Existing enterprise SSDs form factors are not a good fit in modern data centers. Servers and storage appliances, generally use several types of SSD for booting, performance, or capacity, and that usually requires using more than one SSD form factor (M.2, U.2, or PCIe card). Aiming to overcome the limitations of existing interfaces in the data center, a new storage form factor was created, the Enterprise & Data Center SSD Form Factor (EDSFF).
The EDSFF states the following challenges in today's data center.
Existing enterprise SSDs form factors are not a good fit in modern data centers. Servers and storage appliances, generally use several types of SSD for booting, performance, or capacity, and that usually requires using more than one SSD form factor (M.2, U.2, or PCIe card). Aiming to overcome the limitations of existing interfaces in the data center, a new storage form factor was created, the Enterprise & Data Center SSD Form Factor (EDSFF).
The EDSFF states the following challenges in today's data center.
- Flash proliferation in compute and storage (JBOD to JBOF).
- PCIe – Transitioning from Gen3 to Gen4. And Gen5 is coming.
- New storage technologies are challenging NAND.
- Rotating media form factors constrain density and cooling.
- Lack of hotplug support constrains serviceability.
- Divergence of FFs constrains system design flexibility.
The key goal of EDSFF is to have a datacenter system-optimized design. Also, meet everyday customer needs for storage devices having high density, capacity, and performance options.
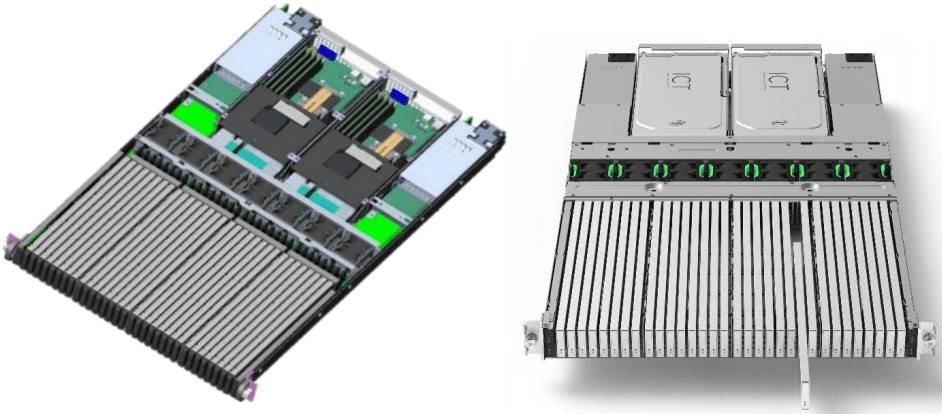
EDSFF is promoted by some of the biggest names in the industry, Intel, Facebook, DellEMC, Hewlett Packard, Lenovo, Microsoft, and Samsung. The EDSFF form factors included in the specification are the E1.S (short), and the E1.L (long), formerly known as ruler.
E1.S – EDSFF 1U Short
The E1.S makes use of an x4 interface and is designed to fit vertically in a 1U enclosure. It is defined in the SNIA specification SFF-TA-1006. The key technical specifications include 111.5 x 31.5mm, supports over 12W, supports up to Gen4 PCIe using the NVMe protocol, and up to 12 standard NAND sites.
This form factor was designed for servers and storage systems in the data center and allows to improve flexibility, storage density, modular scaling, serviceability, and more efficient cooling optimized for 1U appliances.
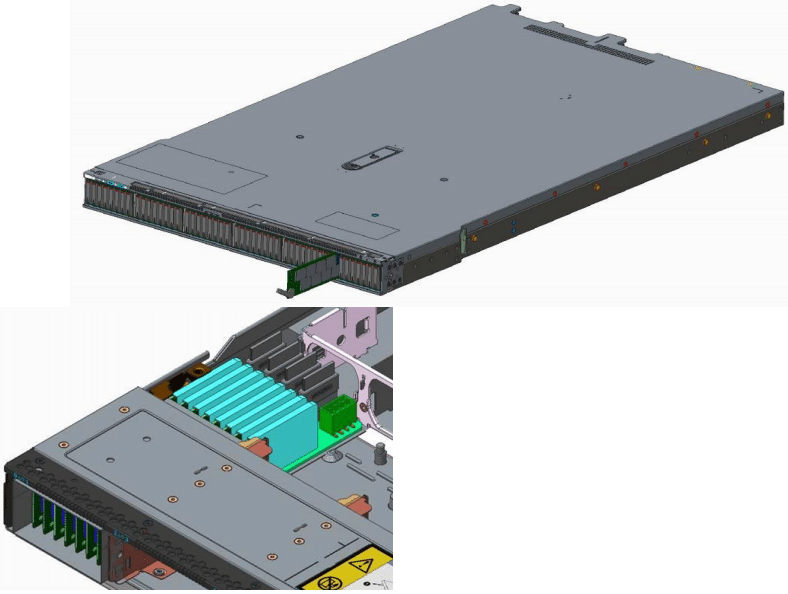
E1.L – EDSFF 1U Long
The E1.L utilizes up to an x8 interface and is designed to fit vertically in a 1U enclosure and is about three times the length of an E1.S. The E1.L is defined in the SNIA specification SFF-TA-1007. The key technical specifications include 318.75 x 38.4mm, supports over 40W, supports up to Gen4 PCIe using the NVMe protocol, and up to 48 standard NAND sites.
The E1.L provides high capacity per server, enabling up to 32 drives per rack unit for massive storage power. In addition to capacity, E1.L allows improving flexibility, storage density, modular scaling, serviceability, and performance.
With the E1.L form factor, a single 1U enclosure can store up to 32 drives. And, using the Intel-based SSD DC P4500 drive of 32TB, an entire 1U enclosure can support up to 1PB. If a full 42U rack is utilized, the total storage capacity is close to 43PB (1,344 drives). EDSFF allows for a 10x increase in storage density, compared with the Intel 8TB U.2 form factor drives.