The RackStation RS10613xs+ offers the greatest maximum capacity and performance in Synology’s network storage portfolio with the ability to manage total raw capacity as high as 424TB and maximum throughput specified at 2,000MB/s with 400,000 IOPS when both SSD caching and optional dual aggregated 10GbE interfaces are enabled. Running its DiskStation Manager (DSM) operating system, Synology is marketing the device as a convergence of NAS and SAN capabilities. As with the RackStation RS3412xs we benchmarked at the beginning of the year, Synology’s approach with the RS10613xs+ is to unify file-level NAS storage with block-level SAN functions while providing hooks and integrations for a wide spectrum of common enterprise and SMB applications.

The DSM operating system, already familiar to Synology administrators, provides a proven and actively updated suite of functionality that will allow the unit to keep pace with diversifying technical requirements in growing organizations. Synology also offers the RX1213sas expansion shelf to push maximum storage beyond the internal 40TB capacity max (4TB x 10 bays). Organizations can install as many as eight RX1213sas expansion shelves for 106 total drives–up to 424TB of total raw storage. The Synology units support SATA and SAS connectivity for HDDs and SSDs so organizations can balance performance and capacity to meet specific workload needs.
The RS10613xs+ has been designed with redundant data paths, power supplies, fans, and network interfaces, and it features proactive hot-sparing along with hot-swappable drives. Synology’s High Availability solution allows administrators to deploy multiple RackStation and DiskStation servers in pairs of active and passive servers. A graceful Switchover mode can be initiated by administrators for system maintenance, or the RS10613xs+ Failover mode can be configured to automatically switch to the passive server in the case of an active server malfunction.
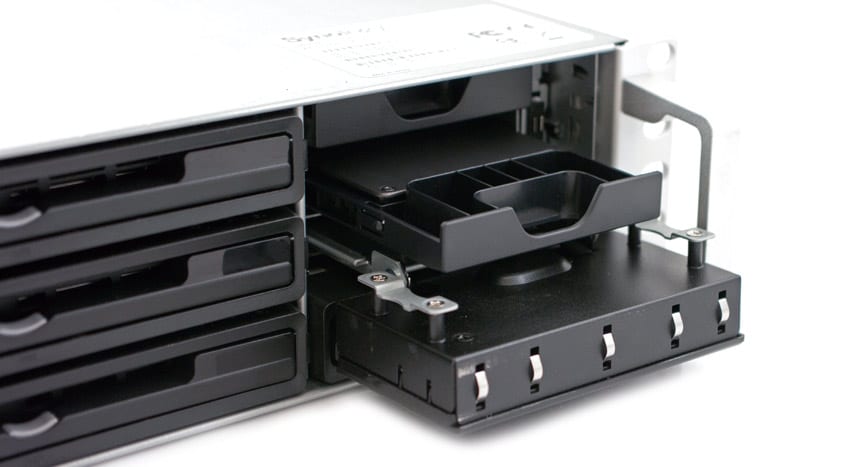
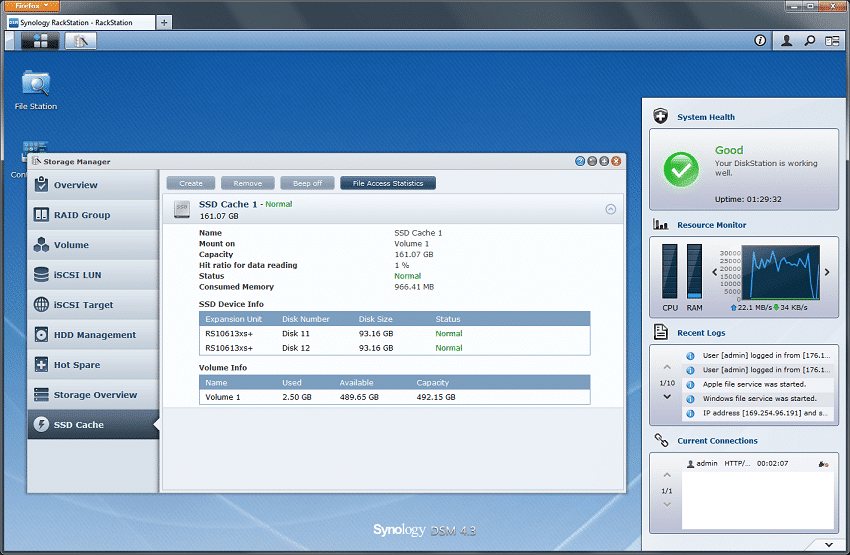
The RS10613xs+ offers Synology’s proprietary read-only SSD cache technology that can be used across up to two SSDs, with each SSD mapped to a single storage volume or block-level iSCSI LUN. One handy feature that distinguishes the RS10613xs+ chassis design from others available in the space is a dual SSD bay hidden behind the administration panel on the front of the unit. This engineering move means that SSD cache drives don’t tie up the ten primary drive bays.
The RS10613xs+ is engineered to ease the process of data management and is particularly suited for virtualized environments. The unit is certified to work with VMware, Citrix, and Hyper-V, as well as being integration with VMware vSphere 5 and VAAI.
The Synology RackStation RS10613xs+ is available now and carries Synology’s three-year warranty (extendable to five years) that includes next business day shipping on all replacement parts and complete units. As with other Synology units, the Synology RackStation RS10613xs+ is sold bare without disks, enabling organizations to populate the bays with whatever drives they choose from Synology’s compatibility list.
Synology RackStation RS10613xs+ Specifications
- Performance and Storage
- CPU Frequency: Intel Xeon E3-1230 Quad-Core (8M Cache, 3.20 GHz)
- Memory: DDR3 4GB x 2 ECC RAM (Expandable, up to 32GB)
- Internal HDD/SSD: 3.5-inch or 2.5-inch SATAII/SATAIII/SAS x 10; 2.5-inch SSD Cache x 2 (Hard drives not included)
- Max Internal Capacity: 40TB (10 x 4TB HDD) (Capacity varies by RAID; see supported HDD list)
- Hot Swappable HDD
- External HDD Interface: USB 2.0 Port X 4, Expansion Port X 2
- LAN: Gigabit x 4 (optional 10GbE x 2 add-on card is supported)
- Link Aggregation
- Wake on LAN/WAN
- System Fan: 80x80mm x 4
- Easy Replacement System Fan
- Wireless Support (dongle)
- Power
- Power Supply: 400W x 2 (Redundant Power Supply)
- AC Input Power Voltage: 100V to 240V AC
- Power Frequency: 50/60 Hz, Single Phase
- Power Consumption: 142W (Access); 110W (HDD Hibernation)
- Environmental
- Operating Temperature: 5°C to 35°C (40°F to 95°F)
- Storage Temperature: -10°C to 70°C (15°F to 155°F)
- Noise Level: 54.6 dB(A)
- Relative Humidity: 5% to 95% RH
- Maximum Operating Altitude: 6,500 feet
- Certification: FCC Class A, CE Class A, BSMI Class A
- Rail Kit: Synology 2U Rail Kit Sliding (optional)
- Dimensions (HxWxD): 88 x 445 x 570 mm
- Weight: 15.7Kg
- Warranty: 3 Years (Extendable to 5 Years)
Design and Build
The Synology RackStation RS10613xs+ is a 2U rack-mounted SAN/NAS designed to meet the needs of medium to large businesses, with a particular emphasis on virtualized environments. The RS10613xs+ provides 10 front-mounted hot-swappable 3.5-inch bays that can be populated with drives featured on Synology’s compatibility list (which includes both 3.5-inch and 2.5-inch HDDs and SSDs).
The front panel features ten primary storage drive bays with removable caddies, as well as an administrative interface on the right side with a two-line text display and controls to navigate its menu system. The panel allows users to perform simple management and displays the RS10613xs+’s overall health and health of individual components. Synology also includes LED indicators for each drive and network connection, making it simple for IT administrators to assess overall system operation and perform maintenance accordingly.
A finger pull on the right side of the administrative interface reveals two, 2.5-inch SSD caddies designated for use with the SSD Cache feature.
The rear panel provides access to both power supplies, serial and VGA ports, four USB ports, four 1GbE ports, two RX1213sas expansion ports, and a reset button. The RS10613xs+ supports an additional dual-10GbE interface card on the right side, which is the configuration featured on our review unit.
Management and Operating System
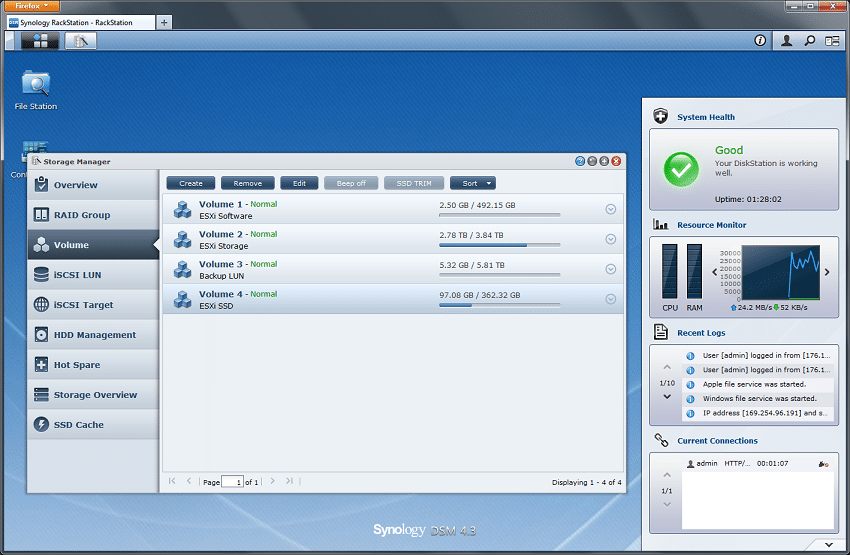
The RS10613xs+ runs Synology’s DiskStation Manager (DSM) operating system and currently ships with DSM 4.3. DSM’s Storage Manager handles LUN and iSCSI Target configuration, with a number of features that should benefit from the RS10613xs+ hardware configuration, which has the most powerful specifications in the product line. LUN Clone creates virtual copies of a LUN that minimize storage and performance requirements at the time of creation, while LUN Snapshot manages up 256 snapshots per LUN.
DSM offers thin provisioning for file-level iSCSI LUN, which increases storage utilization by enabling administrators to oversubscribe during the initial provisioning and only grow the storage space once it is needed. iSCSI LUN Backup powers storage-based backup tasks in order to avoid the more intensive compute requirements of application-driven backup processes.
Cloud and mobile synchronization are also becoming expected features in corporate storage scenarios. Synology’s Cloud Station pushes files to PCs and mobile devices, including iOS and Android clients, and can proactively push files to such remote clients in order to support offline viewing.
Testing Background
The StorageReview Enterprise Test Lab allows us to provide relevant and unbiased benchmarks of enterprise storage devices by establishing a testing environment comparable to what IT administrators encounter in real datacenter and field deployments. The Enterprise Test Lab incorporates a variety of servers, networking, power conditioning, and other infrastructure to design real-world configurations that accurately reflect the performance of storage devices during reviews.
We incorporate details about our lab environment and testing protocols into reviews so that storage administrators and those responsible for equipment acquisition can fairly gauge the conditions under which we have achieved the published results. None of our reviews are paid for or overseen by the manufacturer of equipment we are testing. Additional details about the StorageReview Enterprise Test Lab and an overview of its networking capabilities are available on those respective pages.
In order to fairly evaluate the performance of the Synology RackStation RS10613xs+, we established an environment that ensures that the RS10613xs+ is the I/O bottleneck rather than the network. This review employs dual Lenovo ThinkServer RD630s paired with a Mellanox SX1036 10/40Gb Ethernet Switch, with connectivity via Mellanox ConnectX-3 PCIe adapters.
Lenovo ThinkServer RD630
- 2 x Intel Xeon E5-2620 (2.0GHz, 15MB Cache, 6-cores)
- Intel C602 Chipset
- Memory – 16GB (2 x 8GB) 1333Mhz DDR3 Registered RDIMMs
- Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 64-bit, Windows Server 2012 Standard, CentOS 6.3 64-Bit
- 100GB Micron RealSSD P400e Boot SSD
- LSI 9211-4i SAS/SATA 6.0Gb/s HBA (For boot SSDs)
- LSI 9207-8i SAS/SATA 6.0Gb/s HBA (For benchmarking SSDs or HDDs)
- Intel X540-T2 10GbE PCIe 2.1 Adapter
- Mellanox ConnectX-3 10GbE PCIe 3.0 Adapter
- Mellanox ConnectX-3 InfiniBand PCIe 3.0 Adapter
Mellanox SX1036 10/40Gb Ethernet Switch and Hardware
- 36 40GbE Ports (Up to 64 10GbE Ports)
- QSFP splitter cables 40GbE to 4x10GbE
- Mellanox ConnectX-3 EN PCIe 3.0 Twin 10G Ethernet Adapter
In order to understand how the RS10613xs+ performs in the real world, this review employs a series of synthetic workload analyses with the unit populated with a variety of storage media which we have already benchmarked independently of the unit. In order to assess its performance with the types of drives commonly found in SMB and enterprise deployments, we will use the HGST Ultrastar 7K4000 HDD which operates at 7,200RPM, the 15K Toshiba MK01GRRB/R, and Intel’s SSD 520.
Enterprise Synthetic Workload Analysis
The StorageReview Enterprise Synthetic Workload Analysis includes common sequential and random profiles intended to reflect real-world activity. These profiles are based on similarity with historical benchmark protocols as well as to help compare against widely-published values such as 4K read and write speed and the 8K 70/30 benchmark which is often used to evaluate enterprise storage.
- 4K (Random)
- 100% Read or 100% Write
- 8K (Sequential)
- 100% Read or 100% Write
- 8K 70/30 (Random, Uncached)
- 70% Read, 30% Write
- 8K 70/30 (Random, Cached)
- 70% Read, 30% Write
- 128K (Sequential)
- 100% Read or 100% Write
In order to best simulate real-world usage conditions for the RS10613xs+, two compute servers will independently drive I/O workloads to the unit. Results for each server are charted individually and then as an aggregate number for both. We will benchmark the RS10613xs+ with 7K enterprise HDDs, 15K HDDs, and SSDs. Because of the RS10613xs+’s SSD Cache function, note that there are two separate 8k 70/30 tests: one that is uncached and one with a protocol subset that specifically examines cached performance with an array of 15K enterprise HDDs.
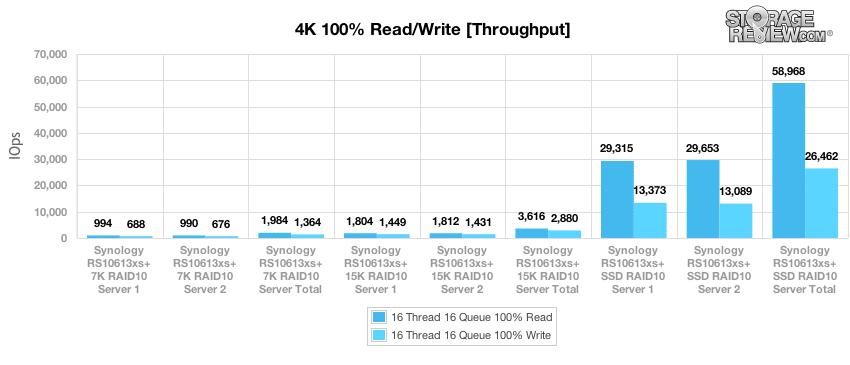
With 100% random 4K read activity across 16 threads with a queue depth of 16, we measured nearly linear performance gains moving from 7K HDDs to 15K HDDs, as expected with the storage medium as the performance bottleneck. Equipped with SSDs, the RS10613xs+ achieved read performance in the mid 29,000 IOPS for both servers, and write performance in the low 13,000 IOPS.
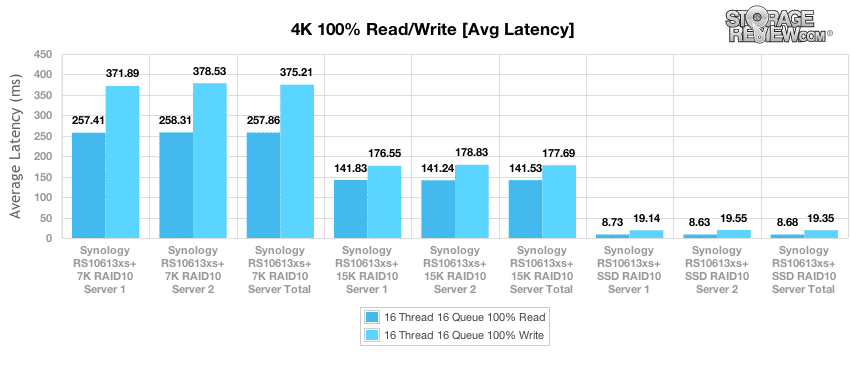
Measuring average latency in the 4k benchmark, the RS10613xs+ was able to maintain near-parity in read latency across both servers during testing of both HDD arrays: an average of 257.86ms for 7K HDDs and 141.53ms for the 15K HDD array. Overall results for HDD write latency fall within the expected pattern, at 375.21ms for the 7K array and 177.69ms for the 15K HDD array. 4k read and write latencies were consistent throughout testing of the SSD array, with average results of 8.68ms for read operations and 19.14ms for read operations across the dual servers.
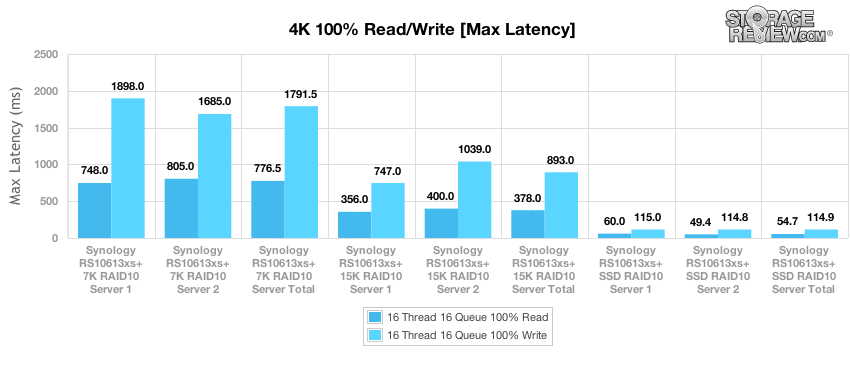
The 4k maximum latency benchmark reflects the inherent limitations of the various storage media across our benchmark protocol. The 7K HDD array achieved an maximum read latency of 775.5ms and a maximum write latency of 1791.5ms with both servers averaged. We noted a minor discrepancy of almost 400ms in maximum latency between the two servers during the 15K HDD write benchmark, which did not skew overall results however. The 15K HDD array was able to bring the averaged maximum latency down to 378.0ms for read operations and 893.0ms for write operations. With an array of SSDs, the RS10613xs+ was able to achieve an averaged performance of 54.7ms for 4k read operations and 114.9ms for write operations across both servers.
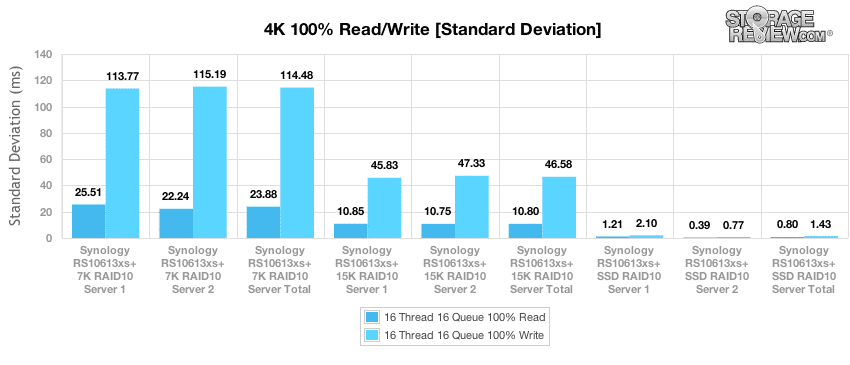
The standard deviation results indicate how much fluctuation existed in latency benchmarks during the 4k testing protocol, which can be useful in identifying trouble spots where the average and maximum latency results fall in line with expectations but specific scenarios have caused inconsistent results that don’t show up in other visualizations. Plotting standard deviation doesn’t reveal surprises for either HDD array, with an average standard deviation of 23.88ms for read operations and 114.48ms for write on the 7K HDD array and 10.80ms for read and 46.58ms for write on the 15K HDD array. The RS10613xs+ showed a small preference for Sever 2 when examining standard deviation for the 4k test of our SSD array, which achieved standard deviations of 0.39ms in read operations and 0.77ms for write compared to 1.21ms read and 2.10ms write for Server 1.
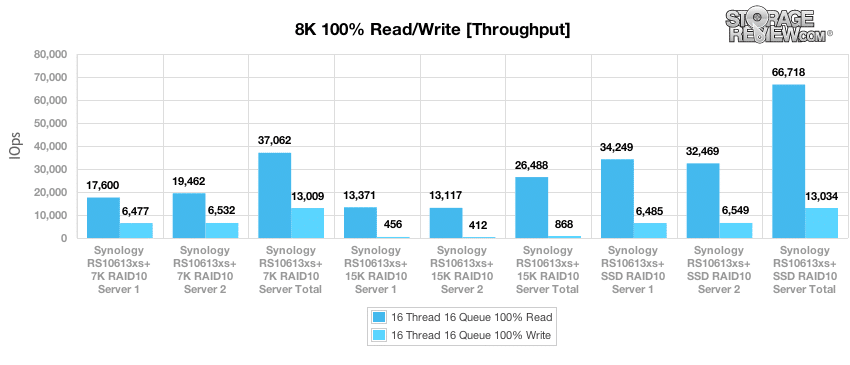
The next benchmark measures 100% 8K sequential throughput with a 16T/16Q load in 100% read and 100% write operations. Outfitted with an array of 7K enterprise HDDs, the RS10613xs+ was able to attain a combined read throughput of 37,062 IOPS and a write throughput of 13,009 IOPS, with only a small discrepancy in read performance favoring Server 1. With 15K HDDs, the RackStation unit demonstrated near equal performance for both servers and attained an aggregate read performance of 26,488 IOPS and write performance of 868 IOPS. Switching over to SSDs, the RS10613xs+ reached a combined read throughput of 66,718 IOPS and 13,034 IOPS of write performance.
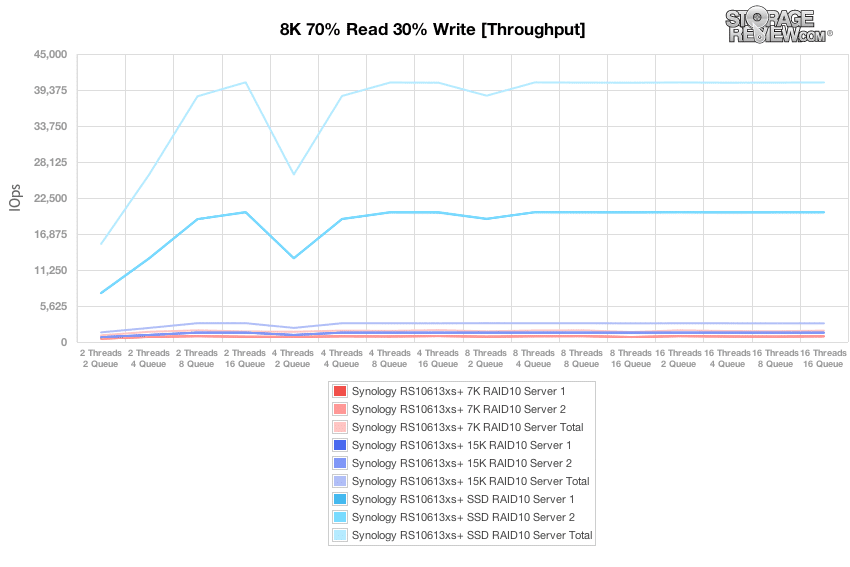
In an 8k benchmark with 70% read operations and 30% write operations, we tested the three array configurations across a variety of thread and queue depth combinations from 2 threads and a queue of 2 up to 16 threads and a queue depth of 16. Performance with an array of 7K enterprise HDDs remained consistent throughout the benchmark, with the exception of somewhat weaker performance at 8T/8Q for both servers. The 15K HDD array did not experience this dip, performing comparably across the workloads once the benchmark reached 4T/4Q. With the exception of slower performance at very low queue depths and thread counts of less than 8, the SSD array was able to hold its aggregated IOPS above 40,000 throughout this test.
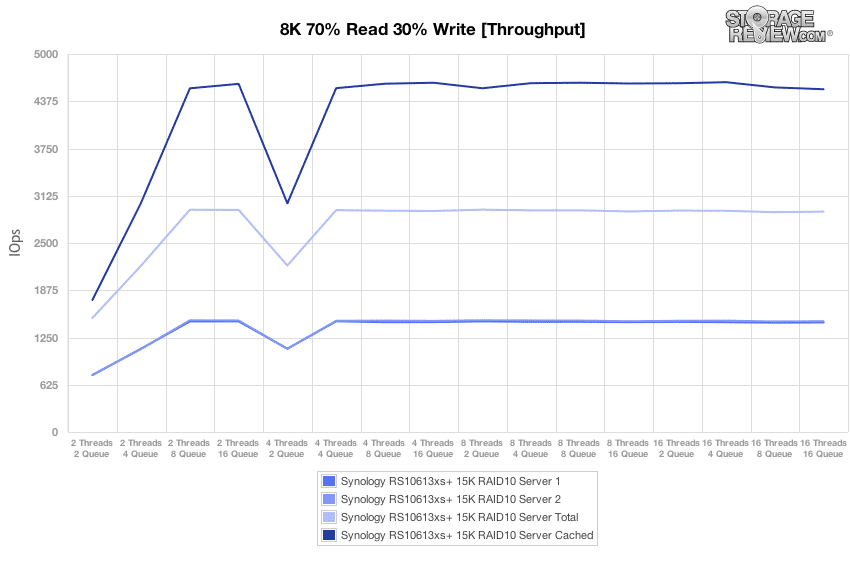
The next benchmark examines the RS10613xs+’s performance for the same workload with an array of 15K HDDs in order to compare the array’s performance with and without its SSD Cache function enabled. Regardless of the cache, the array’s weakest performance occurs at low thread and low queue combinations, as expected. With the SSD Cache engaged, aggregated performance across both servers jumps from values averaging in the 2,900 IOPS range up to values averaging near 4,600 IOPS.
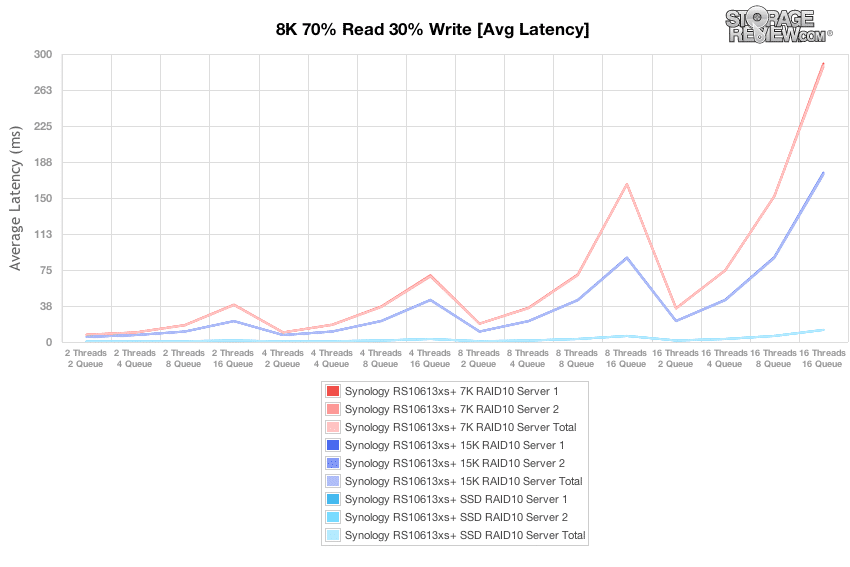
Average latency in the 8k benchmark revealed no surprises across the three array configurations. All three types of media–7K HDD, 15K HDD, and SSDs–achieved their best latencies at lower thread counts and queue depths. The 7K RPM HDDs were able to compete with the 15K HDDs through the 4T tests, where the higher rotational speed and performance of the 15K HDDs clearly outpaced the slower 7K drives.
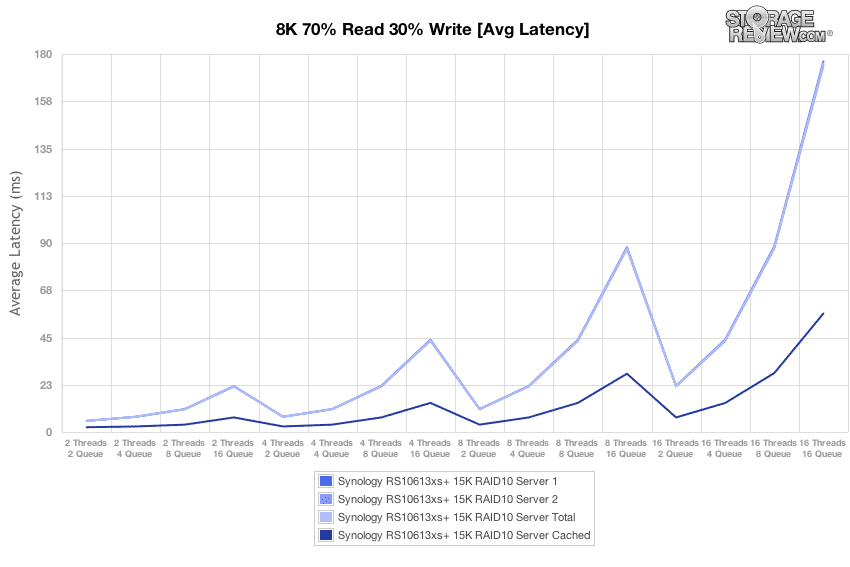
Performing the same average latency benchmark with an array of 15K HDDs and the SSD Cache enabled dramatically improved the array’s performance, especially at the highest load of 16T/16Q where enabling the cache brought average latency from 175.49ms down to 56.44ms.
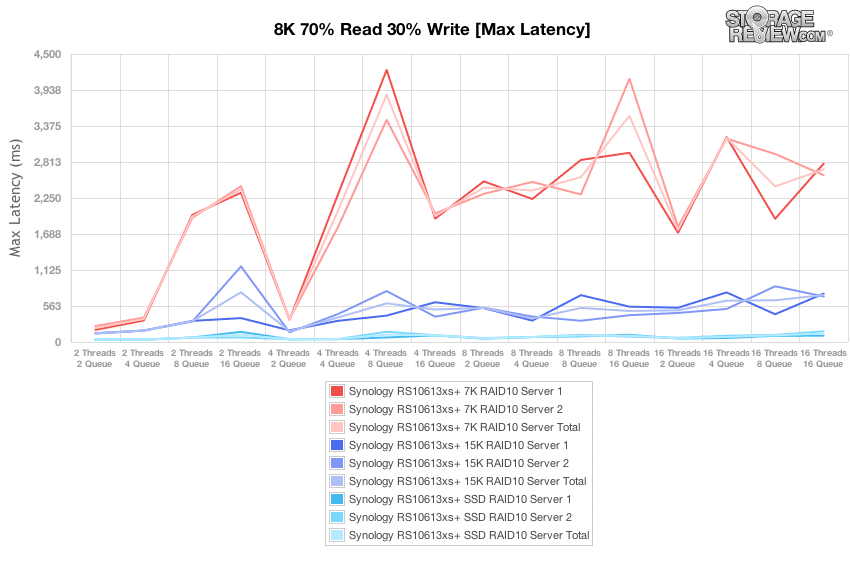
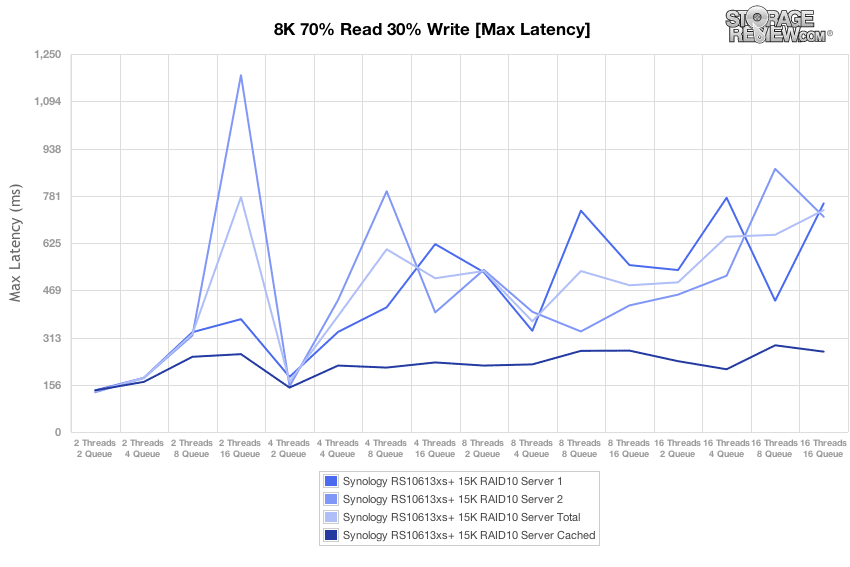
In the maximum latency chart, which indicates worst-case latency across the various workloads and array configurations, the 7K HDD array demonstrates greater variability between the two servers and greater variability overall than experienced by the 15K HDD array.
Enabling the SSD Cache during the 15K HDD maximum latency benchmark demonstrated the more consistent latency results possible from SSDs, although the raw numbers aren’t as markedly different with the SSD Cache enabled until the portions of the benchmark with the highest thread counts and queue depths.
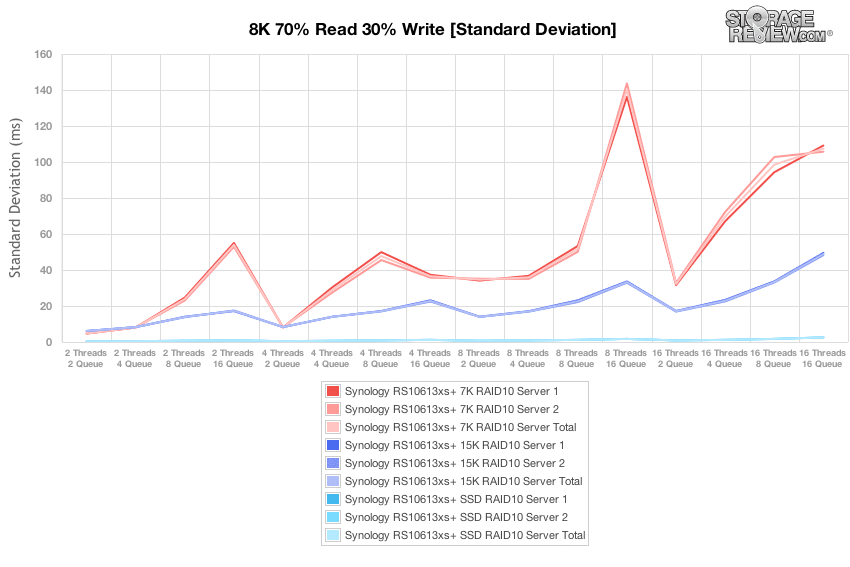
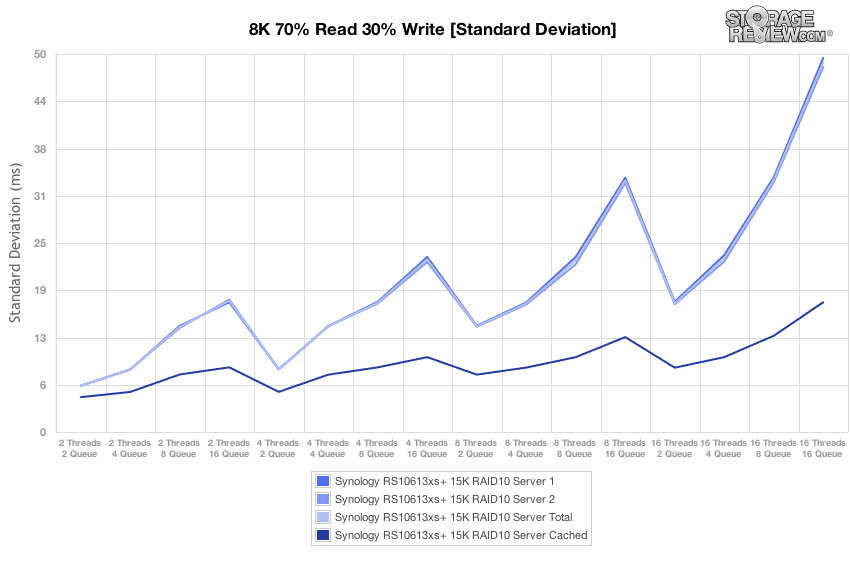
Charting standard deviation for the 8k 70/30 benchmark results reflects the consistent latency performance experienced across the two servers used in the testing protocol regardless of the drive media used to build the array.
With the SSD Cache enabled for the array of 15K HDDs, standard deviation results suggest that the best use cases for the cache function is in scenarios where many threads are making simultaneous I/O demands on the storage system.
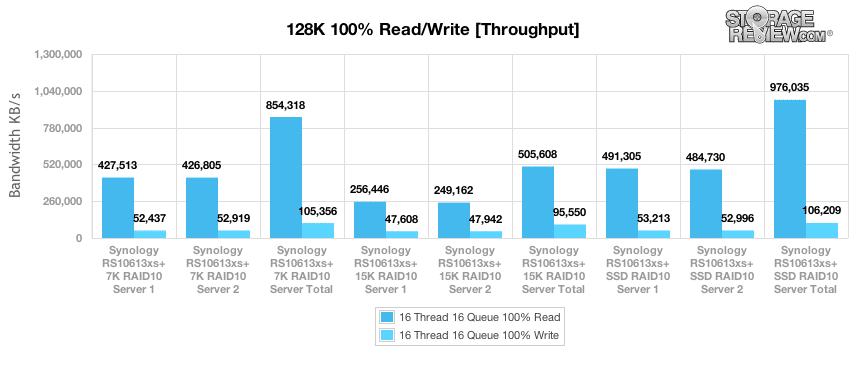
Our last benchmark of the RackStation RS10613xs+ examines sequential 128K transfer speed with a 16T/16Q workload on 100% read and 100% write operations. In this scenario the Ultrastar 7K4000 was able to outperform the 15K Toshiba drive, presumably on the basis of its higher density which can improve performance in larger transfers such as the 128k benchmark. While the SSD array was able to demonstrably outperform the 7K HDD in the 128k read test, the write results were much closer, with the SSD barely edging out the Ultrastar HDD.
Conclusion
The RackStation RS10613xs+ is Synology’s most robust offering with capacity ranging up to 424TB and the ability to offer 2,000MB/s throughput and 400,000 IOPS at the top end via SSD caching and aggregated 10GbE interfaces. The key strength of the RS10613xs+, however, is to drive convergence of NAS and SAN capabilities by unifying file-level NAS storage with block-level SAN functions. Synology offers excellent support with VMware ESXi environments, offering extensive VAAI support to offload file-system requests into the RackStation instead of at the host system level. As with all other Synology offerings, the RS10613xs+ runs DiskStation Manager to simplify management and offer a easy to use interface that ranks near the top in both consumer and enterprise markets with extensive app support.
When it came to performance, the Synology RackStation RS10613xs+ has plenty of muscle to throw around. In our tests we focused on bulk storage performance with 7,200RPM HDDs, faster platter storage with 15K SAS HDDs, as well as high-performance flash storage leveraging all SSDs to show how the array would perform in a number of use-cases. While our platform-inclusive configurations leveraged all 10-bays for each setup, nothing is stopping buyers from leveraging multiple storage tiers via multiple SAS expansion shelves. Leveraging a multi-threaded large-block sequential transfer test, we saw speed ranging from 500-976MB/s read, with write speeds coming in between 95-105MB/s. Shifting to a small-block sequential load, performance peaked at 66k IOPS read with SSDs and 37k IOPS with HDDs. Mixed workload performance was also strong in our 8K 70/30 test, with peak throughput scaling from 1,773 IOPS with 7K HDDs, up to 2,915 IOPS with 15K SAS HDDs, to 4,534 IOPS with 15K SAS+Cache all the way up to 40,553 IOPS from an all-flash configuration.
Synology’s RackStation lineup has a lot to offer corporate storage environments where its dual proficiencies in block and file can be put to use. As the most powerful unit in the RackStation line, the RS10613xs+ is able to make full use of the DiskStation Manager operating system, which provides a graceful learning curve but also exposes powerful functionality for complex deployments. With support for SSD Cache and two dedicated SSD drive bays along with the optional dual-10GbE interface card, the RackStation RS10613xs+ does not disappoint on throughput. Read operations that benefit from Synology’s SSD Cache technology demonstrate the potential of a converged NAS/SAN unit to drive high performance storage, even in environments where the server is supporting a variety of applications.
Pros
- Massive storage scalability up from an initial 2U footprint
- Powered by the versatile DiskStation Manager (DSM) operating system
- SSD Cache technology with dedicated, front-accessible SSD bays
Cons
- Each cached volume requires two SSDs dedicated to it
Bottom Line
Synology’s RS10613xs+ represents an excellent blend of features, ease of use, flexibility and pricing in the NAS market making it an easy choice for any SMB/branch office/remote office user who wants a great NAS storage system without a big budget.
Synology RackStation RS10613xs+ at Amazon