IT environments rely on systems, applications, and data to continuously deliver business and services. All these resources are critical parts of running a modern business. But data is the key factor in maintaining an operation successful; all business data could be gone in the blink of an eye due to a computer system or application crash, a disaster, or human error. Without the data, the business simply doesn’t exist. Backing data up and planning for disaster recovery is among the top IT solutions that no modern business could dare to prevail without. Data backup systems and disaster recovery (DR) solutions are accomplished by either using an on-premise or a remote cloud solution, both requiring storing massive amounts of information.

The problem is that with the exponential growth of data, complex backup and DR, and the demanding archiving storage requirements, the costs of IT can get out of control. Moreover, backup jobs can take too long to complete, not matching the modern business demands of always on and always available IT environments; and with slow and unpredictable WAN connections, using the cloud for DR can be challenging. Quest QoreStor aims to turn these complex problems into simple and cost-effective solutions by offering organizations less time on IT administration and more time on business innovation.

QoreStor is part of the Quest’s Data Protection business unit solutions portfolio, and it is a software-defined secondary storage platform designed to complement any backup solution. Software-defined secondary storage is the merge of traditional secondary storage platforms that were hardware bound with software-defined principles, such as software-defined storage and network. Quest uses QoreStor as an API-driven deduplication engine for backup storage that can be run as a VM in the cloud, or on top of physical hardware. It supports current backup applications in today’s data centers, and is flexible enough for where and when it could be run. A software-defined secondary storage strategy can help system administrators be flexible and more dynamic with their IT environments.
QoreStor is backup vendor agnostic and leverages enterprise-class compression and deduplication technology; this is a crucial QoreStor component that can carry out data reduction before it is transmitted across the network to the backup target. The hardware-agnostic nature of the platform means organizations can use it with their existing hardware, which means cost savings. Quest goes on to state that it works with most backup vendors, including Veeam, CommVault, Dell/EMC, Veritas, and IBM, as well as virtualization platforms – VMWare, Hyper-V and KVM – and cloud service providers including Azure and AWS. QoreStor also comes as a cloud portal, allowing customers to monitor it from any location.
Among the top backup software solution vendors that Quest can work with, we have Veeam, which can be easily integrated with QoreStor. This integration helps to accelerate Veeam backups significantly, and Quest states to reduce backup storage more than 95%. QoreStor has been qualified and tested with Veeam Backup & Replication and has been verified as a Veeam Ready Repository. Besides accelerating backups and reduced storage costs through powerful deduplication and compression, Quest’s customers can use resilient replication technology to leverage the cloud for archiving and disaster recovery. As mentioned before, in addition to Veeam, QoreStor supports many backup software solutions, but also including Quest’s own NetVault backup product.
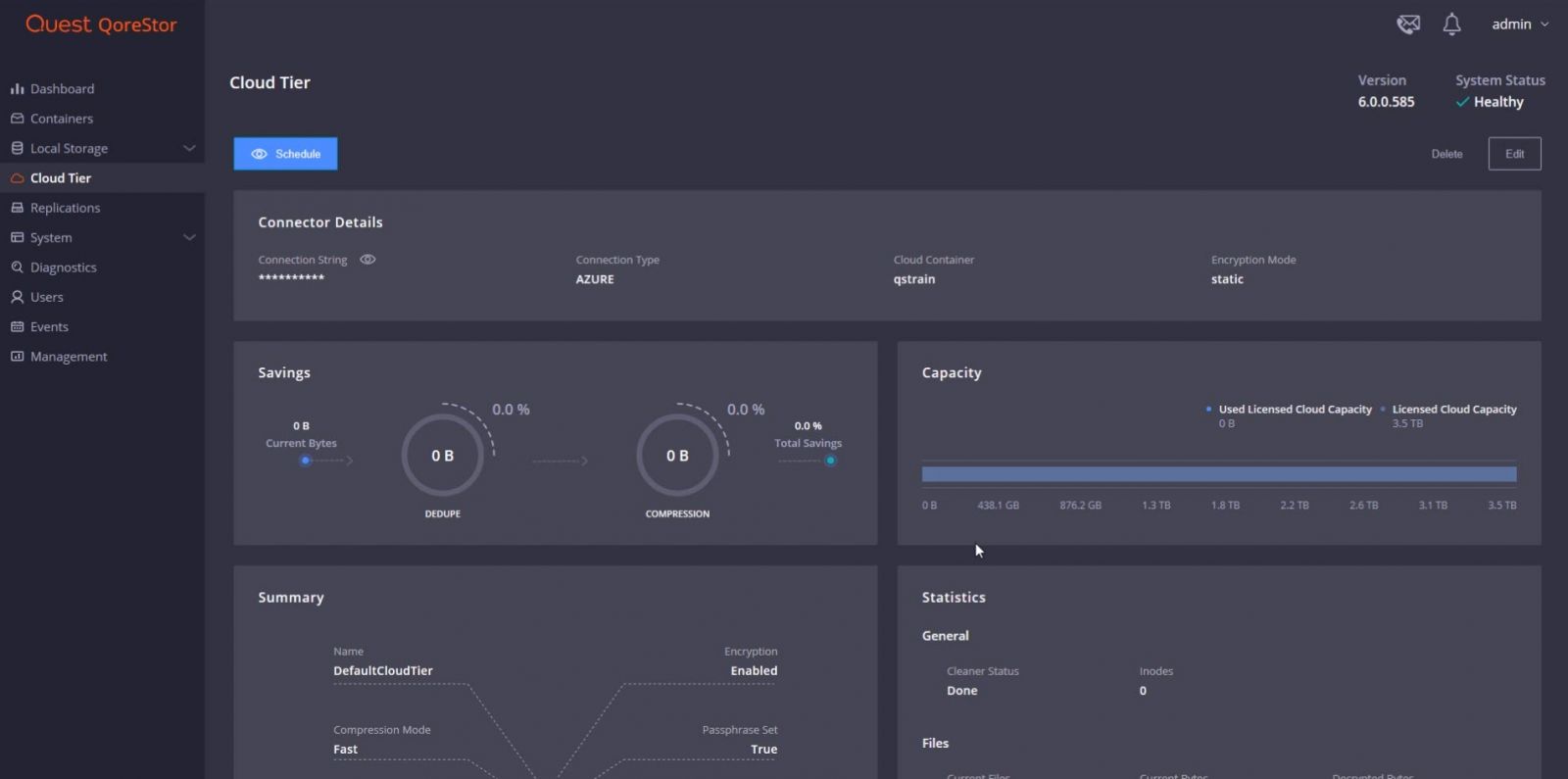
The latest version of QoreStor includes additional support and services for cloud services, such as the two new cloud-centric tiers; Cloud Tier and Performance Tier. Cloud Tier is a policy-driven cloud extension to QoreStor, which offers the ability to move and recover data from cloud storage. Performance tier is a high-speed Storage Group that allows for faster backup and instant recovery technologies. Performance Tier also provides 2x recovery point objectives (RPOs) that enable quick recovery.
QoreStor Features and Functionality
- Cloud Tier — Move and recover data from cloud storage quickly and easily with this policy-driven, seamless cloud extension.
- Performance Tier — Recover instantly, without having to compromise on deduplication, with this high-speed storage group.
- Hardware- and software-agnostic platform — Employ any storage hardware, backup software, virtualization platform or cloud provider to reduce costs, simplify your IT environment and maximize your ROI.
- Next-generation storage dedupe engine — Lower your backup storage requirements by an average of 20:1, and take advantage of enterprise-class variable-block deduplication.
- Built-in protocol accelerators with Secure Connect technology — Accelerate data ingest by up to 20 terabytes per hour to address your ever-shortening backup windows. Ensure complete backups, even over poor links that disconnect often.
- Remote replication for disaster recovery — Replicate only unique data to a remote site, reduce replication windows by 10 to 15 times, reduce network bandwidth requirements by 85 percent and shorten overall replication time.
- Back up to the cloud — Back up directly to the cloud over your WAN, but with LAN-like speeds through source-side deduplication where only the changes are transmitted. Achieve recovery point objectives (RPOs) that are typical of on-premises deployments, even over the WAN.
- Direct-to-target backup — Bypass the media server and back up directly to the target storage device.
- Data security — Meet demanding security requirements with built-in encryption at rest, secure erase and FIPS 140-2 compliance. Encryption at rest uses industry-standard 256-bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) keys.
- Best-in-class data integrity — Count on data verification and file system health checks to overcome potential storage failures and help ensure recoverability.
- Multitenancy and role-based access — Create storage groups easily — and containers within those storage groups — to define separate storage policies and capacities. Advanced user roles allow for more granular control.
- Global View Cloud — Administer all QoreStor instances in a single console, from anywhere, on any device, making QoreStor easy to use, manage and maintain.
Data Protection and Deduplication
One of the keys to ensuring the data is protected is to use an efficient algorithm that not only compresses but also removes data redundancies, so the minimal amount of data is transferred for the maximum amount of data protection. To achieve this, (backup) vendors utilize data deduplication. Data deduplication reduces the amount of data to be stored by identifying and eliminating duplicate files and blocks of data. With the right data deduplication solution, organizations are allowed not to have to back up as much data to a storage device; therefore, they can store more data while using less network bandwidth to transmit the data to and from the storage site. This last one is crucial for cloud-based DR.
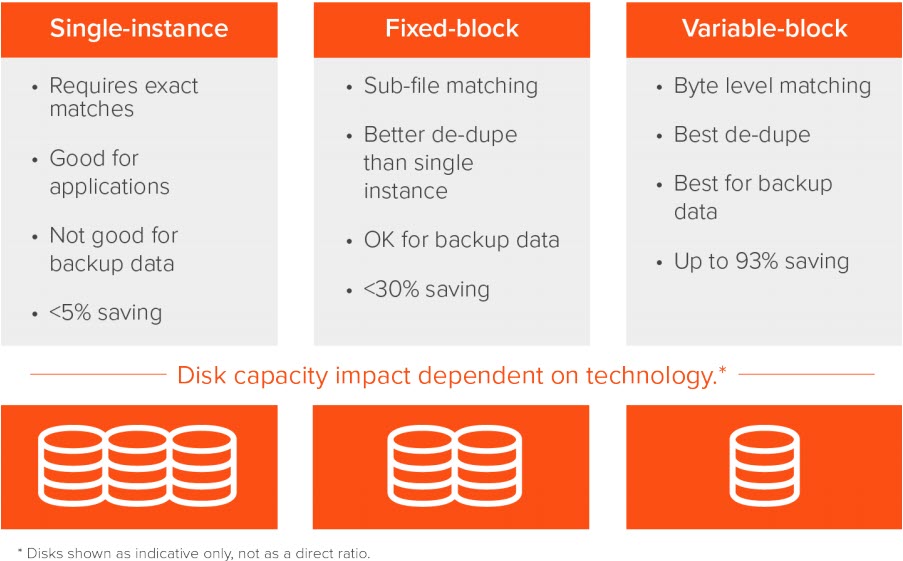
But not all deduplication is the same, and understanding their differences can aid in ensuring that organizations meet their data protection objectives. Among the different data reduction technologies, we find compression and deduplication. There are several approaches to deduplication to help combat an increased need for data storage.
- The most basic method is single-instance or file-level deduplication. In this method, identical files are tracked, referenced, and then only the unique files are stored. However, if a file is changed, it is treated as a new file and stored alongside the previous version. Since this deduplication method is relatively simple, it is suitable for application use, but not very good for data backup and, typically, results in a less than 5% storage savings.
- Fixed-blocked deduplication is where sub-file matching occurs, but the block size never changes. This is because the block size is set by the software managing the deduplication. This method allows for changed parts of a file to be stored, rather than storing a unique instance of the whole file. This method is better than single-instance dedupe but is only OK for housing backup data and, typically, results in a less than 30% storage savings.
- Variable-block deduplication will change the size of the blocks to provide an optimal level of deduplication for storage utilization. Hash fingerprints are assigned via an algorithm. The data sets are then scanned for the matching fingerprints. If there are no matching fingerprints, then the data will be stored as unique blocks. If there are matching fingerprints, a reference will be made and the incoming blocks will be discarded. This method accounts for shifts in blocks within the file. New header information that will be smaller than a fixed block can now be captured as a new block at a smaller size.
Overall, variable-block deduplication provides more matches and therefore reduces the unique data that has to be stored. But Quest goes beyond this kind of deduplication to provide even further savings, being aware of the content of the stream itself. Quest QoreStor adds a content-aware algorithm to its variable-size chunking. The algorithm identifies patterns in the data, in spite of the shifting that results from additions or deletions in the data stream, then aligns the block start- and endpoints to duplicate chunks while identifying only the changed chunks as unique. Using content-aware variable-block deduplication with built-in compression and encryption is the reason that Quest can assure unparalleled storage savings, up to 93%.
Quest QoreStor GUI
QoreStor offers a web-based user interface that administrators can use to configure, manage, and monitor the QoreStor system. QoreStor UI can be used to perform tasks such as Configure containers, storage groups, and cloud storage groups, add and manage replications, View system information and monitor performance, manage user accounts and generate and download diagnostic bundles.
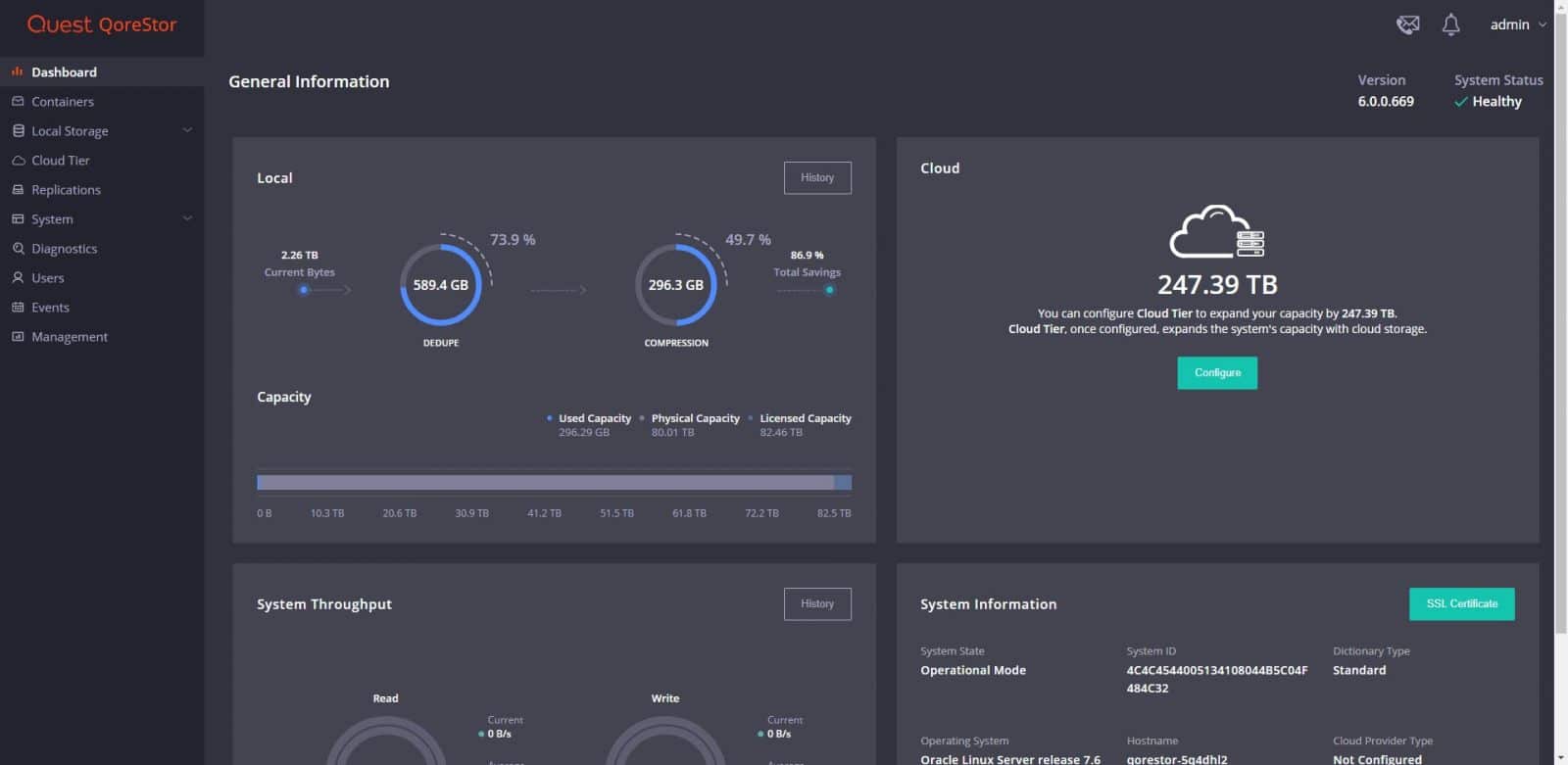
After accessing the QoreStor UI, we are brought directly on the Dashboard page. The UI consists of the Header pane, the Navigation pane, a Status pane, and the Operations pane. From the dashboard, we see general information of local and cloud storage — also, system throughput and system information. On the Cloud area, by clicking in Configure, one can configure Cloud Tier based on cloud providers.
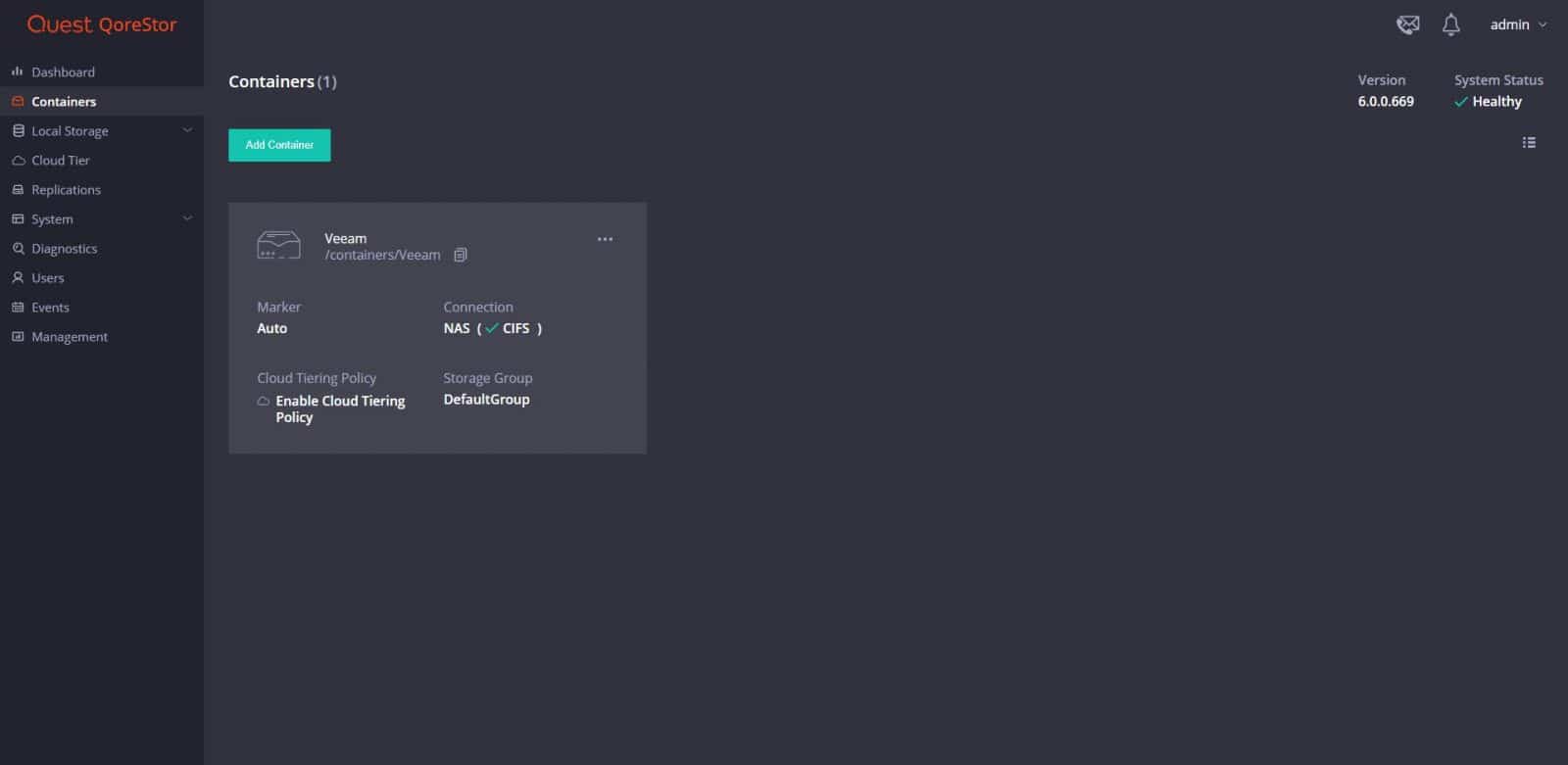
From the Containers page, we can view the general information about a selected container and add new containers.
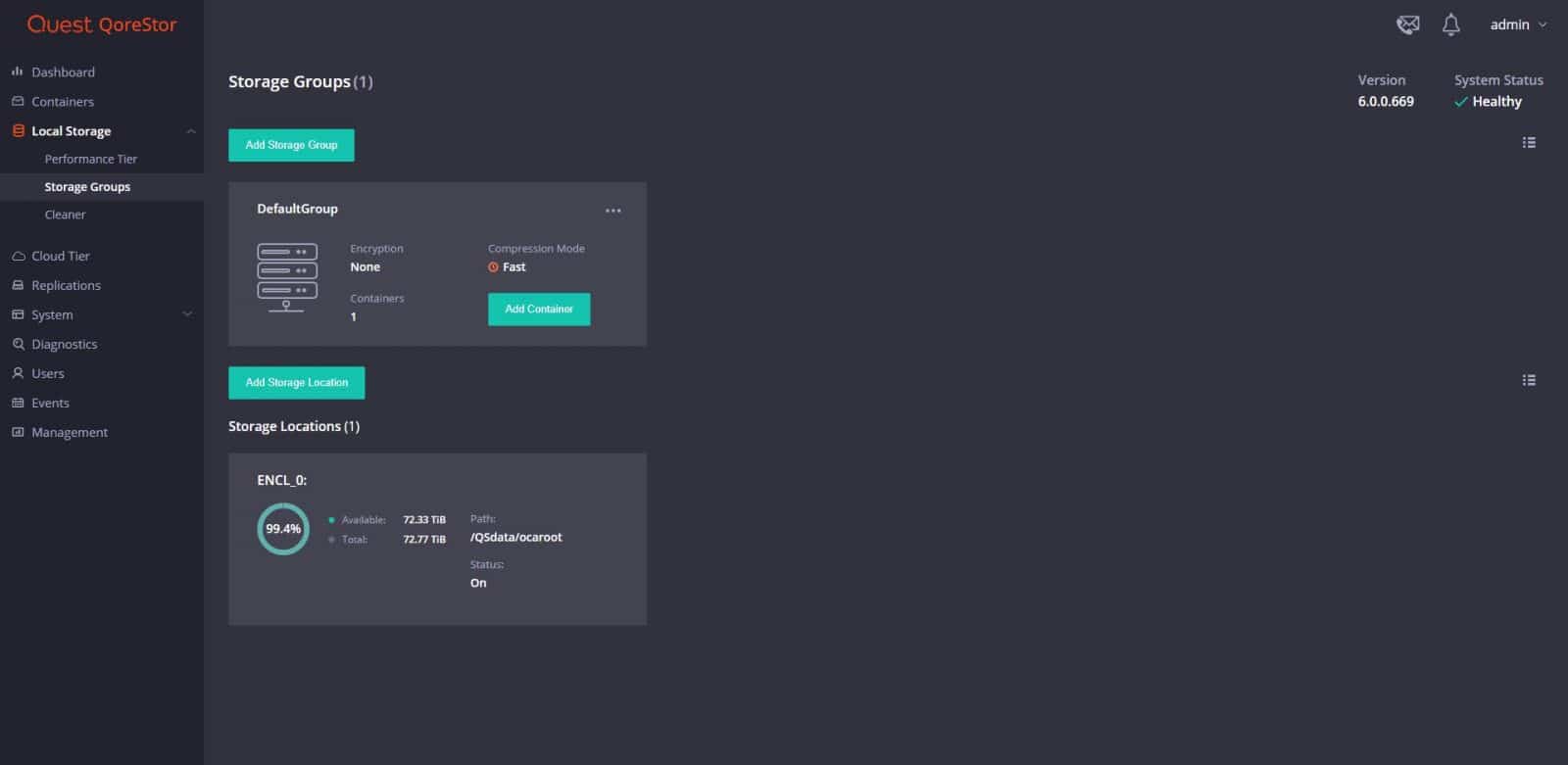
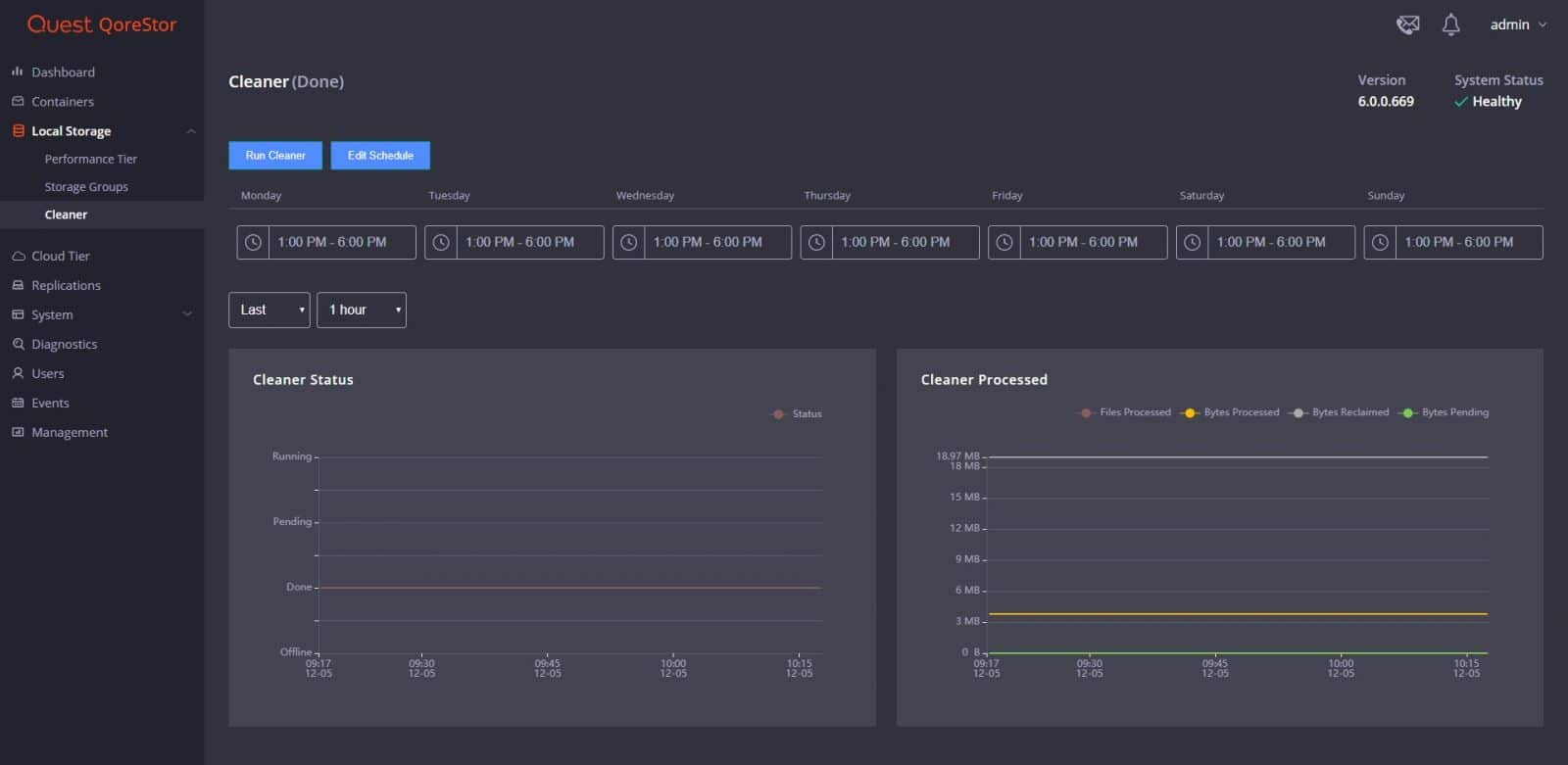
From Local Storage, we can move on Performance Tier, Storage Groups, and Cleaner. Performance Tier is useful in situations where specific workloads have requirements for faster recovery and ensuring that only the most critical workloads are written to higher-performing storage. From Storage Groups, administrators can manage storage groups and data containers, including viewing, modifying, and creating new storage groups and containers, and viewing current statistics.
Quest recommends the system cleaner area or space reclamation as a method for recovering disk space from system containers in which files were deleted as a result of deduplication.
From the Cloud Tier page, we can monitor Cloud Tiers previously configured. Cloud tiering feature enables on-premises QoreStor data to be quickly and easily accelerated to the cloud.
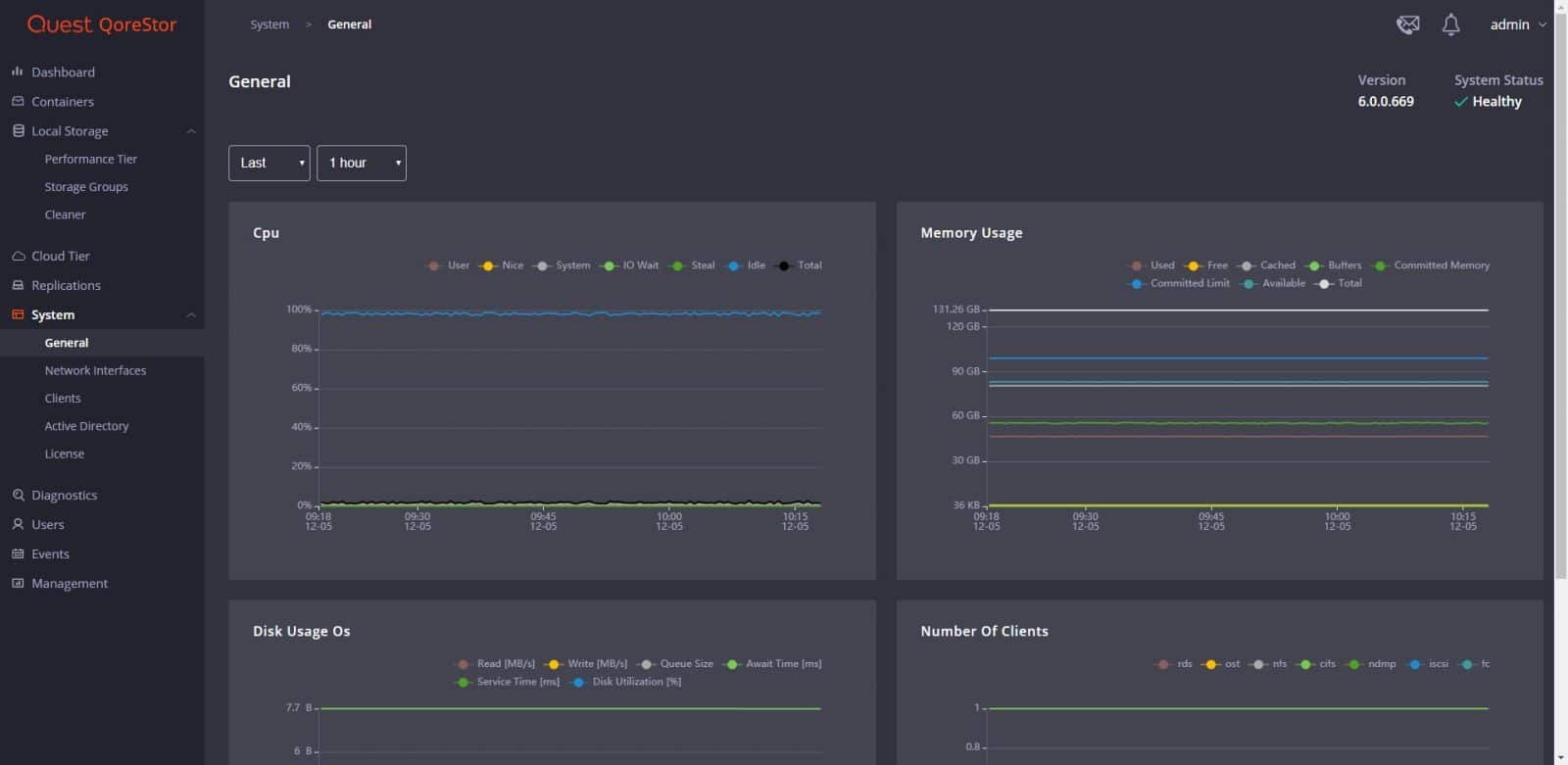
CPU, Memory, and other system metrics can be monitored from the General page under System.
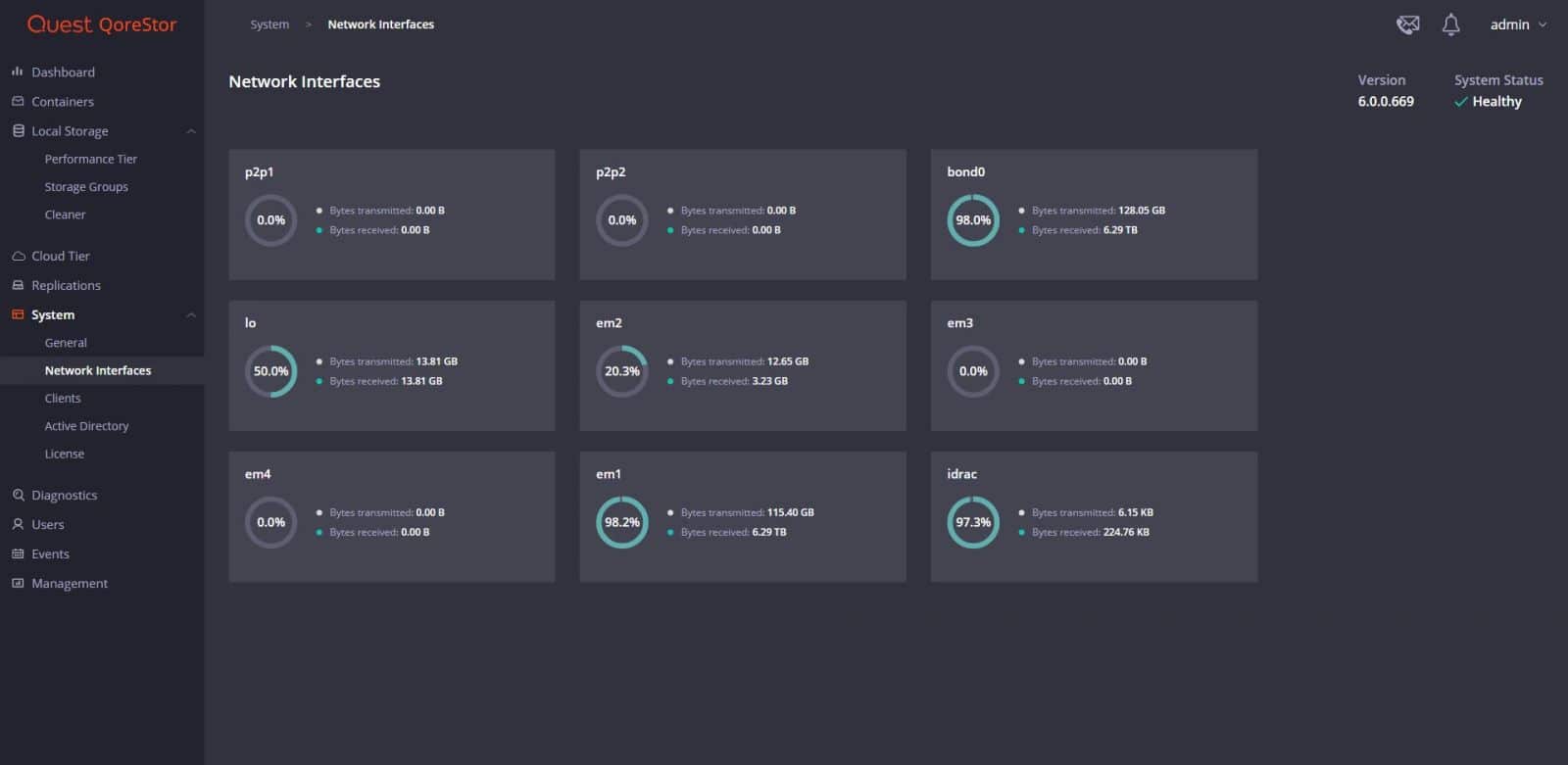
From Network Interfaces, we can monitor the transmitted and received network traffic of the available network interfaces.
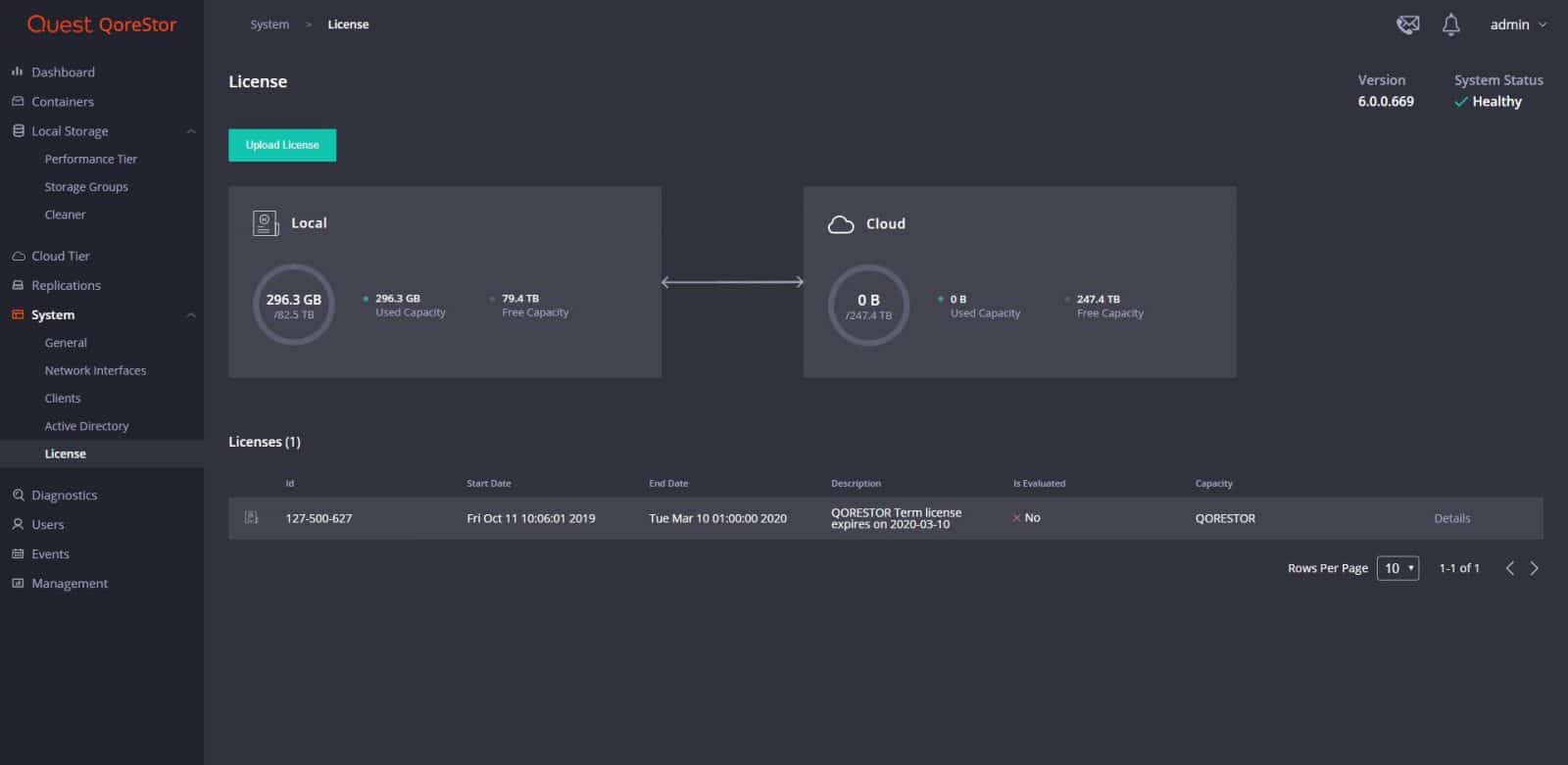
Other pages under System include Clients, Active Directory, and License. From this last one, we can monitor the active licenses of the system.
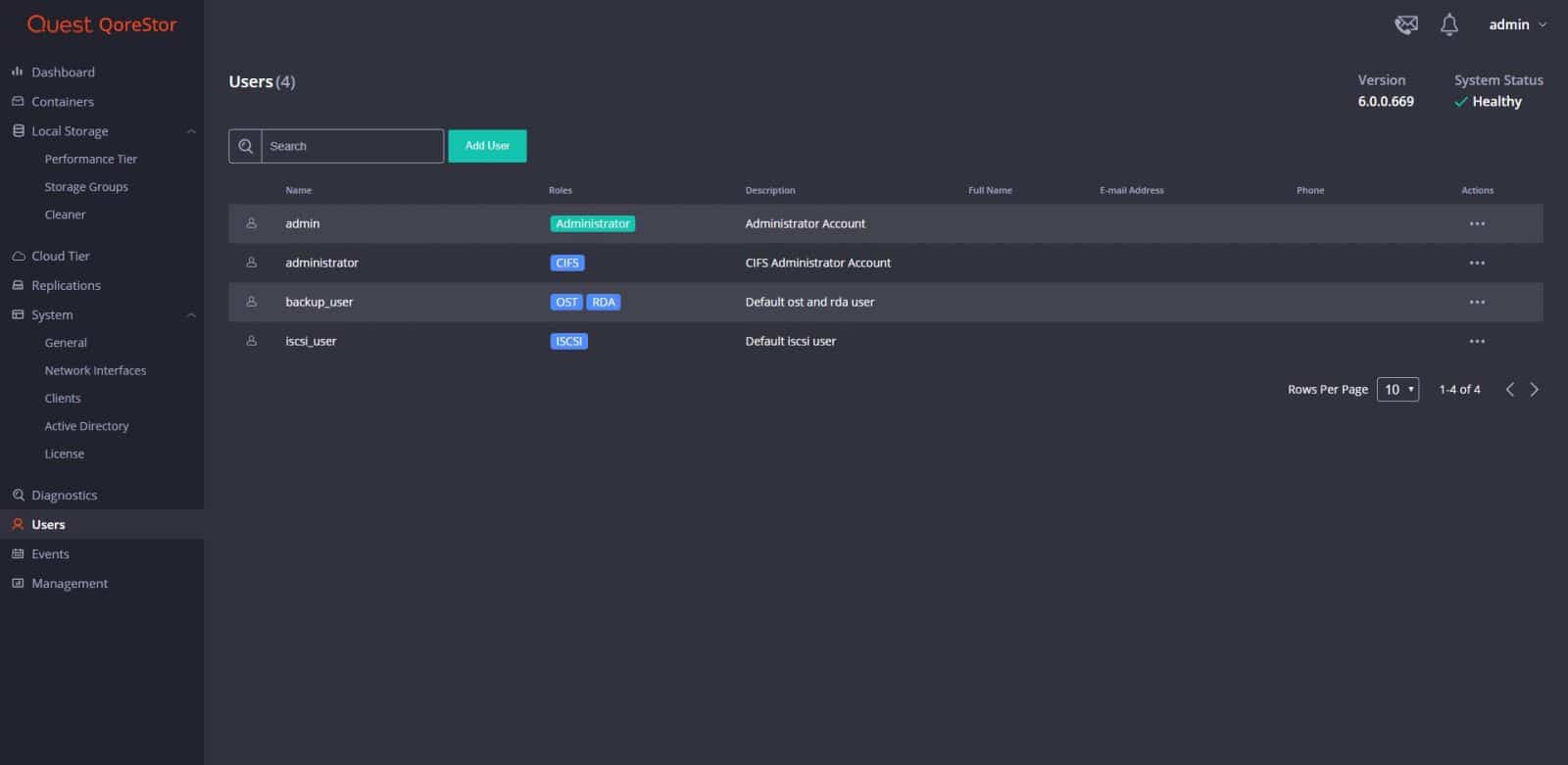
Under Users, one can view user accounts and settings. We can see roles and descriptions of current users, also, add new ones.
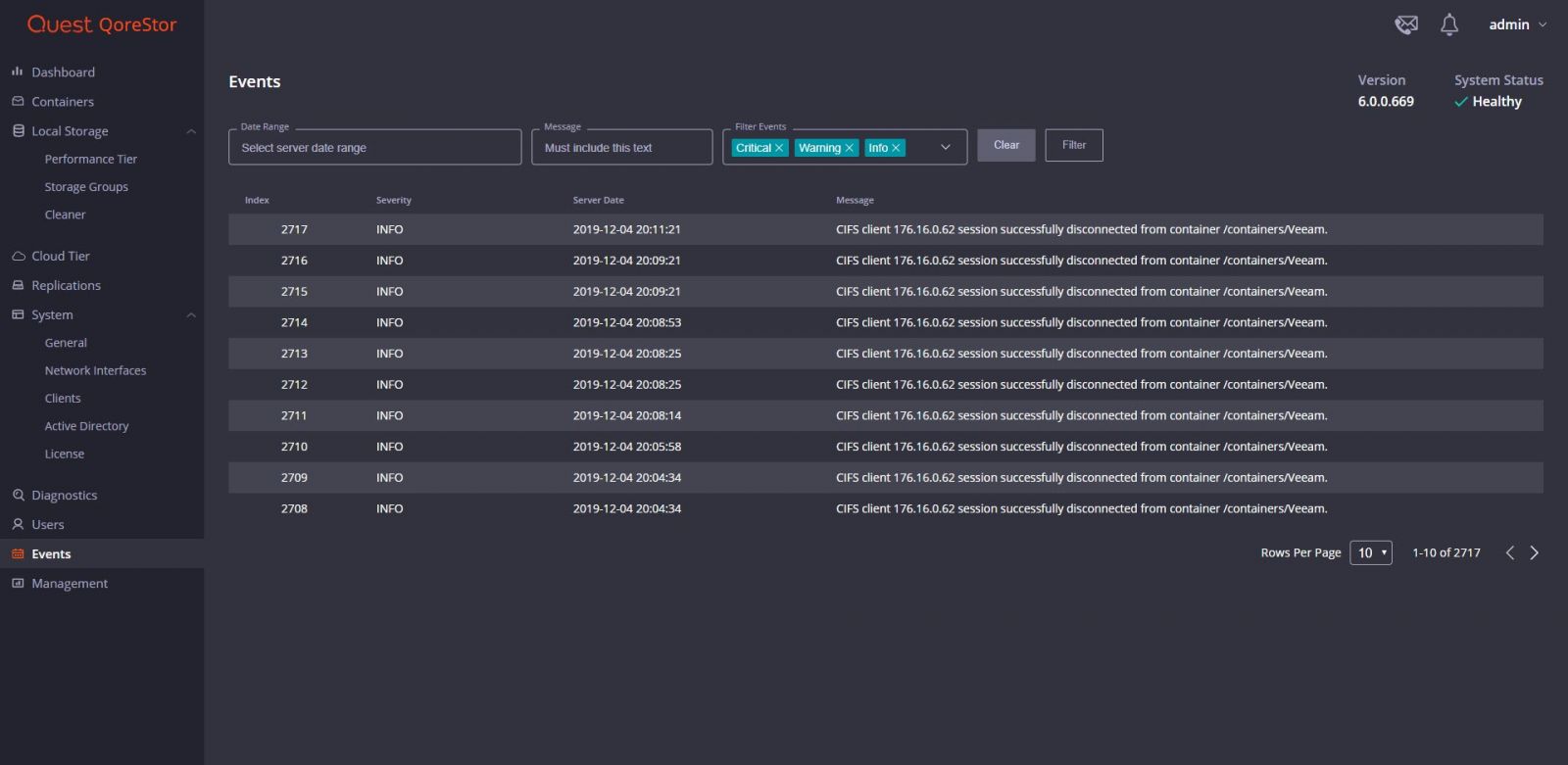
From the Event page, one can easily view and filter current system events.
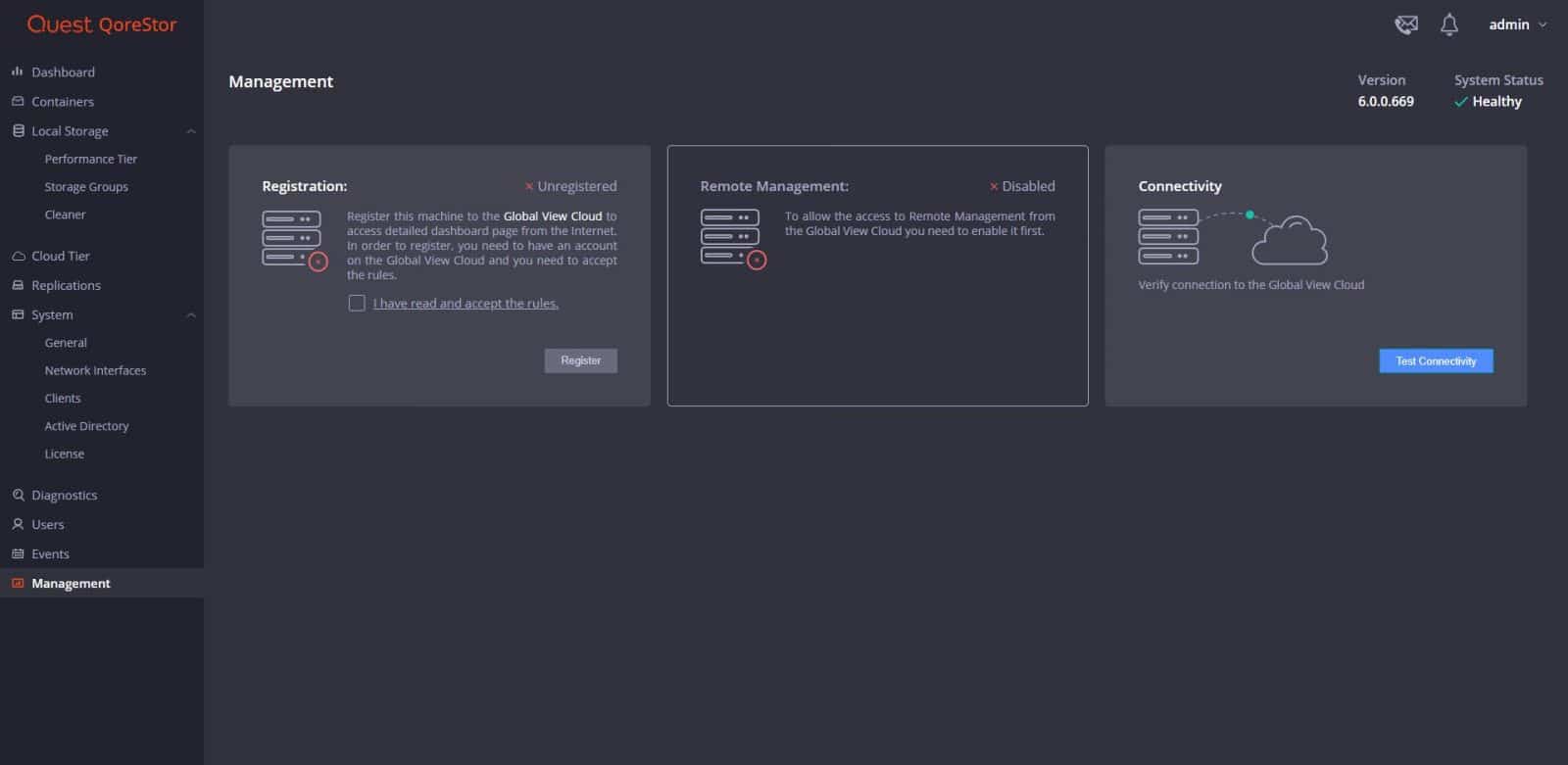
Under the last page, management, we can register the system to a Global View Cloud, allow access to Remote Management and verify the connectivity to the Global View Cloud.
Conclusion
Managing modern data protection environments is not a simple task for system administrators. IT departments have always been requested to improve the service levels for backup and recovery, and the two main inputs on which to base data protection are RPO and RTO. These inputs are considered to be a top challenge since large amounts of data can slow down backup to the cloud, and the cost on-prem and in the cloud increases. Quest QoreStor is an emerging software-defined platform with which IT administrators can build backup target hardware. This a platform based on a background of deduplication and replication technologies that helps organizations reduce storage requirements and costs, accelerate backups, and better leverage the cloud for archiving, disaster recovery, and business continuity. While the Quest QoreStor application is delivered as software, the underlying hardware can’t be discounted. In this case we were shipped a Dell EMC PowerEdge R740, which is well suited for this task. Further, the system management software from Dell EMC is also very strong, which may mitigate concerns an organization may have about taking care of the hardware over time.
In this review, we also took a look at the QoreStor UI. It offered an easy-to-use web-based user interface that administrators can leverage to configure, manage, and monitor the QoreStor system. To get QoreStor up and running, we integrated the backup target with our core lab infrastructure. We already use Veeam as our regular backup and recovery application. Getting Veeam set up with QoreStor was a trivial task, relatively uneventful in fact from initial deployment to the time of this review, many weeks later. From a capacity consumption perspective, we sent roughly 2.2TB to the target with less than 300GB actually landing on disk. QoreStor also has several cloud connectivity options, which were outside of the scope of this review, but worth noting.
Overall the QoreStor solution was very easy to deploy and manage. The UI is generally intuitive and straightforward as well, meaning just about anyone in the IT org should be able to pick up and run with it. Further, Quest believes they have a cost advantage over dedicated backup appliances that tend to have a lot of legacy cost built in. Given the entire package, which is comprehensive, QoreStor looks to be a viable alternative in the backup target space.
Sign up for the StorageReview newsletter