The Samsung SSD 845DC EVO line of drives are specifically designed to provide high performance and reliability–though cost-effective–solutions for today’s increasing data traffic in servers and data centers. Samsung indicates its new family of SSDs will deliver a very high level of sustained performance as well as consistent low latency over the life of the drive, giving it the ability to meet demands of increasing data handling. Under the hood, the 845DC Evo is equipped with Samsung's 19nm Toggle 3bit NAND, making it the first enterprise-class SSD to use TLC NAND. This new use of NAND combined with its MEX controller allows the Samsung 845DC EVO to be one more energy-efficient drives on the market, all the while maintaining the excellent performance.

As noted, the SSD 845DC EVO and it's OEM focused cousin, the Samsung PM853T, are the first enterprise SSDs to ship with TLC NAND. Samsung has already been shipping the TLC-based 840 EVO in the client space for nearly a year, so the idea of TLC NAND in SSDs isn't entirely foreign. It's just that in the enterprise, there's a tremendous amount of fear and reluctance to change. SSD penetration at large is still in the single digits in the enterprise and many are still buying 3.5" 15K hard drives, despite consistent proof that there's a better choice.
Samsung components are clearly trusted though and the interest in SSDs in the entry enterprise space where workloads are read heavy is climbing. Those buyers appear to be more open to managing the TCO of the datacenter, where flash helps tremendously. Samsung is also mitigating the endurance argument by posting some pretty good endurance numbers, 600TBW for instance on the top capacity 900GB drive. It's important to look at these within context however. The new Micron M500DC for instance posts a 1.9PB figure for its 800GB SSD but the Intel S3500 is only 450TB for its 800GB drive. Further, Samsung is targeting this drive at the lowest possible enterprise price point, a place where client drives like their own 840 Pro are picking up share as many buyers are looking for the lowest cost alternative. The 845DC EVO then stakes it claim by offering such a price-based alternative, with a drive that's specifically designed for data center use with appropriate firmware and features.
Samsung's 845DC EVO also offers an extra level of security to ensure that valuable write information is well protected, as it is built with tantalum capacitors to protect all data in the write cache in case of a sudden, unexpected power failure. This is also a very attractive functionality for enterprises across all types of industries. The drive also carries a 2 million hour MTBF spec and a five year warranty.
The Samsung SSD 845DC EVO SSDs come in capacities of 240GB, 480GB, and 960GB with suggested pricing of $249.99, $489.99 and $969.20 respectively. Our review units include 16 of the 480GB capacity drive.
Specifications
- Capacities:
- 240GB (MZ-7GE240EW)
- 480GB (MZ-7GE480EW)
- 960GB (MZ-7GE960EW)
- Application: Mixed and Read-centric usages are recommended
- Interface:
- Serial ATA 6Gb/s (compatible with SATA 3Gb/s and SATA 1.5Gb/s)
- Fully complies with ATA/ATAPI-7 Standard (Partially Complies with ATA/ATAPI-8)
- Support NCQ: Up to 32 depth
- Asynchronous Signal Recovery
- Form Factor: 2.5” type
- NAND Flash Memory: Samsung 19nm Toggle 3bit NAND
- Performance Sequential Read: Up to 530MB/s
- Sequential Write:
- Up to 410MB/s (480GB, 960GB)
- Up to 270MB/s (240GB)
- Random Read (4KB, QD32):
- Max. 87,000IOPS
- Random Write (4KB, QD32):
- Max. 14,000IOPS (960GB)
- Max. 14,000IOPS (480GB)
- Max. 12,000IOPS (240GB)
- Quality of Service (4KB, QD32):
- 99.90% Read: 0.6ms, Write:7ms
- Max. Read: 3ms, Write:8ms
- Latency:
- Sequential (4KB): Read: 55us, Write : 45us
- Random (4KB): Read:115us, Write : 55us
- Reliability: 2,000,000 hours Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
- TBW:
- 240GB: 150TBW
- 480GB: 300TBW
- 960GB: 600TBW
- Supply Voltage: 5.0V ±5%
- Power Consumption:
- Active Read/Write: 2.7Watt/3.8Watt
- Idle: 1.2Watt
- Temperature:
- Operating: 0°C to 70°C
- Non-Operating: -40°C to 85°C
- Humidity: 5% to 95%, non-condensing
- Vibration: Non-Operating, 20~2000Hz, 20G
- Shock: Non-Operating,1500G, duration 0.5m sec, 3 axis
- Dimensions (LxWxH): (100.00±0.25) x (69.85±0.25) x (6.80±0.20) mm
- Weight Max: 63g (960GB)
- Warranty: 5-year
Design and Build
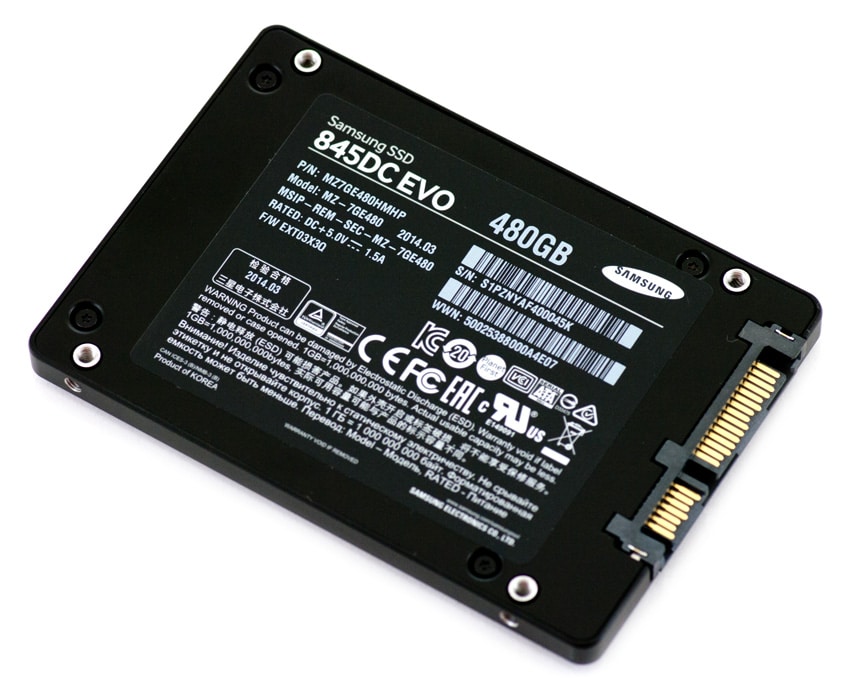
The Samsung SSD 845DC EVO sports an updated style and chassis color from the EVO series, though it has still kept its sleek, minimalistic design. The 2.5-inch, 7mm enclosure is a charcoal color in a solid metal construction for a rugged composition. The Samsung logo and “Solid State Drive” text in white font.
The 845DC EVO's thin design supports a wide range of applications ranging from ultra-high density enterprise applications like the EchoStreams 48-bay 2U SAN chassis to enterprise client applications including notebooks, desktops, and ultrabooks.
The reverse side of the Samsung SSD displays the product information label, which provides relevant information such as the capacity and serial number. The side profiles show the four screw holes, allowing the 845DC EVO to be mounted with ease.
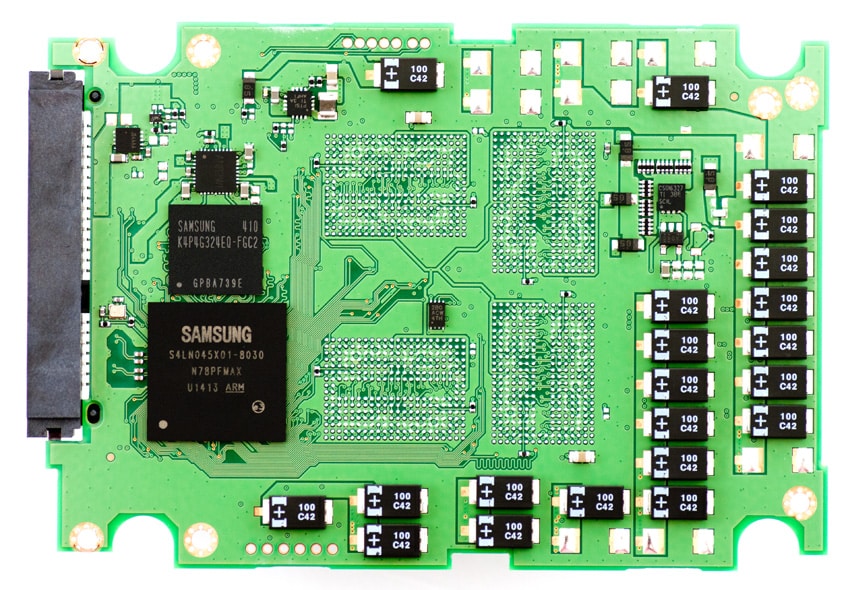
At the heart of the Samsung 845DC EVO is the new 400 MHz MEX controller, the Samsung MEX S4LN045X01-803, which is 100MHz faster than the 840 and 840 Pro's controller and shared with the 840 EVO.
The 845DC EVO’s storage comes from the Samsung 19nm Toggle 3bit NAND. Additionally, it is also built with tantalum capacitors, which protects all data in the write cache in the event of an unexpected power failure.
Testing Background and Comparables
The StorageReview Enterprise Test Lab provides a flexible architecture for conducting benchmarks of enterprise storage devices in an environment comparable to what SAN administrators encounter in real deployments. The Enterprise Test Lab incorporates a variety of servers, networking, power conditioning, and other network infrastructure that allows our staff to establish real-world conditions to accurately gauge performance during our reviews.
We incorporate these details about the lab environment and protocols into reviews so that IT professionals and those responsible for storage acquisition can understand the conditions under which we have achieved the following results. None of our reviews are paid for or overseen by the manufacturer of equipment we are testing. Additional details about the StorageReview Enterprise Test Lab and an overview of its networking capabilities are available on those respective pages.
The Samsung SSD 845DC EVO uses Samsung 19nm Toggle 3bit NAND and a Samsung MEX S4LN045X01-803 controller with a SATA 6.0Gb/s interface. SSD comparables for this review:
- Samsung SSD 840 Pro (512GB, 300mhz Samsung 3-core MCX controller, Samsung 2x nm Toggle NAND Flash, 6.0Gb/s SATA)
- Samsung SM843 (240GB, 300mhz Samsung 3-core MCX controller, Samsung 2x nm Toggle NAND Flash, 6.0Gb/s SATA)
- SMART Storage CloudSpeed 1000E (400GB, Marvell 9187 controller, 19nm Toshiba MLC NAND, 6.0Gb/s SATA)
- SMART Storage CloudSpeed 500 (240GB, SandForce SF-2581 controller, 2x 4nm MLC NAND die, 6.0Gb/s SATA)
- Micron M500 960GB (960GB, Marvell 9187 controller, Micron 20nm MLC NAND, 6.0Gb/s SATA)
- Micron M500DC (480GB, Marvell 9187 controller, 20nm MLC NAND, 6.0Gb/s SATA)
- Micron P400m (400GB, Marvell 9187 controller, Micron 25nm MLC NAND, 6.0Gb/s SATA)
- Intel SSD DC S3500 (480GB, Intel PC29AS21CA0 controller, Intel 20nm MLC NAND, 6.0Gb/s SATA)
- Intel SSD DC S3700 (200GB, Intel PC29AS21CA0 controller, Intel 25nm MLC NAND, 6.0Gb/s SATA)
SAS and SATA enterprise SSDs are benchmarked on our second-generation enterprise testing platform based on a Lenovo ThinkServer RD630. This testing platform includes the latest interconnect hardware such as the LSI 9207-8i HBA as well as I/O scheduling optimizations geared towards best-case flash performance. For synthetic benchmarks, we utilize FIO version 2.0.10 for Linux and version 2.0.12.2 for Windows.
- 2 x Intel Xeon E5-2620 (2.0GHz, 15MB Cache, 6-cores)
- Intel C602 Chipset
- Memory – 16GB (2 x 8GB) 1333Mhz DDR3 Registered RDIMMs
- Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 64-bit, Windows Server 2012 Standard, CentOS 6.3 64-Bit
- 100GB Micron RealSSD P400e Boot SSD
- LSI 9211-4i SAS/SATA 6.0Gb/s HBA (For boot SSDs)
- LSI 9207-8i SAS/SATA 6.0Gb/s HBA (For benchmarking SSDs or HDDs)
- Mellanox ConnectX-3 10GbE PCIe 3.0 Adapter
- Mellanox ConnectX-3 InfiniBand PCIe 3.0 Adapter
Application Workload Analysis
In order to understand the performance characteristics of enterprise storage devices, it is essential to model the infrastructure and the application workloads found in live production environments. Our first three benchmarks of the Samsung 845DC EVO are therefore the MarkLogic NoSQL Database Storage Benchmark, MySQL OLTP performance via SysBench and Microsoft SQL Server OLTP performance with a simulated TCP-C workload.
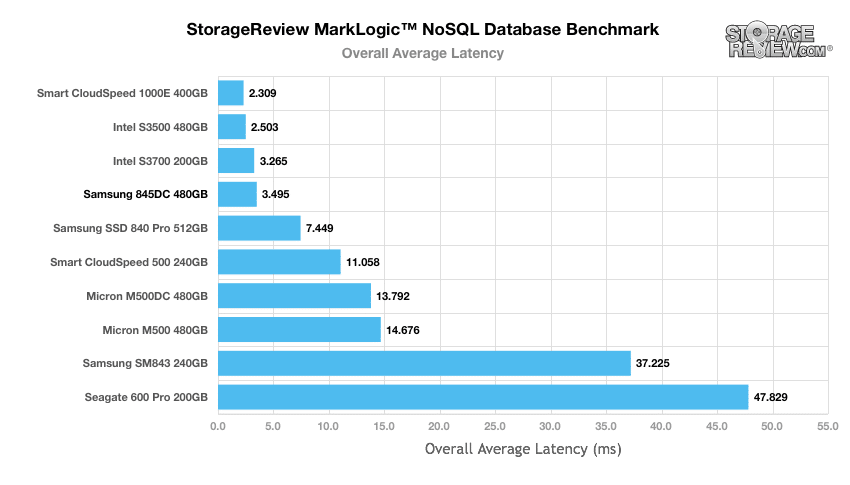
Our MarkLogic NoSQL Database environment requires groups of four SSDs with a usable capacity of at least 200GB, since the NoSQL database requires roughly 650GB of space for its four database nodes. Our protocol uses an SCST host and presents each SSD in JBOD, with one allocated per database node. The test repeats itself over 24 intervals, requiring between 30-36 hours total. MarkLogic records total average latency as well as interval latency for each SSD.
The Samsung SSD 845DC EVO was able to keep up with class-leading MLC SSDs from SanDisk and Intel and handedly beat the client-focused Samsung SSD 840 Pro with an overall average latency of 3.7495ms.
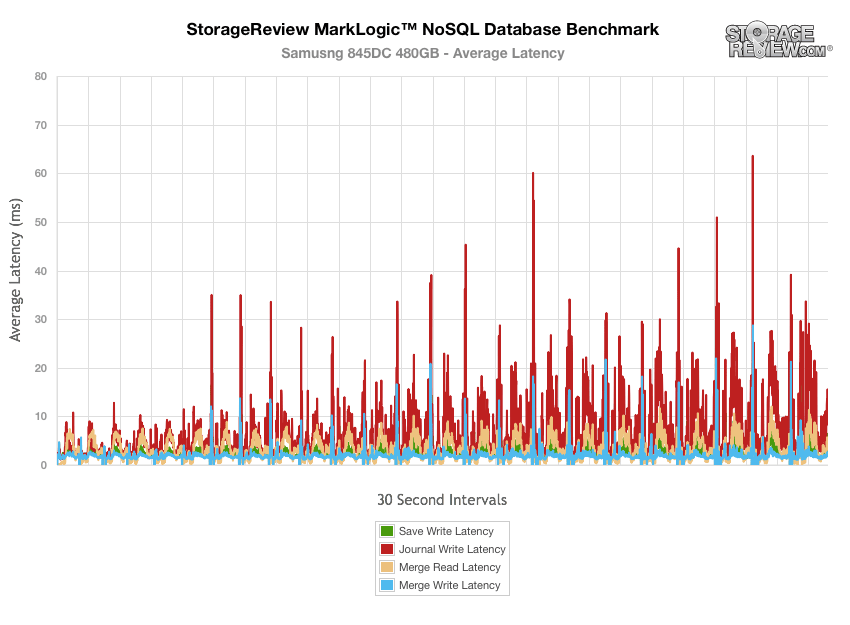
The latency results for the majority of operations during the NoSQL benchmark below 30ms, though the 845DC EVO did experience a number of latency spikes, which is not abnormal for SSDs.
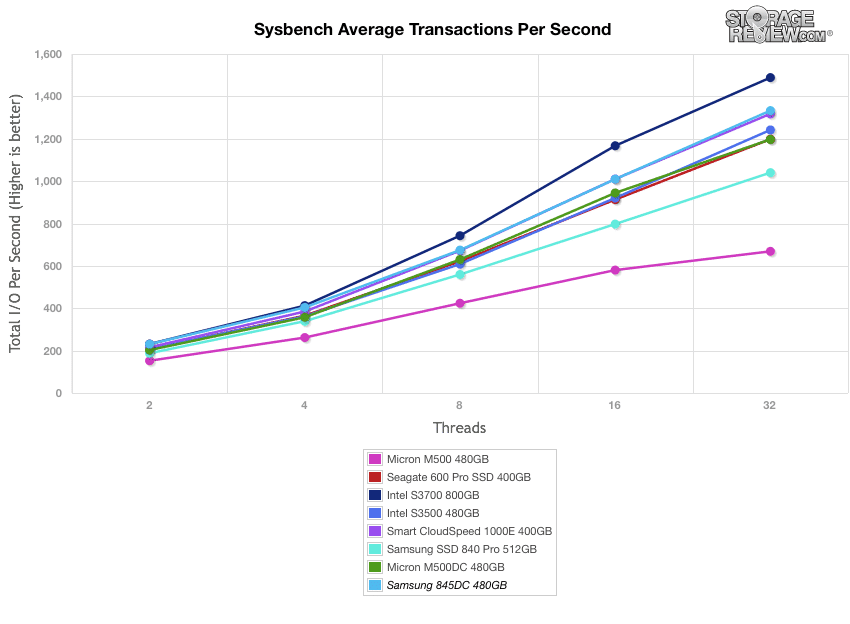
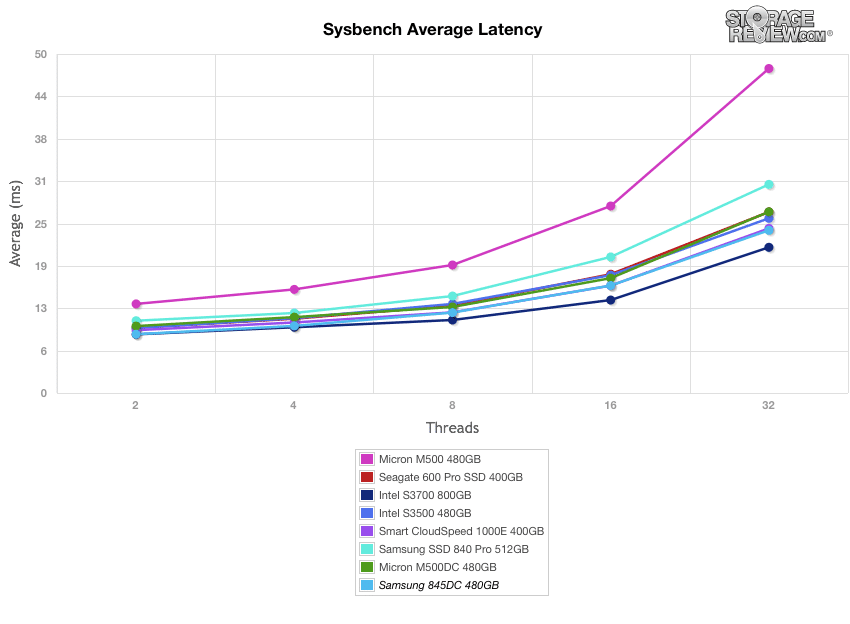
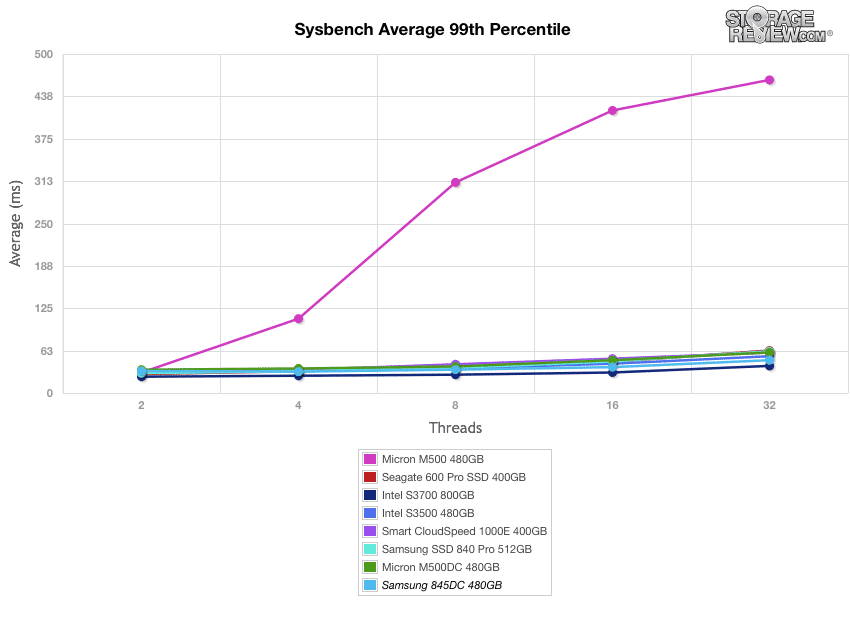
The next application benchmark consists of a Percona MySQL OLTP database measured via SysBench. In this configuration, we use a group of Lenovo ThinkServer RD630s as database clients and the database environment stored on a single drive. This test measures average TPS (Transactions Per Second), average latency, as well as average 99th percentile latency over a range of 2 to 32 threads. Percona and MariaDB are using the Fusion-io flash-aware application APIs in the most recent releases of their databases, although for the purposes of this comparison we test each device in their "legacy" block-storage modes.
At the time of this review, we recently upgraded the Lenovo ThinkServer RD630 used in Sysbench tests from dual Intel E5-2650 CPUs to dual E5-2690 CPUs, which slightly skews performance data from historical comparables. We included the data as reference, and will be re-benchmarking previously reviews SSDs for proper comparison.
The Samsung 845DC EVO remained near the top of the charts throughout the MySQL benchmark with 1,333 transactions per second at 32 threads workload.
The Samsung 845DC EVO showed great average latency results during the MySQL benchmark.
In our worst-case MySQL latency scenario, the Samsung 845DC EVO ranked second-place result overall.
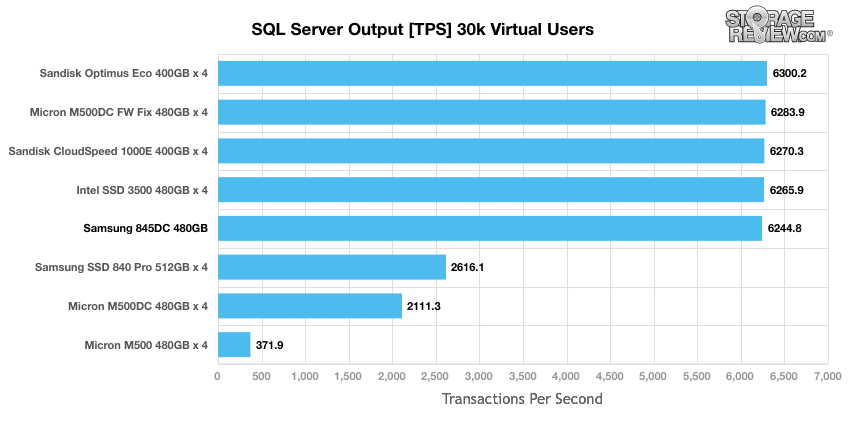
StorageReview’s Microsoft SQL Server OLTP testing protocol employs the current draft of the Transaction Processing Performance Council’s Benchmark C (TPC-C), an online transaction processing benchmark that simulates the activities found in complex application environments. The TPC-C benchmark comes closer than synthetic performance benchmarks to gauging the performance strengths and bottlenecks of storage infrastructure in database environments. Our SQL Server protocol uses a 685GB (3,000 scale) SQL Server database and measures the transactional performance and latency with a 30,000 VU Load.
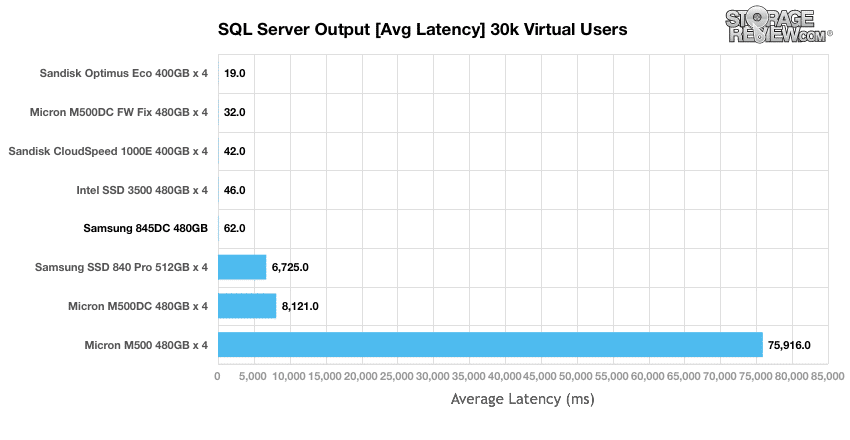
In our SQL Server test, the Samsung 845DC EVO came in 5th place, it kept close pace with the other top-in-class models on the leaderboard. But in the SQL Server test, the TPS is less of an issue, it's how fast you deliver them.
Switching our focus to the overall average latency, the Samsung 845DC trails a bit further from the top of the pack (though still close); however, the SSDs below show a huge leap in latency. This is a huge deal for Samsung, since many of the drives it closely trails are high-performance MLC SSDs.
Synthetic Workload Analysis
Our synthetic benchmark protocols each begin by preconditioning the target storage into steady-state with the same workload that will be used to test the device. The preconditioning process uses a heavy load of 16 threads with an outstanding queue of 16 per thread.
Preconditioning and Primary Steady-State Tests:
- Throughput (Read+Write IOPS Aggregate)
- Average Latency (Read+Write Latency Averaged Together)
- Max Latency (Peak Read or Write Latency)
- Latency Standard Deviation (Read+Write Standard Deviation Averaged Together)
Once preconditioning is complete, each device being compared is then tested across multiple thread/queue depth profiles to show performance under light and heavy usage. Our synthetic workload analysis for the Samsung 845DC uses 4k and 8k profiles which are widely used in manufacturer specifications and benchmarks.
- 4k Profile
- 100% Read and 100% Write
- 8K Profile
- 70% Read, 30% Write
- 100% 8K
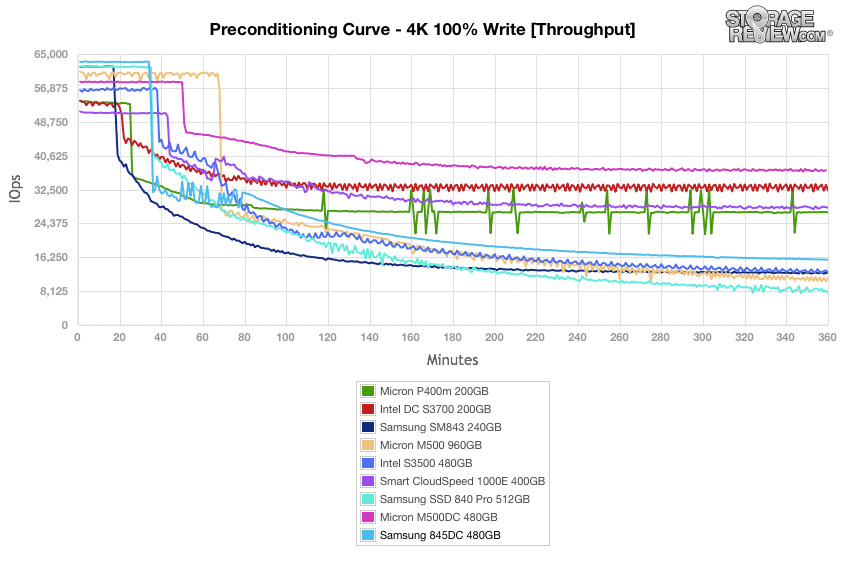
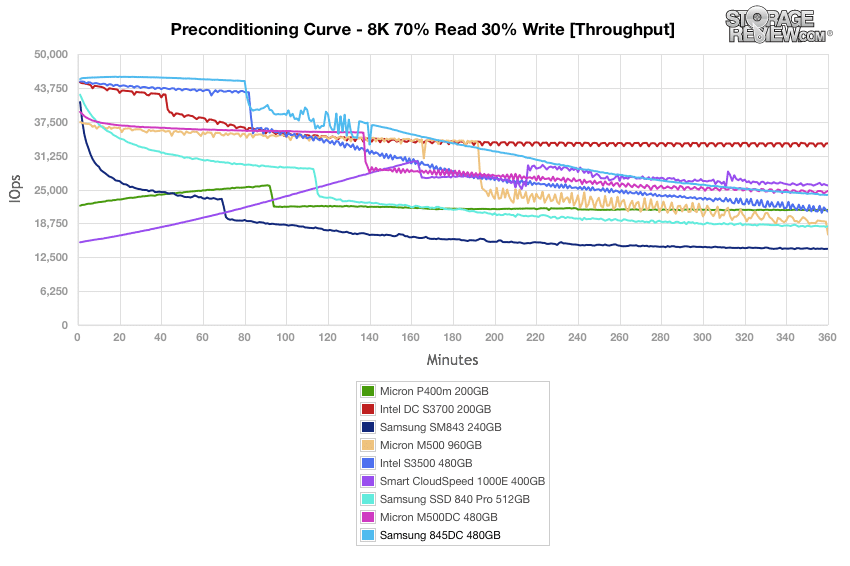
During the preconditioning process, the Samsung 845DC showed great results at the get go, but tapered off from the top of the pack as it approached a steady state near 15,750IOPS.
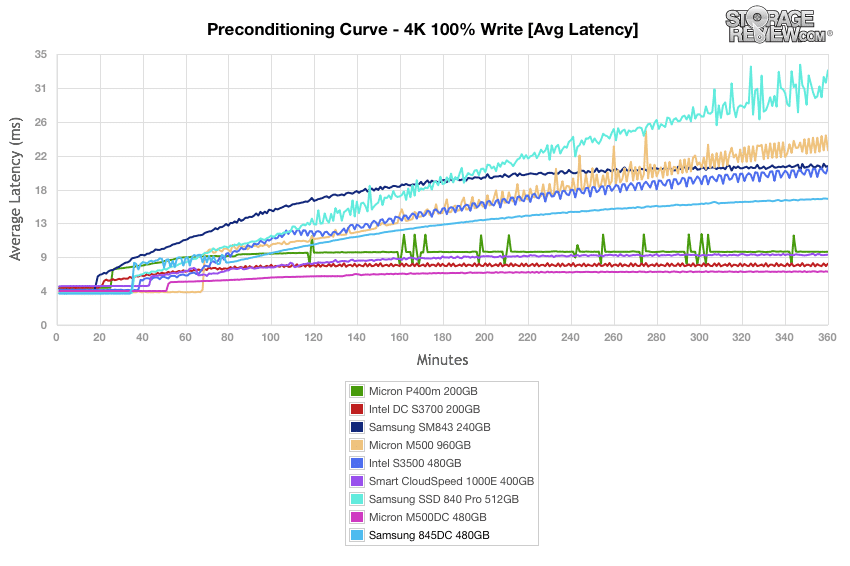
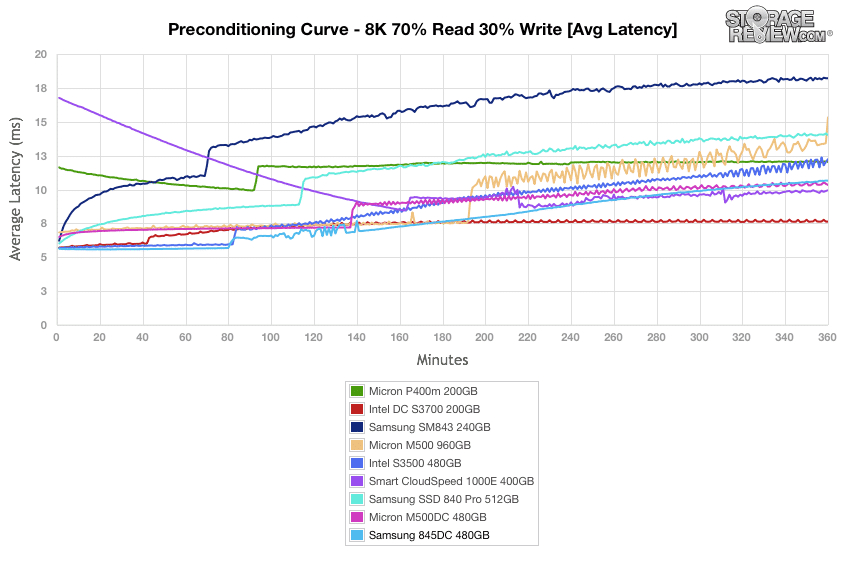
The Samsung 845DC performed in the middle of the pack the during 4k preconditioning average latency. The Micron M500DC showed the best results.
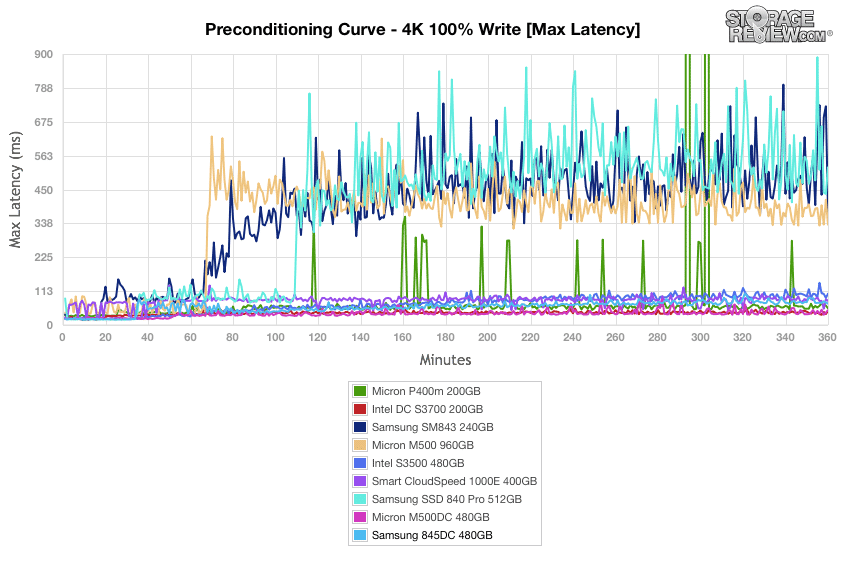
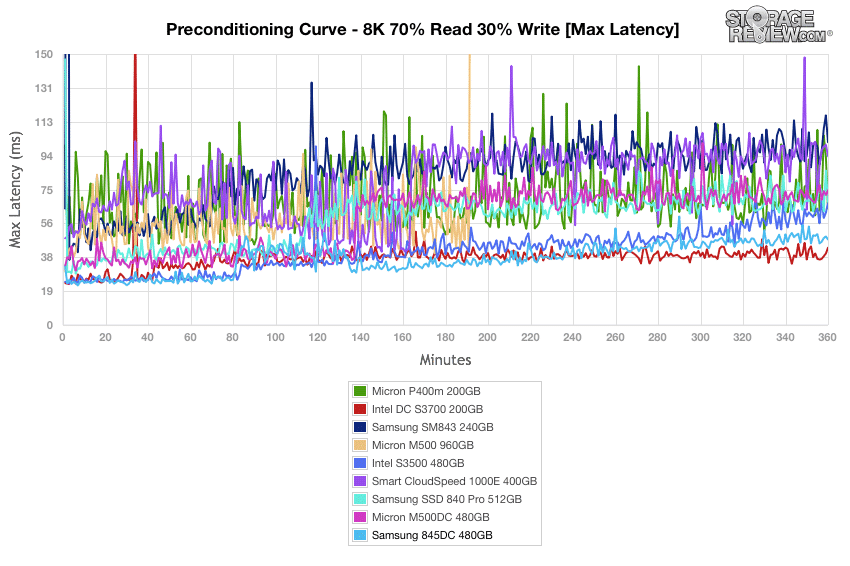
The Samsung 845DC sustained its maximum latency values near the top of the pack during 4k preconditioning, winding up just behind the Micron P400m 200GB.
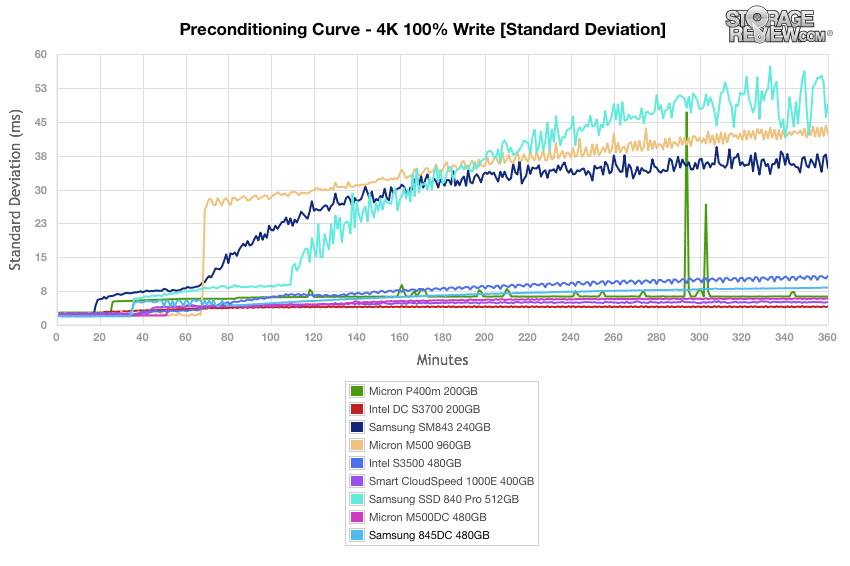
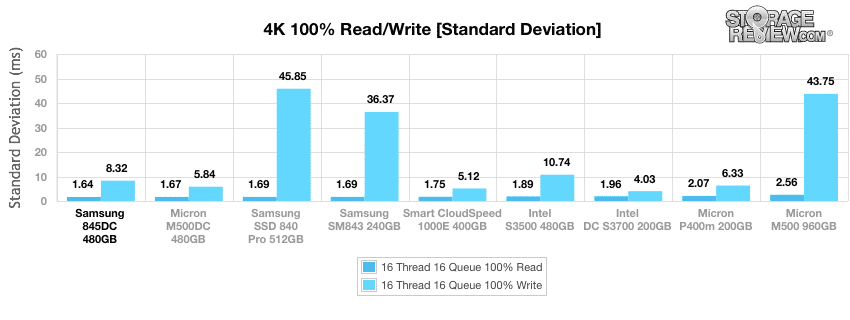
Our standard deviation results from the 4k preconditioning process demonstrate the Samsung 845DC continued strong performance with random 4k transfers, which approached the 8.3ms mark at a very steady pace with very few spikes along the way.
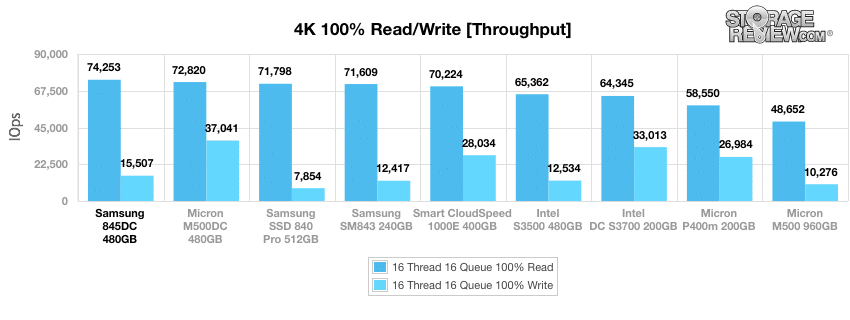
During the primary 4k synthetic benchmark, the Samsung 845DC was able to boast a top performing 74,253IOPS for read operations and but a lesser placing 15,507IOPS for write operations.
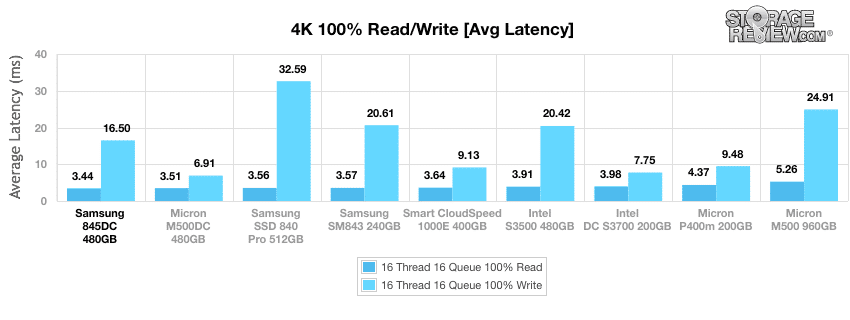
Average latency results for the 4k workloads were excellent for the Samsung 845DC SSD, with a very low 16.5ms average read and 3.4ms average write, which was first and second place respectively.
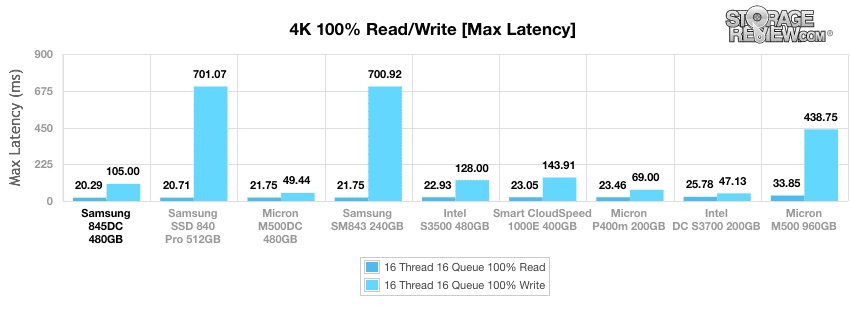
The maximum read latency recorded during the 4k benchmark of the Samsung 845DC was the top performer in both read and write latency at 3.44ms and 16.5ms respectively.
Calculating the standard deviation of the 4k latency results show continued dominance of the Samsung 845DC in our primary 4k synthetic benchmarks, though it was a tight race.
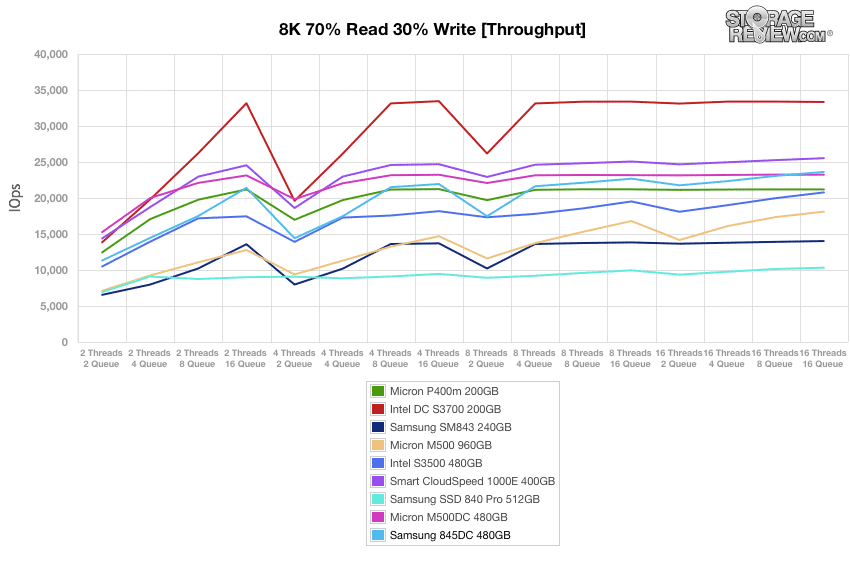
Our next workload uses 8k transfers with a ratio of 70% read operations and 30% write operations. After burst performance in the middle of the pack, the Samsung 845DC settled into third place by 16T16Q.
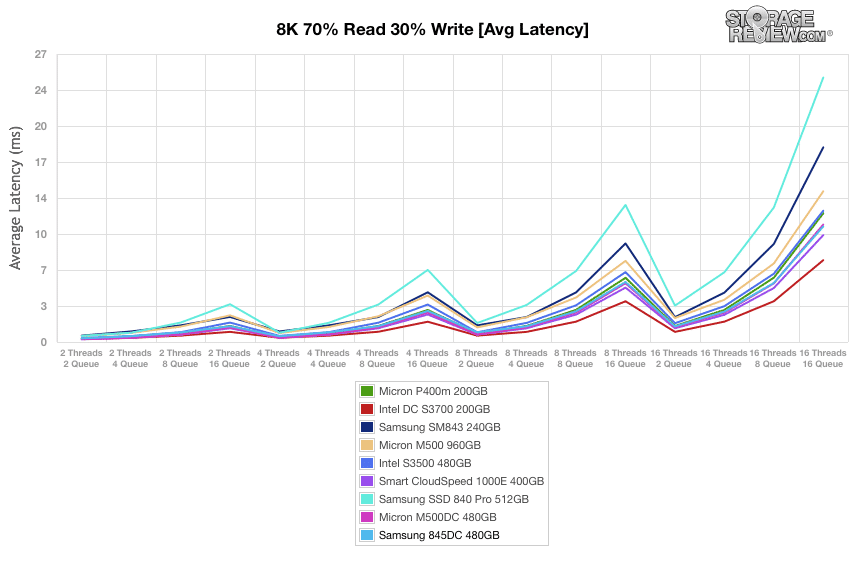
In our average latency tests, the Samsung 845DC approached 11ms during preconditioning for the 8k 70/30 profile.
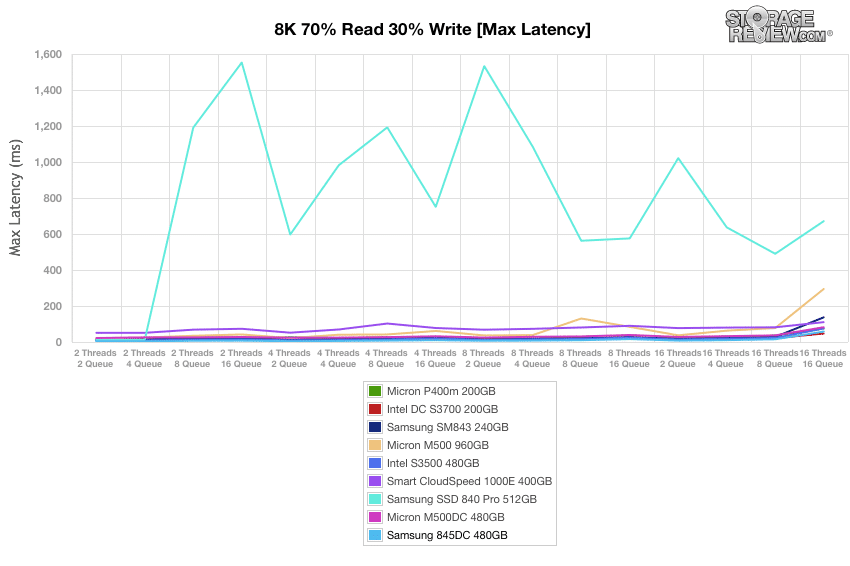
Our 8k 70/30 maximum latency results during preconditioning showed steady performance by the Samsung 845DC, finishing near the top of the pack at 58ms.
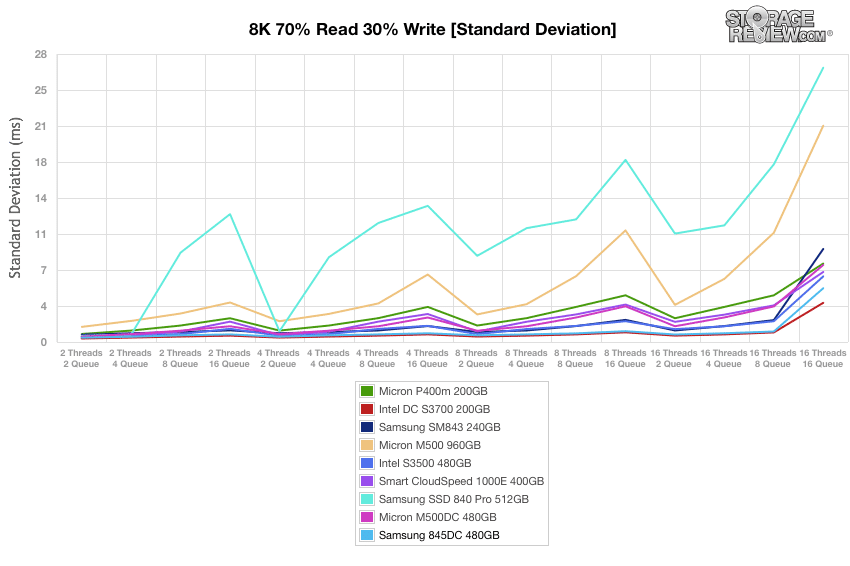
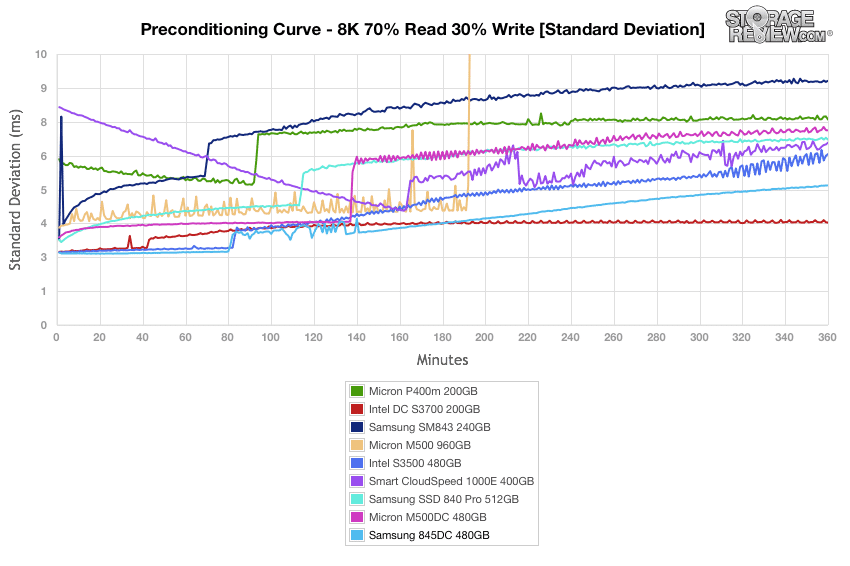
Standard deviation calculations during the 8k 70/30 preconditioning process shows the Samsung 845DC approaching 5.23ms at steady state, taking second place to the Intel DC SSD.
Our next workload uses 8k transfers with a ratio of 70% read operations and 30% write operations. After a very strong burst performance that kept the Samsung 845DC at the top until roughly the 180 minute mark, the drive settled into steady downturn, which ended up placing in the middle of the pack.
Our plot of average latency results during the 8k 70/30 preconditioning process are generally a mirror image of throughput performance during preconditioning. The Samsung 845DC showed poor initial bursts but ended up settling into a stead rise by the 140 minute mark.
Maximum latency results for the Samsung 845DC during our 8k 70/30 preconditioning oscillated up to near 48ms and ended up having one of the lowest max latencies with no major spikes whatsoever.
Standard deviation calculations for the 8k 70/30 preconditioning place the Samsung 845DC as a top performer once again, with a steady rise to only 5.15ms by the end.
Conclusion
With the SSD 845DC EVO, Samsung is the first to offer enterprise SSDs with TLC NAND. The net result of this precedent is extremely impressive performance numbers when compared to both the client drives it intends to fight and the more expensive MLC-based entry-enterprise SSDs. Samsung has optimized the 845DC EVO for servers and data centers with sustained performance in steady state. In addition, the Samsung 845DC EVO offers extremely low latency for a drive in this class, which is critical when it comes to delivering responsive applications.
Looking at its performance in further detail, the Samsung 845DC EVO posted excellent results across our application and synthetic benchmarks. In our synthetic tests, the Samsung 845DC EVO was the top performer in our 4K random read and write performance benchmarks, and well towards the top of the pack in our 8k 70/30 workload. In our MarkLogic NoSQL benchmark, the TLC-based 845DC EVO had no trouble ranking near the top of the pack, ahead of some MLC-based comparables. In our SQL Server test, the 845DC performed very strong as well, having no trouble staying with the high-performance MLC SSDs. The Sysbench MySQL numbers told a similar story.
As far as pricing goes, Samsung offers a competitive price point across all capacities for their enterprise 845DC EVO line. While volume pricing will vary, the 845DC EVO is expected to be the lowest cost enterprise SSD in the market. Samsung is able to offer this in part due to owning its own NAND fabs and in-house componentry, giving it a substantial advantage over other companies as it allows them to produce a more reliable product at a lesser cost. The drive cost is clearly critical as the 845DC EVO goes head to head with high end client drives in this space. In that market adding on the additional enterprise features like power-fail protection and known endurance support should push many of those buyers toward the 845DC EVO. Mainstream enterprise buyers, who only buy enterprise-grade product, may be a harder sell because of the uncertainty over TLC; but like they found on the client side time probably helps mitigate some of that concern.
Pros
- Consistent, strong performance across the board
- Impressive latency compared to both MLC enterprise drives and client SSDs
- Reliable pedigree
- Competitive price point
Cons
- Lacks reliability/endurance track record
Bottom Line
The Samsung 845DC EVO SSD is an entry-enterprise drive that delivers consistent high-performance and low-latency in virtually every category. This, in addition to its enterprise feature set and low cost, make it a very attractive option for read-heavy data centers looking to deliver applications reliably with the lowest possible TCO.
Learn More About Samsung Enterprise SSDs