performance and low latency throughout.
All told, the SR650 V2 is a strong 2U, two-socket server, with lots of promise for versatile deployments. In fact, it’s more flexible in configuration than most others in this class, which makes it a great fit for software-defined solutions.
Engage with StorageReview
Newsletter | YouTube | Podcast iTunes/Spotify | Instagram | Twitter | Facebook | RSS Feed